
Amniotes are tetrapod vertebrate animals belonging to the clade Amniota, a large group that comprises the vast majority of living terrestrial and semiaquatic vertebrates. Amniotes evolved from amphibian ancestors during the Carboniferous period and further diverged into two groups, namely the sauropsids and synapsids. They are distinguished from the other living tetrapod clade — the non-amniote lissamphibians — by the development of three extraembryonic membranes, thicker and keratinized skin, and costal respiration.

"Labyrinthodontia" is an informal grouping of extinct predatory amphibians which were major components of ecosystems in the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. Traditionally considered a subclass of the class Amphibia, modern classification systems recognize that labyrinthodonts are not a formal natural group (clade) exclusive of other tetrapods. Instead, they consistute an evolutionary grade, ancestral to living tetrapods such as lissamphibians and amniotes. "Labyrinthodont"-grade vertebrates evolved from lobe-finned fishes in the Devonian, though a formal boundary between fish and amphibian is difficult to define at this point in time.

Reptiliomorpha is a clade containing the amniotes and those tetrapods that share a more recent common ancestor with amniotes than with living amphibians (lissamphibians). It was defined by Michel Laurin (2001) and Vallin and Laurin (2004) as the largest clade that includes Homo sapiens, but not Ascaphus truei. Laurin and Reisz (2020) defined Pan-Amniota as the largest total clade containing Homo sapiens, but not Pipa pipa, Caecilia tentaculata, and Siren lacertina.

Diadectomorpha is a clade of large tetrapods that lived in Euramerica during the Carboniferous and Early Permian periods and in Asia during Late Permian (Wuchiapingian), They have typically been classified as advanced reptiliomorphs positioned close to, but outside of the clade Amniota, though some recent research has recovered them as the sister group to the traditional Synapsida within Amniota, based on inner ear anatomy and cladistic analyses. They include both large carnivorous and even larger herbivorous forms, some semi-aquatic and others fully terrestrial. The diadectomorphs seem to have originated during late Mississippian times, although they only became common after the Carboniferous rainforest collapse and flourished during the Late Pennsylvanian and Early Permian periods.

Captorhinidae is an extinct family of tetrapods, typically considered primitive reptiles, known from the late Carboniferous to the Late Permian. They had a cosmopolitan distribution across Pangea.

Seymouria is an extinct genus of seymouriamorph from the Early Permian of North America and Europe. Although they were amphibians, Seymouria were well-adapted to life on land, with many reptilian features—so many, in fact, that Seymouria was first thought to be a primitive reptile. It is primarily known from two species, Seymouria baylorensis and Seymouria sanjuanensis. The type species, S. baylorensis, is more robust and specialized, though its fossils have only been found in Texas. On the other hand, Seymouria sanjuanensis is more abundant and widespread. This smaller species is known from multiple well-preserved fossils, including a block of six skeletons found in the Cutler Formation of New Mexico, and a pair of fully grown skeletons from the Tambach Formation of Germany, which were fossilized lying next to each other.

Caseasauria is one of the two main clades of early synapsids, the other being the Eupelycosauria. Caseasaurs are currently known only from the Late Carboniferous and the Permian, and include two superficially different families, the small insectivorous or carnivorous Eothyrididae, and the large, herbivorous Caseidae. These two groups share a number of specialised features associated with the morphology of the snout and external naris.

Seymouriamorpha were a small but widespread group of limbed vertebrates (tetrapods). They have long been considered stem-amniotes (reptiliomorphs), and most paleontologists still accept this point of view, but some analyses suggest that seymouriamorphs are stem-tetrapods. Many seymouriamorphs were terrestrial or semi-aquatic. However, aquatic larvae bearing external gills and grooves from the lateral line system have been found, making them unquestionably amphibians. Though as they matured, they became more terrestrial and reptile-like. They ranged from 30 cm long lizard-sized creatures to the 1.5 m long Enosuchus. If seymouriamorphs are reptiliomorphs, they were the distant relatives of amniotes. Seymouriamorphs form into three main groups, Kotlassiidae, Discosauriscidae, and Seymouriidae, a group that includes the best known genus, Seymouria. The last seymouriamorph became extinct by the end of the Permian.

Parareptilia ("near-reptiles") is a subclass or clade of basal sauropsids/reptiles, typically considered the sister taxon to Eureptilia. Parareptiles first arose near the end of the Carboniferous period and achieved their highest diversity during the Permian period. Several ecological innovations were first accomplished by parareptiles among reptiles. These include the first reptiles to return to marine ecosystems (mesosaurs), the first bipedal reptiles, the first reptiles with advanced hearing systems, and the first large herbivorous reptiles. The only parareptiles to survive into the Triassic period were the procolophonoids, a group of small generalists, omnivores, and herbivores. The largest family of procolophonoids, the procolophonids, rediversified in the Triassic, but subsequently declined and became extinct by the end of the period.

