Bimal Kumar Bachhawat | |
|---|---|
| Born | 16 August 1925 Kolkata, West Bengal, India |
| Died | 23 September 1996 (aged 71) India |
| Occupation(s) | Neurochemist Glycobiologist |
| Years active | 1949–1996 |
| Known for | Glycobiology Neurochemistry |
| Awards | Padma Bhushan Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize J. C. Bose Award R. D. Birla Smarak Kosh Award Outstanding Teacher Award INSA S. S. Bhatnagar Medal IISc Golden Jubilee Award FICCI Award Amrut Mody Research Foundation Award |
Bimal Kumar Bachhawat (1925–1996; Kolkata, West Bengal) was an Indian neurochemist and glycobiologist, known for his discovery of HMG-CoA lyase, an intermediate in the mevalonate and ketogenesis pathway, and for the elucidation of the molecular cause of metachromatic leukodystrophy, a hereditary disease of the brain [1] [2] His studies on sugar-bearing liposomes led to its use as a carrier for in situ delivery of drugs and hormones to diseased organs and he pioneered the therapy of systemic fungal infections using liposomal formulations. [3] He was a recipient of several awards including the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Award, the highest Indian honor in science and technology [4] and an elected fellow of three major Indian science academies. The Government of India awarded him the third highest civilian honour of the Padma Bhushan, in 1990, for his contributions to science. [5]
Dr. Bachhawat has contributed to the knowledge on the metabolism of mucopolysaccharides, gangliosides and cerebrosulphatides, especially in relation to brain function, citation of the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize. [6]
Bimal Kumar Bachhawat was born on 26 August 1925 as one among five brothers and three sisters in Kolkata, in the Bengal region of British India. [7] His graduate degree in chemistry and master's degree in applied chemistry came from the University of Calcutta after which he pursued his doctoral research in antibiotics at the Department of Food Technology of Jadavpur University under the supervision of A. N. Bose. [1] Moving to US, he continued his research at the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign under the guidance of Carl Swensson Vestling and obtained his doctoral degree (PhD) in 1953. [8] Subsequently, he worked with Minor J. Coon, first at University of Pennsylvania and then at the University of Michigan, working on the formation of ketone bodies in mammals. [8]
Bachhawat return to India in 1957 to join Christian Medical College and Hospital (CMC), Vellore and established a centre for advanced research in neurochemistry and glycobiology. [8] Here, he did research on glycolipids, glycosaminoglycans and glycoproteins and their role in neural development and neurological disorders. After working close to two decades at CMC, he moved to his native place, Kolkata, to take up the position as the director of the Indian Institute of Chemical Biology (IICB) in 1976. [1] It was during this time, he was elected as the president of the Federation of Asian and Oceanian Biochemists (FAOB), the first Indian to be elected to the post and held the position from 1983 to 1985. [3] He stayed with IICB till 1985 when he was appointed as the head of the Department of Biochemistry at the University of Delhi and superannuated from service in 1990 as the Dean of the Faculty of Interdisciplinary and Applied Sciences. [1] After retirement from academic career, he served as the president of the Society of Biological Chemists for a second time (he had served the Society as its president in 1970 for a two year-term) and remained as the president till 1994 during which time the society organized the 1994 congress of the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (IUBMB). [3] He was associated with the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) as the chairman of its technical advisory board on biological studies [7] and was a council member (1975–77) and vice president (1987–88) of the Indian National Science Academy. [1]
Bachhawat was married to Kamala and the couple had two daughters, Kalpana and Kiran, and a son, Anand. [7] He died on 23 September 1996, at the age of 71, survived by his wife and children. [7]
Bachhawat's principal contributions are spread in three areas; institution building, researches in neurochemistry and glycobiology, and academics. At Christian Medical College, he established a centre of excellence for advanced research in neurochemistry and glycobiology, known to be the first of its kind in the world. [3] Under his directorship, Indian Institute of Chemical Biology, developed into a major research center of contemporary biology. Later, at the University of Delhi, he established the Department of Biochemistry. [3]
