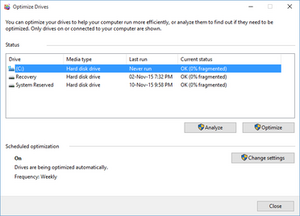
In the maintenance of file systems, defragmentation is a process that reduces the amount of fragmentation. It does this by physically organizing the contents of the mass storage device used to store files into the smallest number of contiguous regions (fragments). It also attempts to create larger regions of free space using compaction to impede the return of fragmentation. Some defragmentation utilities try to keep smaller files within a single directory together, as they are often accessed in sequence.
An NTFS junction point is a symbolic link to a directory that acts as an alias of that directory. This feature of the NTFS file system offers benefits over a Windows shell shortcut (.lnk) file, such as allowing access to files within the directory via Windows Explorer, the Command Prompt, etc.
PageDefrag is a program, developed by Sysinternals, for Microsoft Windows that runs at start-up to defragment the virtual memory page file, the registry files and the Event Viewer's logs.
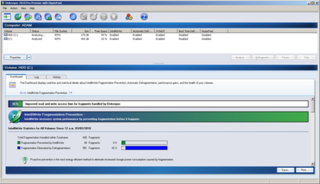
Diskeeper is a defragmentation program designed for Microsoft Windows. It was developed by Executive Software International, Inc., which later changed its name to Diskeeper Corporation, and is now called Condusiv Technologies.
Robocopy, or "Robust File Copy", is a command-line directory and/or file replication command. Robocopy functionally replaces Xcopy, with more options. It has been available as part of the Windows Resource Kit starting with Windows NT 4.0, and was first introduced as a standard feature in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008. The command is robocopy.
Contig is a command line defragmentation utility for Windows currently owned by Microsoft subsidiary SysInternals.

In computing, file system fragmentation, sometimes called file system aging, is the tendency of a file system to lay out the contents of files non-continuously to allow in-place modification of their contents. It is a special case of data fragmentation. File system fragmentation increases disk head movement or seek time, which are known to hinder throughput. In addition, file systems cannot sustain unlimited fragmentation. The correction to existing fragmentation is to reorganize files and free space back into contiguous areas, a process called defragmentation.
NTBackup is the built-in backup application introduced in Windows NT around 1997 and part of all subsequent versions up to and including Windows 2000, Windows XP and Windows Server 2003. It uses a proprietary backup format (BKF) to back up files. Files can be backed up to tape, ZIP drives, floppy disks, and hard drives. It also features integration with Task Scheduler and has several command line switches for scheduled automated backups.
Windows Vista contains a range of new technologies and features that are intended to help network administrators and power users better manage their systems. Notable changes include a complete replacement of the "Windows Setup" process, completely rewritten deployment mechanisms, support for per-application Remote Desktop sessions, new diagnostic and health monitoring tools, and a range of new Group Policy settings covering many of the features new to Windows Vista.
Condusiv Technologies is a software company based in Burbank, California. The company was formerly known as Diskeeper Corporation, a name derived from its flagship product, Diskeeper, a file-system defragmentation software package for Microsoft Windows and OpenVMS. Before adopting the Diskeeper name, the company was known as Executive Software International, Inc.

O&O Defrag is a Windows defragmentation utility sold by German software developer O&O Software. It has won several awards by PC journals and magazines, and is certified by Microsoft for all its current NTFS-based operating systems, including Windows 2000, Server 2003, Vista, 7, and 10.

Vopt is a Windows defragmentation utility sold by Golden Bow Systems. It is one of the oldest defragmentation products, and has supported MS-DOS and all versions of Microsoft Windows. The convenience of quick processing time is offset by less optimal performance, but when used in conjunction with the built-in optimization of the Windows prefetch folder, system performance is maintained without major reorganization of all the files on the drive. In February 2016, the registration key is released free in accordance with the author Barry Emerson's wish.

Defraggler is a freemium defragmentation utility developed by Piriform, which can defragment individual files or groups of files on computer system. Defraggler runs on Microsoft Windows; it has support for all versions since Windows XP. It includes support for both IA-32 and x64 versions of these operating systems.
UltraDefrag is a disk defragmentation utility for Microsoft Windows. Prior to version 8.0.0 it was released under the GNU General Public License. The only other Windows-based defragmentation utility licensed under the GNU GPL was JkDefrag, discontinued in 2008.

JkDefrag is a free open-source disk defragmenting utility computer program for Windows. It was developed by Jeroen Kessels beginning in 2004 and is released under the GNU General Public License. The "Jk" part of the utility name is taken from the developer's name, Jeroen Kessels. In 2008, from version 4, much changed from previous versions; JkDefrag was renamed MyDefrag by its developer, and JkDefrag was discontinued, although still available. MyDefrag is closed source freeware. MyDefrag website is defunct as of 2016. The JKdefrag website is still active, but all download files have been removed.
UltimateDefrag is a retail file-system defragmentation utility made by DiskTrix. An older version of the program is available as the UltimateDefrag Freeware Edition.
The following is a comparison of notable file system defragmentation software:
Auslogics Disk Defrag is a freemium software application for Microsoft Windows intended to defragment files and folders on a hard drive, consolidate free space and optimize file placement using different criteria. It is available in both a free and a proprietary "Pro" version with extended functionality.
PerfectDisk is a defragmentation software product for Windows developed by Raxco.