Biodiversity in Israel and Palestine is about the fauna and flora in the geographical region of Israel and of the Palestinian National Authority (the West Bank and the Gaza Strip). This geographical area within the historical region of Palestine extends from the Jordan River and Wadi Araba in the east, to the Mediterranean Sea and the Sinai desert in the west, to Lebanon in the north, and to the gulf of Aqaba, or Eilat in the south.
The area is part of the Palearctic realm, located in the Mediterranean Basin, whose climate supports the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome. This includes the Eastern Mediterranean conifer-sclerophyllous-broadleaf forests and the Southern Anatolian montane conifer and deciduous forests ecoregions.
There are five different geographical zones and the climate varies from semi-arid to temperate to subtropical. The region is home to a variety of plants and animals; at least 47,000 living species have been identified, with another 4,000 assumed to exist. 116 species of mammals are native to Palestine/Israel, as well as 511 bird species, 97 reptile species, and seven amphibian species. There are also an estimated 2,780 plant species.
The region of Palestine with the Gaza Strip, Israel, and the West Bank are located at the eastern end of the Mediterranean Sea, traditionally called the Levant. Israel is bounded on the north by Lebanon and on the northeast by Syria. Jordan lies to the east and southeast of the West Bank and Israel; Israel and the Gaza Strip are bordered on the southwest by the Egyptian Sinai Peninsula and on the west by the Mediterranean Sea.
The region is divided into three major climate zones, and one microclimate zone:
The climate is determined by the location between the subtropical aridity of the Sahara and the Arabian deserts, and the subtropical humidity of the Levant or eastern Mediterranean. The climate conditions are highly variable within the area and modified locally by altitude, latitude, and the proximity to the Mediterranean sea.
The following is a taxonomical classification up to Phylum level of all species found in the area.
The following are online well prepared databases about the biodiversity in the Palestine Israel area.

The geography of Israel is very diverse, with desert conditions in the south, and snow-capped mountains in the north. Israel is located at the eastern end of the Mediterranean Sea in West Asia. It is bounded to the north by Lebanon, the northeast by Syria, the east by Jordan and the West Bank, and to the southwest by Egypt. To the west of Israel is the Mediterranean Sea, which makes up the majority of Israel's 273 km (170 mi) coastline, and the Gaza Strip. Israel has a small coastline on the Red Sea in the south.

The Palearctic or Palaearctic is the largest of the eight biogeographic realms of the Earth. It stretches across all of Eurasia north of the foothills of the Himalayas, and North Africa.
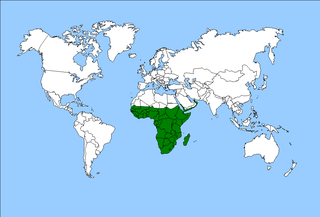
The Afrotropical realm is one of the Earth's eight biogeographic realms. It includes Sub-Saharan Africa, the southern Arabian Peninsula, the island of Madagascar, and the islands of the western Indian Ocean. It was formerly known as the Ethiopian Zone or Ethiopian Region.

Southwest Australia is a biogeographic region in Western Australia. It includes the Mediterranean-climate area of southwestern Australia, which is home to a diverse and distinctive flora and fauna.

In biogeography, the Mediterranean Basin, also known as the Mediterranean Region or sometimes Mediterranea, is the region of lands around the Mediterranean Sea that have mostly a Mediterranean climate, with mild to cool, rainy winters and warm to hot, dry summers, which supports characteristic Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub vegetation. It was a very important part of Mediterranean civilizations.

Israeli coastal plain is the Israeli segment of the Levantine coastal plain of the Mediterranean Sea, extending 187 kilometres (116 mi) north to south. It is a geographical region defined morphologically by the sea, in terms of topography and soil, and also in its climate, flora and fauna. It is narrow in the north and broadens considerably towards the south, and is continuous, except the short section where Mount Carmel reaches almost all the way to the sea. The Coastal Plain is bordered to the east by – north to south – the topographically higher regions of the Galilee, the low and flat Jezreel Valley, the Carmel range, the mountains of Samaria, the hill country of Judea known as the Shephelah, and the Negev Mountains in the south. To the north it is separated from the coastal plain of Lebanon by the cliffs of Rosh HaNikra, which jut out into the sea from the Galilee mountains, but to the south it continues into the Egyptian Sinai Peninsula.
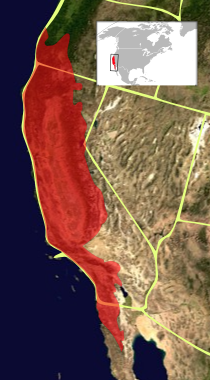
The California Floristic Province (CFP) is a floristic province with a Mediterranean-type climate located on the Pacific Coast of North America with a distinctive flora similar to other regions with a winter rainfall and summer drought climate like the Mediterranean Basin. This biodiversity hotspot is known for being the home of the Sierran giant sequoia tree and its close relative the coast redwood. In 1996, the Province was designated as a biodiversity hotspot allowing it to join ranks among 33 other areas in the world with many endemic species. To be named a biodiversity hotspot, an area has to contain species and plant life that cannot be found anywhere else in the world. The California Floristic Province is home to over 3,000 species of vascular plants, 60% of which are endemic to the province.

