Microeconomics is a branch of economics that studies the behavior of individuals and firms in making decisions regarding the allocation of scarce resources and the interactions among these individuals and firms. Microeconomics focuses on the study of individual markets, sectors, or industries as opposed to the economy as a whole, which is studied in macroeconomics.
A monopoly, as described by Irving Fisher, is a market with the "absence of competition", creating a situation where a specific person or enterprise is the only supplier of a particular thing. This contrasts with a monopsony which relates to a single entity's control of a market to purchase a good or service, and with oligopoly and duopoly which consists of a few sellers dominating a market. Monopolies are thus characterised by a lack of economic competition to produce the good or service, a lack of viable substitute goods, and the possibility of a high monopoly price well above the seller's marginal cost that leads to a high monopoly profit. The verb monopolise or monopolize refers to the process by which a company gains the ability to raise prices or exclude competitors. In economics, a monopoly is a single seller. In law, a monopoly is a business entity that has significant market power, that is, the power to charge overly high prices, which is associated with unfair price raises. Although monopolies may be big businesses, size is not a characteristic of a monopoly. A small business may still have the power to raise prices in a small industry.

In economics, specifically general equilibrium theory, a perfect market, also known as an atomistic market, is defined by several idealizing conditions, collectively called perfect competition, or atomistic competition. In theoretical models where conditions of perfect competition hold, it has been demonstrated that a market will reach an equilibrium in which the quantity supplied for every product or service, including labor, equals the quantity demanded at the current price. This equilibrium would be a Pareto optimum.

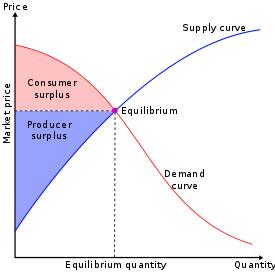
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It postulates that, holding all else equal, the unit price for a particular good or other traded item in a perfectly competitive market, will vary until it settles at the market-clearing price, where the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied such that an economic equilibrium is achieved for price and quantity transacted. The concept of supply and demand forms the theoretical basis of modern economics.
Taxes and subsidies change the price of goods and, as a result, the quantity consumed. There is a difference between an ad valorem tax and a specific tax or subsidy in the way it is applied to the price of the good. In the end levying a tax moves the market to a new equilibrium where the price of a good paid by buyers increases and the proportion of the price received by sellers decreases. The incidence of a tax does not depend on whether the buyers or sellers are taxed since taxes levied on sellers are likely to be met by raising the price charged to buyers. Most of the burden of a tax falls on the less elastic side of the market because of a lower ability to respond to the tax by changing the quantity sold or bought. Introduction of a subsidy, on the other hand, may either lowers the price of production which encourages firms to produce more, or lowers the price paid by buyers, encouraging higher sales volume. Such a policy is beneficial both to sellers and buyers.

In economics, deadweight loss is the loss of societal economic welfare due to production/consumption of a good at a quantity where marginal benefit does not equal marginal cost – in other words, there are either goods being produced despite the cost of doing so being larger than the benefit, or additional goods are not being produced despite the fact that the benefits of their production would be larger than the costs. The deadweight loss is the net benefit that is missed out on. While losses to one entity often lead to gains for another, deadweight loss represents the loss that is not regained by anyone else. This loss is therefore attributed to both producers and consumers.

This aims to be a complete article list of economics topics:
Price discrimination is a microeconomic pricing strategy where identical or largely similar goods or services are sold at different prices by the same provider to different buyers based on which market segment they are perceived to be part of. Price discrimination is distinguished from product differentiation by the difference in production cost for the differently priced products involved in the latter strategy. Price discrimination essentially relies on the variation in customers' willingness to pay and in the elasticity of their demand. For price discrimination to succeed, a seller must have market power, such as a dominant market share, product uniqueness, sole pricing power, etc.

In economics, elasticity measures the responsiveness of one economic variable to a change in another. For example, if the price elasticity of the demand of a good is −2, then a 10% increase in price will cause the quantity demanded to fall by 20%. Elasticity in economics provides an understanding of changes in the behavior of the buyers and sellers with price changes. There are two types of elasticity for demand and supply, one is inelastic demand and supply and the other one is elastic demand and supply.