The first of Bachhawat's major research findings came when he was working with Minor J. Coon at the University of Michigan. Both the scientists together discovered HMG-CoA lyase, an intermediate in the mevalonate and ketogenesis pathway, thus broadening the understanding of the formation of ketone bodies in mammals, which was later elucidated further in his article Enzymic cleavage of p-Hydroxy-f3-Methyl-Glutaryl coenzyme A 10 acetoacctate and acetyl coenzyme A., published in 1995. [3] On his return to India, he focused his studies on amino acids and inorganic sulphate metabolism, as well as glycosaminoglycan. [1] His researches revealed, for the first time, that metachromatic leukodystrophy, an autosomal recessive disease, was caused by the absence of Arylsulfatase A, an enzyme responsible for the breaking down on sulfatides. [9] This discovery assisted other scientists in the elucidation of similar glycolipid storage diseases such as Gaucher's disease and Tay–Sachs disease and in their prenatal diagnosis. His proposals on the biosynthesis and degradation of cerebroside-3-sulfate, a lipid found in high concentrations in patients afflicted with metachromatic leukodystrophy were known to have helped in the latter-day therapeutic protocols. [3]
Bachhawat and his colleagues were credited with the discovery of CMP-N-acetylneuraminic acid which led to the understanding of the occurrence of N-acetylneuraminic acid at cell-surfaces. [7] His studies explained the role of glycosaminoglycans in neuronal development and the property of glycolipids as biological receptors. [10] On the therapeutic side, he proposed ways for in situ delivery of drugs and enzymes to the affected organs, using sugar-bearing liposomes. [7] He also worked on the therapy of systemic fungal infections by developing liposomal formulations. [8]
On the academic front, he contributed in developing the departments he helped establish at CMC Vellore and Delhi University into centes of excellence in research. [2] His researches have been documented by way of over 150 scientific papers published in refereed journals and he has also edited a number of books. [1] He served as a member of the editorial board of Indian Journal of Biochemistry and Biophysics and he mentored 42 research scholars for master's and doctoral studies. [1] Apart from the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology congress of 1994, he was a part of the organizing committee of many other international conferences held in India. [3]
Bimal Kumar Bachhawat received the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Biological sciences of the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, the highest Indian award in science and technology, in 1962. [6] He was awarded Amrut Mody Research Foundation Award in 1974, the Golden Jubilee Award of the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) in 1976, and the FICCI Award of the Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce & Industry in 1982. [7] [11] R. D. Birla Smarak Kosh Award reached him in 1986 and the Government of India included him the Republic Day Honours list for the civilian award of the Padma Bhushan in 1990. [2] A recipient of the Outstanding Teacher Award, Bachhawat also delivered several award orations; J. C. Bose Memorial Award (1980) and B. C. Guha Award (1984) of the Indian Science Congress Association, R. N. Chopra Lectureship (1977), Prof, J. B. Chatterji Memorial Oration and Gold Medal of Calcutta School of Tropical Medicine and Distinguished Scientist Lecture of the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (1989) are some of the notable ones among them. [11]
Bachhawat was elected as a fellow by the Indian National Science Academy in 1973, [1] and a year later, the Indian Academy of Sciences inducted him as their fellow. [12] He was also an elected fellow of the National Academy of Sciences, India [13] and held the Bhatnagar Fellowship of the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research since 1990. [2] The National Academy of Sciences, India, jointly with Jaypee Institute of Information Technology (JIIT), have instituted an annual oration, Professor B. K. Bachhawat Memorial Lecture, in his honor. [11] [14] Phytochemicals & Human Health: Pharmacological & Molecular Aspects - A Tribute to Late Professor Bimal Kumar Bachhawat is a text on phytochemicals published by Nova Science Publishers in honor of Bachhawat in 2011. [15]
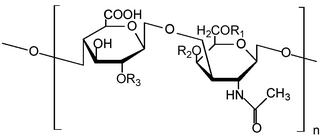
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) or mucopolysaccharides are long, linear polysaccharides consisting of repeating disaccharide units. The repeating two-sugar unit consists of a uronic sugar and an amino sugar, except in the case of the sulfated glycosaminoglycan keratan, where, in place of the uronic sugar there is a galactose unit. GAGs are found in vertebrates, invertebrates and bacteria. Because GAGs are highly polar molecules and attract water; the body uses them as lubricants or shock absorbers.

