
Fimbrin also known as is plastin 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PLS1 gene. Fimbrin is an actin cross-linking protein important in the formation of filopodia.
Actin-binding proteins are proteins that bind to actin. This may mean ability to bind actin monomers, or polymers, or both.

Pleckstrin homology domain or (PHIP) is a protein domain of approximately 120 amino acids that occurs in a wide range of proteins involved in intracellular signaling or as constituents of the cytoskeleton.

Utrophin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UTRN gene. The name is a short form for ubiquitous dystrophin.
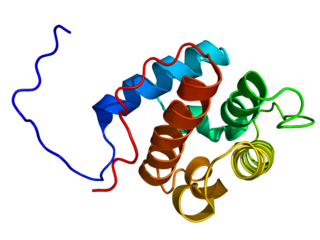
Calponin is a calcium binding protein. Calponin tonically inhibits the ATPase activity of myosin in smooth muscle. Phosphorylation of calponin by a protein kinase, which is dependent upon calcium binding to calmodulin, releases the calponin's inhibition of the smooth muscle ATPase.
Actinin is a microfilament protein. The functional protein is an anti-parallel dimer, which cross-links the thin filaments in adjacent sarcomeres, and therefore coordinates contractions between sarcomeres in the horizontal axis. Alpha-actinin is a part of the spectrin superfamily. This superfamily is made of spectrin, dystrophin, and their homologous and isoforms. In non-muscle cells, it is found by the actin filaments and at the adhesion sites.The lattice like arrangement provides stability to the muscle contractile apparatus. Specifically, it helps bind actin filaments to the cell membrane. There is a binding site at each end of the rod and with bundles of actin filaments.

Cell division control protein 42 homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CDC42 gene. Cdc42 is involved in regulation of the cell cycle. It was originally identified in S. cerevisiae (yeast) as a mediator of cell division, and is now known to influence a variety of signaling events and cellular processes in a variety of organisms from yeast to mammals.

Proto-oncogene vav is a protein that in humans is encoded by the VAV1 gene.

Alpha-actinin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACTN1 gene.

Spectrin alpha chain, erythrocyte is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SPTA1 gene.

Alpha II-spectrin, also known as Spectrin alpha chain, brain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SPTAN1 gene. Alpha II-spectrin is expressed in a variety of tissues, and is highly expressed in cardiac muscle at Z-disc structures, costameres and at the sarcolemma membrane. Mutations in alpha II-spectrin have been associated with early infantile epileptic encephalopathy-5, and alpha II-spectrin may be a valuable biomarker for Guillain–Barré syndrome and infantile congenital heart disease.

Tropomyosin alpha-3 chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TPM3 gene.

Ras GTPase-activating-like protein IQGAP1 (IQGAP1) also known as p195 is a ubiquitously expressed protein that in humans is encoded by the IQGAP1 gene. IQGAP1 is a scaffold protein involved in regulating various cellular processes ranging from organization of the actin cytoskeleton, transcription, and cellular adhesion to regulating the cell cycle.
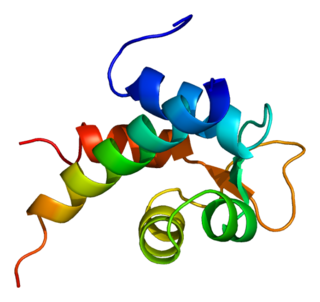
Alpha-actinin-2 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ACTN2 gene. This gene encodes an alpha-actinin isoform that is expressed in both skeletal and cardiac muscles and functions to anchor myofibrillar actin thin filaments and titin to Z-discs.

Alpha-actinin-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACTN4 gene.

Spectrin beta chain, brain 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SPTBN1 gene.

Alpha-centractin (yeast) or ARP1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACTR1A gene.

Ena/VASP-like protein is a member of the Ena/VASP family of proteins that in humans is encoded by the EVL gene.
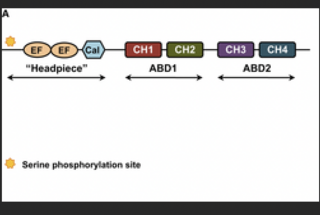
Plastin is part of a family of actin-bundling proteins, specifically the α-actinin family of actin-binding protein, which are found in many lifeforms, from humans and other animals to plants and yeasts. These proteins are known to cross-link actin filaments into bundles for various cell purposes.

Calponin 1 is a basic smooth muscle protein that in humans is encoded by the CNN1 gene.
