In economics, economic equilibrium is a situation in which economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal.
Allocative efficiency is a state of the economy in which production is aligned with the preferences of consumers and producers; in particular, the set of outputs is chosen so as to maximize the social welfare of society. This is achieved if every produced good or service has a marginal benefit equal to the marginal cost of production.

A demand curve is a graph depicting the inverse demand function, a relationship between the price of a certain commodity and the quantity of that commodity that is demanded at that price. Demand curves can be used either for the price-quantity relationship for an individual consumer, or for all consumers in a particular market.

A price floor is a government- or group-imposed price control or limit on how low a price can be charged for a product, good, commodity, or service. It is one type of price support; other types include supply regulation and guarantee government purchase price. A price floor must be higher than the equilibrium price in order to be effective. The equilibrium price, commonly called the "market price", is the price where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change, often described as the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Governments use price floors to keep certain prices from going too low.
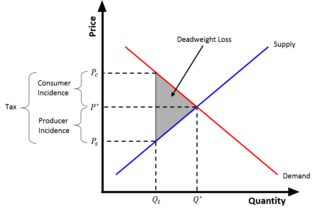
The tax wedge is the deviation from the equilibrium price and quantity as a result of the taxation of a good. Because of the tax, consumers pay more for the good than they did before the tax, and suppliers receive less for the good than they did before the tax. Put differently, the tax wedge is the difference between the price consumers pay and the value producers receive from a transaction. The tax effectively drives a "wedge" between the price consumers pay and the price producers receive for a product.
In economics, tax incidence or tax burden is the effect of a particular tax on the distribution of economic welfare. Economists distinguish between the entities who ultimately bear the tax burden and those on whom the tax is initially imposed. The tax burden measures the true economic effect of the tax, measured by the difference between real incomes or utilities before and after imposing the tax, and taking into account how the tax causes prices to change. For example, if a 10% tax is imposed on sellers of butter, but the market price rises 8% as a result, most of the tax burden is on buyers, not sellers. The concept of tax incidence was initially brought to economists' attention by the French Physiocrats, in particular François Quesnay, who argued that the incidence of all taxation falls ultimately on landowners and is at the expense of land rent. Tax incidence is said to "fall" upon the group that ultimately bears the burden of, or ultimately suffers a loss from, the tax. The key concept of tax incidence is that the tax incidence or tax burden does not depend on where the revenue is collected, but on the price elasticity of demand and price elasticity of supply. As a general policy matter, the tax incidence should not violate the principles of a desirable tax system, especially fairness and transparency. The concept of tax incidence is used in political science and sociology to analyze the level of resources extracted from each income social stratum in order to describe how the tax burden is distributed among social classes. That allows one to derive some inferences about the progressive nature of the tax system, according to principles of vertical equity.

In economics, demand is the quantity of a good that consumers are willing and able to purchase at various prices during a given time. In economics "demand" for a commodity is not the same thing as "desire" for it. It refers to both the desire to purchase and the ability to pay for a commodity.
Rental value is the fair market value of property while rented out in a lease. More generally, it may be the consideration paid under the lease for the right to occupy, or the royalties or return received by a lessor (landlord) under a license to real property. In the science and art of appraisal, it is the amount that would be paid for rental of similar real property in the same condition and in the same area.

In economics, profit is the difference between revenue that an economic entity has received from its outputs and total costs of its inputs, also known as surplus value. It is equal to total revenue minus total cost, including both explicit and implicit costs.
In economics, an excess supply, economic surplus market surplus or briefly supply is a situation in which the quantity of a good or service supplied is more than the quantity demanded, and the price is above the equilibrium level determined by supply and demand. That is, the quantity of the product that producers wish to sell exceeds the quantity that potential buyers are willing to buy at the prevailing price. It is the opposite of an economic shortage.

This glossary of economics is a list of definitions of terms and concepts used in economics, its sub-disciplines, and related fields.