Leukodystrophies are a group of, usually, inherited disorders, characterized by degeneration of the white matter in the brain. The word leukodystrophy comes from the Greek roots leuko, "white", dys, "abnormal" and troph, "growth". The leukodystrophies are caused by imperfect growth or development of the glial cells which produce the myelin sheath, the fatty insulating covering around nerve fibers. Leukodystrophies may be classified as hypomyelinating or demyelinating diseases, respectively, depending on whether the damage is present before birth or occurs after. While all leukodystrophies are the result of genetic mutations, other demyelinating disorders have an autoimmune, infectious, or metabolic etiology.
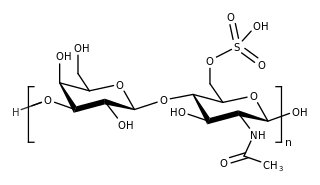
Keratan sulfate (KS), also called keratosulfate, is any of several sulfated glycosaminoglycans that have been found especially in the cornea, cartilage, and bone. It is also synthesized in the central nervous system where it participates both in development and in the glial scar formation following an injury. Keratan sulfates are large, highly hydrated molecules which in joints can act as a cushion to absorb mechanical shock.
Sulfatide, also known as 3-O-sulfogalactosylceramide, SM4, or sulfated galactocerebroside, is a class of sulfolipids, specifically a class of sulfoglycolipids, which are glycolipids that contain a sulfate group. Sulfatide is synthesized primarily starting in the endoplasmic reticulum and ending in the Golgi apparatus where ceramide is converted to galactocerebroside and later sulfated to make sulfatide. Of all of the galactolipids that are found in the myelin sheath, one fifth of them are sulfatide. Sulfatide is primarily found on the extracellular leaflet of the myelin plasma membrane produced by the oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system and in the Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system. However, sulfatide is also present on the extracellular leaflet of the plasma membrane of many cells in eukaryotic organisms.

Arylsulfatase A is an enzyme that breaks down sulfatides, namely cerebroside 3-sulfate into cerebroside and sulfate. In humans, arylsulfatase A is encoded by the ARSA gene.
In biochemistry, sulfatases EC 3.1.6.- are a class of enzymes of the esterase class that catalyze the hydrolysis of sulfate esters into an alcohol and a bisulfate:

Prosaposin, also known as PSAP, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the PSAP gene.

Serine/threonine-protein kinase MARK1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MARK1 gene.

Galactosylceramide sulfotransferase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GAL3ST1 gene.
Linda Carol Hsieh-Wilson is an American chemist and the Milton and Rosalind Chang Professor of Chemistry at the California Institute of Technology. She is known for her work in chemical neurobiology on understanding the structure and function of carbohydrates in the nervous system. Her studies have revealed critical roles for carbohydrates and protein glycosylation in fundamental processes ranging from cellular metabolism to memory storage. She is a member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences and was elected to the National Academy of Sciences in 2022.
Jeffrey David Esko, Ph.D.,M.D. (h.c) is currently a Distinguished Professor of Cellular and Molecular Medicine and Co-Director of the Glycobiology Research and Training Center at the University of California, San Diego. His research has focuses on understanding the structure, biosynthesis and biological roles of proteoglycans in mammalian cells and model organisms. Esko popularized proteoglycans through his pioneering genetic and functional studies in cells and model organisms. He discovered the dependence of tumor formation on heparan sulfate, the first small molecule inhibitors of heparan sulfate, the action of proteoglycans as receptors for hepatic lipoprotein clearance and for delivery of therapeutic agents. Esko cofounded Zacharon Pharmaceuticals. He was an editor and author of the first textbook in the Glycobiology field, Essentials of Glycobiology.