Embolomeri is an order of tetrapods or stem-tetrapods, possibly members of Reptiliomorpha. Embolomeres first evolved in the Early Carboniferous (Mississippian) Period and were the largest and most successful predatory tetrapods of the Late Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian) Period. They were specialized semiaquatic predators with long bodies for eel-like undulatory swimming. Embolomeres are characterized by their vertebral centra, which are formed by two cylindrical segments, the pleurocentrum at the rear and intercentrum at the front. These segments are equal in size. Most other tetrapods have pleurocentra and intercentra which are drastically different in size and shape.

Diplovertebron is an extinct genus of embolomere that lived in the Late Carboniferous period (Moscovian), about 310 million years ago. Diplovertebron was a medium-sized animal, around 50 cm in length. Members of the genus inhabited European Carboniferous swamps in what is now the Czech Republic. They were closely related to larger swamp-dwelling tetrapods like Proterogyrinus and Anthracosaurus. However, Diplovertebron were much smaller than these large, crocodile-like creatures. Known from a single species, Diplovertebron punctatum, this genus has had a complicated history closely tied to Gephyrostegus, another genus of small, reptile-like amphibians.

Kotlassia extinct genus of kotlassiine seymouriamorph from the Late Permian of Russia. The type, and currently only, species is K. prima.

Ariekanerpeton is an extinct genus of seymouriamorph from the lower Permian. Fossils have been found from Tajikistan representing over 900 individuals of various stages of ontogenic development. However, it is thought that none of these specimens are of fully mature animals as poor bone ossification is present and the neural arches are paired and disarticulated from the pleurocentra.

Utegenia is a genus of early tetrapod. It is usually regarded as a basal seymouriamorph, but sometimes included in the Discosauriscidae or as a sister taxon of the latter. Only one species, Utegenia shpinari, found from Kazakhstan, is known. Urumqia, another basal seymouriamorph, from Urumqi, Xinjiang of China is probably a junior synonym of Utegenia.
Spinarerpeton is an extinct genus of discosauriscid seymouriamorph known from the early Permian of Boskovice Furrow, in the Czech Republic. It was first named by Jozef Klembara in 2009 and the type species is Spinarerpeton brevicephalum. A phylogenetic analysis places Spinarerpeton as the sister taxon to Makowskia.
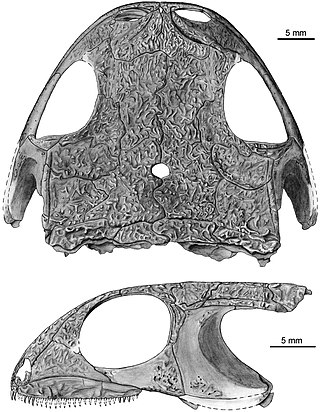
Makowskia is an extinct genus of discosauriscid seymouriamorph known from the early Permian of Boskovice Furrow, in the Czech Republic. It was first named by Jozef Klembara in 2005 and the type species is Makowskia laticephala. The generic name honors Alexander Makowsky for describing the first specimens of discosauriscids from the Boskovice Furrow, and the specific name means “broad” + “head”. Makowskia is known only from one specimen, the holotype SNMZ 26506, a skull and anterior portion of postcranial skeleton. A phylogenetic analysis places Makowskia as the sister taxon to Spinarerpeton.

Laosuchus is an extinct genus of chroniosuchian known from the Permian-Triassic boundary of Asia. Two species have been named.

Postparietals are cranial bones present in fish and many tetrapods. Although initially a pair of bones, many lineages possess postparietals which were fused into a single bone. The postparietals were dermal bones situated along the midline of the skull, behind the parietal bones. They formed part of the rear edge of the skull roof, and the lateral edge of each postparietal often contacts the tabular and supratemporal bones. In fish, the postparietals are elongated, typically the largest components of the skull roof. Tetrapods possessed shorter postparietals, which were reduced further and shifted towards the braincase in amniotes. At several points in synapsid evolution, the postparietals fused to each other and the tabulars during embryological development. This fusion produces the interparietal bone, which is inherited by mammals. Postparietals are common in extinct amphibians and early reptiles. However, most living amphibians and living reptiles lack postparietal bones, with a few exceptions.
This list of fossil amphibians described in 2020 is a list of new taxa of fossil amphibians that were described during the year 2020, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to amphibian paleontology that occurred in 2020.





















