| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|
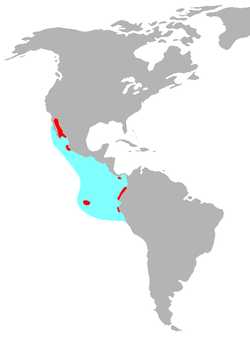
| Blue-footed booby | Sula nebouxii
Milne-Edwards, 1882
- S. n. nebouxii Milne-Edwards, 1882 – Pacific coast of Southern and Middle America
- S. n. excisa Todd, 1948 – Galápagos Islands
| Gulf of California down along the western coasts of Central and South America down to Peru
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
[11]
|
|---|
| Brown booby  | Sula leucogaster
(Boddaert, 1783)
- S. l. leucogaster(Boddaert, 1783) – Caribbean and Atlantic Islands
- S. l. plotus(Forster, JR, 1844) – Red Sea through the Indian Ocean to the west and central Pacific
| Islands and coasts in the pantropical areas of the Atlantic and Pacific oceans
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
[12]
|
|---|
| Cocos booby  | Sula brewsteri
Goss, 1888
- S. b. brewsterGoss, 1888
- S. b. etesiacaThayer & Bangs, 1905
- S. b. nesiotesHeller & Snodgrass, 1901
| East and Central Pacific
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | NE
|
|---|
| Masked booby  | Sula dactylatra
Lesson, 1831
- S. d. dactylatraLesson, 1831
- S. d. melanopsHartlaub, 1859
- S. d. tasmanivan Tets, Meredith, Fullagar & Davidson, 1988
- S. d. personataGould, 1846
| islands in tropical oceans
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
[13]
|
|---|
| Nazca booby  | Sula granti
Rothschild, 1902 | Eastern Pacific from the islands in Baja California to the Galapagos islands and the Isla de la Plata in Ecuador and Malpelo in Colombia
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
[14]
|
|---|
| Peruvian booby  | Sula variegata
(Tschudi, 1843) | Peru
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
[15]
|
|---|
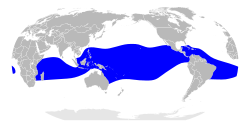
| Red-footed booby  | Sula sula
(Linnaeus, 1766)
- S. s. sula (Linnaeus, 1766) – Caribbean and southwest Atlantic islands
- S. s. rubripes Gould, 1838 – tropical Pacific and Indian Oceans
- S. s. websteri Rothschild, 1898 – eastern central Pacific
| Sri Lanka, Christmas Island, eastern central Pacific
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
[16]
|
|---|