The wildlife of Israel includes the flora and fauna of Israel, which is extremely diverse due to the country's location between the temperate and the tropical zones, bordering the Mediterranean Sea in the west and the desert in the east. Species such as the Syrian brown bear and the Arabian ostrich have become extinct in Israel because of their loss of habitat. As of May 2007, 190 nature reserves have been established in Israel.

The wildlife of Egypt is composed of the flora and fauna of this country in northeastern Africa and southwestern Asia, and is substantial and varied. Apart from the fertile Nile Valley, which bisects the country from south to north, the majority of Egypt's landscape is desert, with a few scattered oases. It has long coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea, the Gulf of Suez, the Gulf of Aqaba and the Red Sea. Each geographic region has a diversity of plants and animals each adapted to its own particular habitat.

The wildlife of South Africa consists of the flora and fauna of this country in Southern Africa. The country has a range of different habitat types and an ecologically rich and diverse wildlife, vascular plants being particularly abundant, many of them endemic to the country. There are few forested areas, much savanna grassland, semi-arid Karoo vegetation and the fynbos of the Cape Floristic Region. Famed for its national parks and big game, 297 species of mammal have been recorded in South Africa, as well as 849 species of bird and over 20,000 species of vascular plants.

The wildlife of Morocco is composed of its flora and fauna. The country has a wide range of terrains and climate types and a correspondingly large diversity of plants and animals. The coastal areas have a Mediterranean climate and vegetation while inland the Atlas Mountains is forested. Further south, the borders of the Sahara Desert are increasingly arid. Large mammals are not particularly abundant in Morocco, but rodents, bats, and other small mammals are more plentiful. Four hundred and ninety species of birds have been recorded here.

The wildlife of Sudan is composed of its flora and fauna. A variety of climate types in Sudan results in a wide range of habitats and the range of wildlife is diverse. Some 287 species of mammal have been recorded in the country and some 634 species of bird.

In our whole Earth and the soil, all of the animals living in Asia and its surrounding seas and islands are considered the fauna of Asia. Since there is no natural biogeographic boundary in the west between Europe and Asia, the term "fauna of Asia" is somewhat elusive but it is a geographical name given. Temperate Asia is the eastern part of the Palearctic realm, and its south-eastern part belongs to the Indomalayan realm. Asia shows a notable diversity of habitats, with significant variations in rainfall, altitude, topography, temperature and geological history, which is reflected in its richness and diversity of animal life.

The Chilean Matorral (NT1201) is a terrestrial ecoregion of central Chile, located on the west coast of South America. It is in the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome, part of the Neotropical realm.

The flora of Italy is all the plant life present in the territory of the Italian Republic. The flora of Italy was traditionally estimated to comprise about 5,500 vascular plant species. However, as of 2019, 7,672 species are recorded in the second edition of the flora of Italy and in its digital archives Digital flora of Italy. In particular, 7,031 are autochthonous and 641 are non native species widely naturalized since more than three decades. Additionally, further 468 exotic species have been recorded as adventitious or naturalized in more recent times.

Mediterranean forests, woodlands and scrub is a biome defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature. The biome is generally characterized by dry summers and rainy winters, although in some areas rainfall may be uniform. Summers are typically hot in low-lying inland locations but can be cool near colder seas. Winters are typically mild to cool in low-lying locations but can be cold in inland and higher locations. All these ecoregions are highly distinctive, collectively harboring 10% of the Earth's plant species.
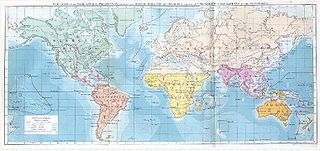
Biogeographic classification of India is the division of India according to biogeographic characteristics. Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species (biology), organisms, and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time. India has a rich heritage of natural diversity. India ranks fourth in Asia and tenth in the world amongst the top 17 mega-diverse countries in the world. India harbours nearly 11% of the world's floral diversity comprising over 17500 documented flowering plants, 6200 endemic species, 7500 medicinal plants and 246 globally threatened species in only 2.4% of world's land area. India is also home to four biodiversity hotspots—Andaman & Nicobar Islands, Eastern Himalaya, Indo-Burma region, and the Western Ghats. Hence the importance of biogeographical study of India's natural heritage.

Geography of the State of Palestine refers to the geographic, climatic and other properties of the areas claimed by State of Palestine.
The wildlife of Syria is the flora and fauna of Syria, a country at the eastern end of the Mediterranean Sea. Besides its coastline, the country has a coastal plain, mountain ranges in the west, a semi-arid steppe area in the centre occupying most of the country, and a desert area in the east. Each of these zones has its own characteristic animals and plants.

The Cañón de Santa Elena Flora and Fauna Protection Area is a protected area for plants and wildlife in the Mexican municipalities of Manuel Benavides and Ojinaga, in the state of Chihuahua. It was founded on November 7, 1994 and has an area of 277,209 hectares.