The economic calculation problem is a criticism of using economic planning as a substitute for market-based allocation of the factors of production. It was first proposed by Ludwig von Mises in his 1920 article "Economic Calculation in the Socialist Commonwealth" and later expanded upon by Friedrich Hayek.

Microeconomics is a branch of economics that studies the behavior of individuals and firms in making decisions regarding the allocation of scarce resources and the interactions among these individuals and firms. Microeconomics focuses on the study of individual markets, sectors, or industries as opposed to the national economy as a whole, which is studied in macroeconomics.

In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It postulates that, holding all else equal, in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded will equal the quantity supplied, resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted. The concept of supply and demand forms the theoretical basis of modern economics.

A market economy is an economic system in which the decisions regarding investment, production and distribution to the consumers are guided by the price signals created by the forces of supply and demand. The major characteristic of a market economy is the existence of factor markets that play a dominant role in the allocation of capital and the factors of production.
This aims to be a complete article list of economics topics:

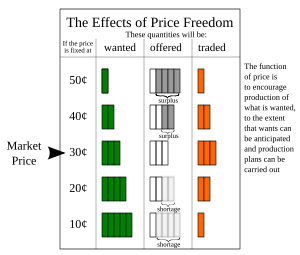
A price is the quantity of payment or compensation expected, required, or given by one party to another in return for goods or services. In some situations, the price of production has a different name. If the product is a "good" in the commercial exchange, the payment for this product will likely be called its "price". However, if the product is "service", there will be other possible names for this product's name. For example, the graph on the bottom will show some situations A good's price is influenced by production costs, supply of the desired item, and demand for the product. A price may be determined by a monopolist or may be imposed on the firm by market conditions.
In economics, economic equilibrium is a situation in which economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal.

In microeconomics, two goods are substitutes if the products could be used for the same purpose by the consumers. That is, a consumer perceives both goods as similar or comparable, so that having more of one good causes the consumer to desire less of the other good. Contrary to complementary goods and independent goods, substitute goods may replace each other in use due to changing economic conditions. An example of substitute goods is Coca-Cola and Pepsi; the interchangeable aspect of these goods is due to the similarity of the purpose they serve, i.e fulfilling customers' desire for a soft drink. These types of substitutes can be referred to as close substitutes.
Allocative efficiency is a state of the economy in which production is aligned with consumer preferences; in particular, the set of outputs is chosen so as to maximize the wellbeing of society. This is achieved if every good or service is produced up until the last unit provides a marginal benefit to consumers equal to the marginal cost of production.

Man, Economy, and State: A treatise on economic principles is a 1962 book of Austrian School economics by Murray Rothbard.

An economic system, or economic order, is a system of production, resource allocation and distribution of goods and services within a society. It includes the combination of the various institutions, agencies, entities, decision-making processes, and patterns of consumption that comprise the economic structure of a given community.
In economics, a price mechanism is the manner in which the profits of goods or services affects the supply and demand of goods and services, principally by the price elasticity of demand. A price mechanism affects both buyer and seller who negotiate prices. A price mechanism, part of a market system, comprises various ways to match up buyers and sellers.

Demand response is a change in the power consumption of an electric utility customer to better match the demand for power with the supply. Until the 21st century decrease in the cost of pumped storage and batteries, electric energy could not be easily stored, so utilities have traditionally matched demand and supply by throttling the production rate of their power plants, taking generating units on or off line, or importing power from other utilities. There are limits to what can be achieved on the supply side, because some generating units can take a long time to come up to full power, some units may be very expensive to operate, and demand can at times be greater than the capacity of all the available power plants put together. Demand response, a type of energy demand management, seeks to adjust in real-time the demand for power instead of adjusting the supply.
Economic systems as a type of social system must confront and solve the three fundamental economic problems:
A price signal is information conveyed to consumers and producers, via the prices offered or requested for, and the amount requested or offered of a product or service, which provides a signal to increase or decrease quantity supplied or quantity demanded. It also provides potential business opportunities. When a certain kind of product is in shortage supply and the price rises, people will pay more attention to and produce this kind of product. The information carried by prices is an essential function in the fundamental coordination of an economic system, coordinating things such as what has to be produced, how to produce it and what resources to use in its production.
In economics, the market mechanism is a mechanism by which the use of money exchanged by buyers and sellers with an open and understood system of value and time trade-offs in a market tends to optimize distribution of goods and services in at least some ways. The mechanism can exist in free markets or in captive or controlling markets seek to use supply and demand, or some other form of charging for scarcity, to choose among production possibilities. In a free market economy, all the resources are allocated by the private sector ; in a planned economy, all the resources are owned by the public sector ; and, in a mixed economy, some resources are owned by both sectors, private and public. In reality the first two are mostly theoretical and the third is common. Resources are allocated according to the forces of supply and demand.
In economics, a market is a composition of systems, institutions, procedures, social relations or infrastructures whereby parties engage in exchange. While parties may exchange goods and services by barter, most markets rely on sellers offering their goods or services to buyers in exchange for money. It can be said that a market is the process by which the prices of goods and services are established. Markets facilitate trade and enable the distribution and allocation of resources in a society. Markets allow any tradeable item to be evaluated and priced. A market emerges more or less spontaneously or may be constructed deliberately by human interaction in order to enable the exchange of rights of services and goods. Markets generally supplant gift economies and are often held in place through rules and customs, such as a booth fee, competitive pricing, and source of goods for sale.
Economic planning is a resource allocation mechanism based on a computational procedure for solving a constrained maximization problem with an iterative process for obtaining its solution. Planning is a mechanism for the allocation of resources between and within organizations contrasted with the market mechanism. As an allocation mechanism for socialism, economic planning replaces factor markets with a procedure for direct allocations of resources within an interconnected group of socially owned organizations which together comprise the productive apparatus of the economy.

In economics, competition is a scenario where different economic firms are in contention to obtain goods that are limited by varying the elements of the marketing mix: price, product, promotion and place. In classical economic thought, competition causes commercial firms to develop new products, services and technologies, which would give consumers greater selection and better products. The greater the selection of a good is in the market, the lower prices for the products typically are, compared to what the price would be if there was no competition (monopoly) or little competition (oligopoly).
This glossary of economics is a list of definitions of terms and concepts used in economics, its sub-disciplines, and related fields.