
A metallocene is a compound typically consisting of two cyclopentadienyl anions (C
5H−
5, abbreviated Cp) bound to a metal center (M) in the oxidation state II, with the resulting general formula (C5H5)2M. Closely related to the metallocenes are the metallocene derivatives, e.g. titanocene dichloride or vanadocene dichloride. Certain metallocenes and their derivatives exhibit catalytic properties, although metallocenes are rarely used industrially. Cationic group 4 metallocene derivatives related to [Cp2ZrCH3]+ catalyze olefin polymerization.

A cyclopentadienyl complex is a coordination complex of a metal and cyclopentadienyl groups. Cyclopentadienyl ligands almost invariably bind to metals as a pentahapto (η5-) bonding mode. The metal–cyclopentadienyl interaction is typically drawn as a single line from the metal center to the center of the Cp ring.

Iron pentacarbonyl, also known as iron carbonyl, is the compound with formula Fe(CO)5. Under standard conditions Fe(CO)5 is a free-flowing, straw-colored liquid with a pungent odour. Older samples appear darker. This compound is a common precursor to diverse iron compounds, including many that are useful in small scale organic synthesis.
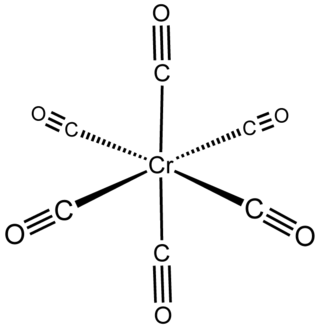
Chromium hexacarbonyl is a chromium(0) organometallic compound with the formula Cr(CO)6. It is a homoleptic complex, which means that all the ligands are identical. It is a colorless crystalline air-stable solid, with a high vapor pressure.

Titanocene dichloride is the organotitanium compound with the formula (η5-C5H5)2TiCl2, commonly abbreviated as Cp2TiCl2. This metallocene is a common reagent in organometallic and organic synthesis. It exists as a bright red solid that slowly hydrolyzes in air. It shows antitumour activity and was the first non-platinum complex to undergo clinical trials as a chemotherapy drug.

In coordination chemistry, hapticity is the coordination of a ligand to a metal center via an uninterrupted and contiguous series of atoms. The hapticity of a ligand is described with the Greek letter η ('eta'). For example, η2 describes a ligand that coordinates through 2 contiguous atoms. In general the η-notation only applies when multiple atoms are coordinated. In addition, if the ligand coordinates through multiple atoms that are not contiguous then this is considered denticity, and the κ-notation is used once again. When naming complexes care should be taken not to confuse η with μ ('mu'), which relates to bridging ligands.

Chromocene is the organochromium compound with the formula [Cr(C5H5)2]. Like structurally related metallocenes, chromocene readily sublimes in a vacuum and is soluble in non-polar organic solvents. It is more formally known as bis(η5-cyclopentadienyl)chromium(II).

Tungsten hexacarbonyl (also called tungsten carbonyl) is an organometallic compound with the formula W(CO)6. This complex gave rise to the first example of a dihydrogen complex.

Dicarbonylbis(cyclopentadienyl)titanium is the chemical compound with the formula (η5-C5H5)2Ti(CO)2, abbreviated Cp2Ti(CO)2. This maroon-coloured, air-sensitive species is soluble in aliphatic and aromatic solvents. It has been used for the deoxygenation of sulfoxides, reductive coupling of aromatic aldehydes and reduction of aldehydes.
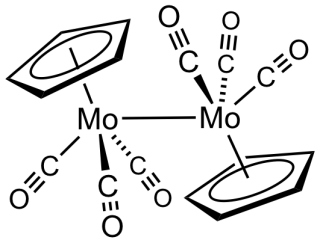
Cyclopentadienylmolybdenum tricarbonyl dimer is the chemical compound with the formula Cp2Mo2(CO)6, where Cp is C5H5. A dark red solid, it has been the subject of much research although it has no practical uses.