Sandip Kumar Basu is an Indian molecular biologist and the holder of the J. C. Bose Chair of the National Academy of Sciences, India, who is credited with innovations in the treatment protocols of leishmaniasis, tuberculosis, viral infections, multidrug resistant cancer and arterosclerosis. He was honored by the Government of India, in 2001, with the fourth highest Indian civilian award of Padma Shri.
Dorairajan Balasubramanian, popularly known as Professor Balu, is an Indian biophysical chemist and ocular biochemist. He is a former President of Indian Academy of Sciences and a director of research at the Prof. Brien Holden Eye Research Centre of L. V. Prasad Eye Institute, Hyderabad. A recipient of the National Order of Merit (France), Balasubramanian was honored by the Government of India, in 2002, with the fourth highest Indian civilian award of Padma Shri.
Minor Jesser Coon was an American biochemist and Victor V Vaughan Distinguished University Professor Emeritus at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. He is best known for his research on cytochrome P-450 and as the co-discoverer of HMG-CoA, along with Bimal Kumar Bachhawat. He died on September 5, 2018, from complications due to Alzheimer's disease.
Balasubramanian Gopal is an Indian structural biologist, molecular biophysicist and a professor at the Molecular Biophysics Unit of the Indian Institute of Science. He is known for his studies on cell wall synthesis in Staphylococcus aureus and is an elected fellow of the National Academy of Sciences, India, Indian National Science Academy and the Indian Academy of Sciences. He received the National Bioscience Award for Career Development of the Department of Biotechnology in 2010. The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, the apex agency of the Government of India for scientific research, awarded him the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology, one of the highest Indian science awards, in 2015, for his contributions to biological sciences.
Uttamchand Khimchand Sheth (1920–2000) was an Indian clinical pharmacologist and the director of King Edward Memorial Hospital and Seth Gordhandas Sunderdas Medical College.
Kochupurackal P. Mohanakumar is an Indian chemical biologist, neuroscientist and the director of Inter University Centre for Biomedical Research and Super Specialty Hospital, Kottayam. He is a former chief scientist at the Indian Institute of Chemical Biology and is known for his studies on Parkinson's disease and Huntington's disease. The Department of Biotechnology of the Government of India awarded him the National Bioscience Award for Career Development, one of the highest Indian science awards, for his contributions to biosciences in 2000.
Anand Kumar Bachhawat is an Indian geneticist, biochemist, professor in biological sciences and the dean of faculty at the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Mohali. Known for his studies on microbial genetics, Bachhawat is an elected fellow of all the three major Indian science academies namely Indian Academy of Sciences, National Academy of Sciences, India and Indian National Science Academy.

Stains-all is a carbocyanine dye, which stains anionic proteins, nucleic acids, anionic polysaccharides and other anionic molecules.
Ashish Arora is an Indian structural biologist and a senior scientist at Central Drug Research Institute. He did his postgraduate studies at Rajasthan University and post-doctoral work at the Max Planck Institute for Biophysical Chemistry, Goettingen, and University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA, before joining the Central Drug Research Institute in 2002. He is known for his studies on Protein NMR Spectroscopy and the pathogenesis of diseases such as tuberculosis and visceral leishmaniasis, commonly known as Kala Azar and has delivered invited speeches at various seminars. The Department of Biotechnology of the Government of India awarded him the National Bioscience Award for Career Development, one of the highest Indian science awards, for his contributions to biosciences, in 2011. He is also a recipient of the 2010 Prof. B. K. Bachhawat Memorial Young Scientist Award of the National Academy of Sciences, India.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link)