
In mathematics, an abelian group, also called a commutative group, is a group in which the result of applying the group operation to two group elements does not depend on the order in which they are written. That is, the group operation is commutative. With addition as an operation, the integers and the real numbers form abelian groups, and the concept of an abelian group may be viewed as a generalization of these examples. Abelian groups are named after early 19th century mathematician Niels Henrik Abel.
A histogram is a visual representation of the distribution of numeric data. The term was first introduced by Karl Pearson. To construct a histogram, the first step is to "bin" the range of values— divide the entire range of values into a series of intervals—and then count how many values fall into each interval. The bins are usually specified as consecutive, non-overlapping intervals of a variable. The bins (intervals) must be adjacent and are often of equal size.

In statistics and probability theory, the median is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a data sample, a population, or a probability distribution. For a data set, it may be thought of as "the middle" value. The basic feature of the median in describing data compared to the mean is that it is not skewed by a small proportion of extremely large or small values, and therefore provides a better representation of the center. Median income, for example, may be a better way to describe the center of the income distribution because increases in the largest incomes alone have no effect on the median. For this reason, the median is of central importance in robust statistics.

In mathematics, a tensor is an algebraic object that describes a multilinear relationship between sets of algebraic objects related to a vector space. Tensors may map between different objects such as vectors, scalars, and even other tensors. There are many types of tensors, including scalars and vectors, dual vectors, multilinear maps between vector spaces, and even some operations such as the dot product. Tensors are defined independent of any basis, although they are often referred to by their components in a basis related to a particular coordinate system; those components form an array, which can be thought of as a high-dimensional matrix.

In mathematics, a permutation of a set is, loosely speaking, an arrangement of its members into a sequence or linear order, or if the set is already ordered, a rearrangement of its elements. The word "permutation" also refers to the act or process of changing the linear order of an ordered set.
In computer science, denotational semantics is an approach of formalizing the meanings of programming languages by constructing mathematical objects that describe the meanings of expressions from the languages. Other approaches providing formal semantics of programming languages include axiomatic semantics and operational semantics.
2 (two) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 1 and preceding 3. It is the smallest and only even prime number. Because it forms the basis of a duality, it has religious and spiritual significance in many cultures.

In mathematics, a dihedral group is the group of symmetries of a regular polygon, which includes rotations and reflections. Dihedral groups are among the simplest examples of finite groups, and they play an important role in group theory, geometry, and chemistry.

Kinetoplastida is a group of flagellated protists belonging to the phylum Euglenozoa, and characterised by the presence of a distinctive organelle called the kinetoplast, a granule containing a large mass of DNA. The group includes a number of parasites responsible for serious diseases in humans and other animals, as well as various forms found in soil and aquatic environments. The organisms are commonly referred to as "kinetoplastids" or "kinetoplasts".
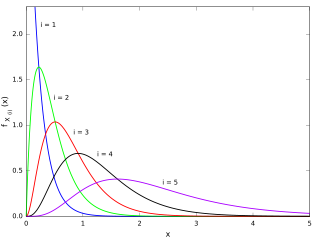
In statistics, the kth order statistic of a statistical sample is equal to its kth-smallest value. Together with rank statistics, order statistics are among the most fundamental tools in non-parametric statistics and inference.
10 (ten) is the even natural number following 9 and preceding 11. Ten is the base of the decimal numeral system, the most common system of denoting numbers in both spoken and written language.
In mathematics, a Coxeter group, named after H. S. M. Coxeter, is an abstract group that admits a formal description in terms of reflections. Indeed, the finite Coxeter groups are precisely the finite Euclidean reflection groups; for example, the symmetry group of each regular polyhedron is a finite Coxeter group. However, not all Coxeter groups are finite, and not all can be described in terms of symmetries and Euclidean reflections. Coxeter groups were introduced in 1934 as abstractions of reflection groups, and finite Coxeter groups were classified in 1935.
1000 or one thousand is the natural number following 999 and preceding 1001. In most English-speaking countries, it can be written with or without a comma or sometimes a period separating the thousands digit: 1,000.

Coccidia (Coccidiasina) are a subclass of microscopic, spore-forming, single-celled obligate intracellular parasites belonging to the apicomplexan class Conoidasida. As obligate intracellular parasites, they must live and reproduce within an animal cell. Coccidian parasites infect the intestinal tracts of animals, and are the largest group of apicomplexan protozoa.
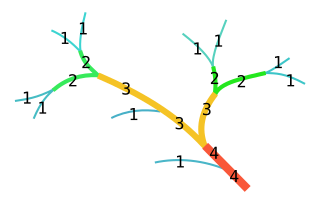
In mathematics, the Strahler number or Horton–Strahler number of a mathematical tree is a numerical measure of its branching complexity.
5 (five) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number, and cardinal number, following 4 and preceding 6, and is a prime number. It has garnered attention throughout history in part because distal extremities in humans typically contain five digits.

In mathematics, a matrix is a rectangular array or table of numbers, symbols, or expressions, arranged in rows and columns, which is used to represent a mathematical object or a property of such an object.
In statistics, L-moments are a sequence of statistics used to summarize the shape of a probability distribution. They are linear combinations of order statistics (L-statistics) analogous to conventional moments, and can be used to calculate quantities analogous to standard deviation, skewness and kurtosis, termed the L-scale, L-skewness and L-kurtosis respectively. Standardised L-moments are called L-moment ratios and are analogous to standardized moments. Just as for conventional moments, a theoretical distribution has a set of population L-moments. Sample L-moments can be defined for a sample from the population, and can be used as estimators of the population L-moments.
Gemmocystis is a genus of apicomplexans.