Decamethyldizincocene is an organozinc compound with the formula [Zn2(η5–C5Me5)2]. It is the first and an unusual example of a compound with a Zn-Zn bond. Decamethyldizincocene is a colorless crystalline solid that burns spontaneously in the presence of oxygen and reacts with water. It is stable at room temperature and especially soluble in diethyl ether, benzene, pentane, or tetrahydrofuran.
In organometallic chemistry, a transition metal indenyl complex is a coordination compound that contains one or more indenyl ligands. The indenyl ligand is formally the anion derived from deprotonation of indene. The η5-indenyl ligand is related to the η5cyclopentadienyl anion (Cp), thus indenyl analogues of many cyclopentadienyl complexes are known. Indenyl ligands lack the 5-fold symmetry of Cp, so they exhibit more complicated geometries. Furthermore, some indenyl complexes also exist with only η3-bonding mode. The η5- and η3-bonding modes sometimes interconvert.
Organoiron chemistry is the chemistry of iron compounds containing a carbon-to-iron chemical bond. Organoiron compounds are relevant in organic synthesis as reagents such as iron pentacarbonyl, diiron nonacarbonyl and disodium tetracarbonylferrate. Although iron is generally less active in many catalytic applications, it is less expensive and "greener" than other metals. Organoiron compounds feature a wide range of ligands that support the Fe-C bond; as with other organometals, these supporting ligands prominently include phosphines, carbon monoxide, and cyclopentadienyl, but hard ligands such as amines are employed as well.
Rhodocene is a chemical compound with the formula [Rh(C5H5)2]. Each molecule contains an atom of rhodium bound between two planar aromatic systems of five carbon atoms known as cyclopentadienyl rings in a sandwich arrangement. It is an organometallic compound as it has (haptic) covalent rhodium–carbon bonds. The [Rh(C5H5)2] radical is found above 150 °C (302 °F) or when trapped by cooling to liquid nitrogen temperatures (−196 °C [−321 °F]). At room temperature, pairs of these radicals join via their cyclopentadienyl rings to form a dimer, a yellow solid.
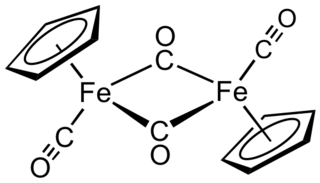
Cyclopentadienyliron dicarbonyl dimer is an organometallic compound with the formula [(η5-C5H5)Fe(CO)2]2, often abbreviated to Cp2Fe2(CO)4, [CpFe(CO)2]2 or even Fp2, with the colloquial name "fip dimer". It is a dark reddish-purple crystalline solid, which is readily soluble in moderately polar organic solvents such as chloroform and pyridine, but less soluble in carbon tetrachloride and carbon disulfide. Cp2Fe2(CO)4 is insoluble in but stable toward water. Cp2Fe2(CO)4 is reasonably stable to storage under air and serves as a convenient starting material for accessing other Fp (CpFe(CO)2) derivatives (described below).

Cyclopentadienyliron dicarbonyl iodide is an organoiron compound with the formula (C5H5)Fe(CO)2I. It is a dark brown solid that is soluble in common organic solvents. (C5H5)Fe(CO)2I, or FpI as it is often known, is an intermediate for the preparation of other organoiron compounds such as in ferraboranes.
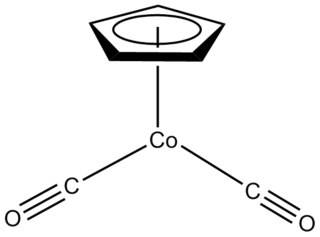
Half sandwich compounds, also known as piano stool complexes, are organometallic complexes that feature a cyclic polyhapto ligand bound to an MLn center, where L is a unidentate ligand. Thousands of such complexes are known. Well-known examples include cyclobutadieneiron tricarbonyl and (C5H5)TiCl3. Commercially useful examples include (C5H5)Co(CO)2, which is used in the synthesis of substituted pyridines, and methylcyclopentadienyl manganese tricarbonyl, an antiknock agent in petrol.

Cyclopentadienyltungsten tricarbonyl dimer is the organotungsten compound with the formula Cp2W2(CO)6, where Cp is C5H5. A dark red crystalline solid, it is the subject of research, although it has no or few practical uses.
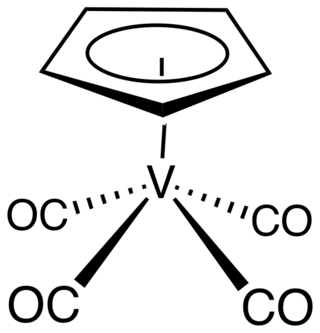
Cyclopentadienylvanadium tetracarbonyl is the organovanadium compound with the formula (C5H5)V(CO)4. An orange, diamagnetic solid, it is the principal cyclopentadienyl carbonyl of vanadium. It can be prepared by heating a solution of vanadocene under high pressure of carbon monoxide. As confirmed by X-ray crystallography, the coordination sphere of vanadium consists of η5-cyclopentadienyl and four carbonyl ligands. The molecule is a four-legged piano stool complex. The compound is soluble in common organic solvents. The compound has no commercial applications.
Organotechnetium chemistry is the science of describing the physical properties, synthesis, and reactions of organotechnetium compounds, which are organometallic compounds containing carbon-to-technetium chemical bonds. The most common organotechnetium compounds are coordination complexes used as radiopharmaceutical imaging agents.

















