
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and other valuable goods. Those who conduct acts of piracy are called pirates, and vessels used for piracy are called pirate ships. The earliest documented instances of piracy were in the 14th century BC, when the Sea Peoples, a group of ocean raiders, attacked the ships of the Aegean and Mediterranean civilisations. Narrow channels which funnel shipping into predictable routes have long created opportunities for piracy, as well as for privateering and commerce raiding.
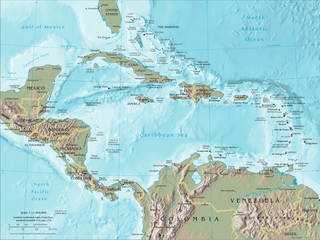
The era of piracy in the Caribbean began in the 1500s and phased out in the 1830s after the navies of the nations of Western Europe and North America with colonies in the Caribbean began hunting and prosecuting pirates. The period during which pirates were most successful was from the 1650s to the 1730s. Piracy flourished in the Caribbean because of the existence of pirate seaports such as Port Royal in Jamaica, Tortuga in Haiti, and Nassau in the Bahamas. Piracy in the Caribbean was part of a larger historical phenomenon of piracy, as it existed close to major trade and exploration routes in almost all the five oceans.

The Blockade of Africa began in 1808 after the United Kingdom outlawed the Atlantic slave trade, making it illegal for British ships to transport slaves. The Royal Navy immediately established a presence off Africa to enforce the ban, called the West Africa Squadron. Although the ban initially applied only to British ships, Britain negotiated treaties with other countries to give the Royal Navy the right to intercept and search their ships for slaves.

The Golden Age of Piracy is a common designation for the period between the 1650s and the 1730s, when maritime piracy was a significant factor in the histories of the North Atlantic and Indian Oceans.

Slavery in ancient Rome played an important role in society and the economy. Unskilled or low-skill slaves labored in the fields, mines, and mills with few opportunities for advancement and little chance of freedom. Skilled and educated slaves—including artisans, chefs, domestic staff and personal attendants, entertainers, business managers, accountants and bankers, educators at all levels, secretaries and librarians, civil servants, and physicians—occupied a more privileged tier of servitude and could hope to obtain freedom through one of several well-defined paths with protections under the law. The possibility of manumission and subsequent citizenship was a distinguishing feature of Rome's system of slavery, resulting in a significant and influential number of freedpersons in Roman society.
Adam Baldridge was an English pirate and one of the early founders of the pirate settlements in Madagascar.
Pierre Lafitte was a pirate in the Gulf of Mexico and smuggler in the early 19th century. He also ran a blacksmith shop in New Orleans, his legitimate business. Pierre was historically less well known than his younger brother, Jean Lafitte. While not as much of a sailor as Jean, Pierre was the public face of the Lafitte operation, and was known for his wit and charm, in addition to his handling of the sale of smuggled goods.
Black suffrage refers to black people's right to vote and has long been an issue in countries established under conditions of black minorities as well as, in some cases black majorities.

Piracy in the 21st century has taken place in a number of waters around the globe, including the Gulf of Guinea, Gulf of Aden, Arabian Sea, Strait of Malacca, Sulu and Celebes Seas, Indian Ocean, and Falcon Lake.
The Antelope, 23 U.S. 66 (1825), was a case in which the Supreme Court of the United States considered, for the first time, the legitimacy of the international slave trade, and determined "that possession on board of a vessel was evidence of property".
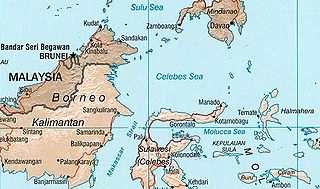
The Sulu and Celebes Seas, a semi-enclosed sea area and porous region that covers an area of space around 1 million square kilometres, have been subject to illegal maritime activities since the pre-colonial era and continue to pose a maritime security threat to bordering nations up to this day. While piracy has long been identified as an ubiquitous challenge, being historically interwoven with the region, recent incidents also include other types of maritime crimes such as kidnapping and the trafficking of humans, arms and drugs. Attacks mostly classify as 'armed robbery against ships' according to the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea as they occur in maritime zones that lie under the sovereignty of a coastal state. Incidents in the Sulu and Celebes Seas specifically involve the abduction of crew members. Since March 2016, the Information Sharing Centre (ISC) of the Regional Cooperation Agreement on Combating Piracy and Armed Robbery against Ships in Asia (ReCAAP) reports a total of 86 abductions, leading to the issue of a warning for ships transpassing the area.

A river pirate is a pirate who operates along a river. The term has been used to describe many different kinds of pirate groups who carry out riverine attacks in Asia, Africa, Europe, North America, and South America. They are usually prosecuted under national, not international law.

The Atlantic World refers to the period between European colonization of the Americas (1492-) and the early nineteenth century. Piracy became prevalent in this era because of the difficulty of policing this vast area, the limited state control over many parts of the coast, and the competition between different European powers. The best known pirates of this era are the Golden Age Pirates who roamed the seas off the coasts of North America, Africa, and the Caribbean.

Percival Keene is a coming-of-age adventure novel published in three volumes in 1842 by Frederick Marryat. The book follows the nautical adventures of the title character, a low-born illegitimate child of a captain in the Royal Navy, as he enters service as a midshipman during the Napoleonic Wars and rises through the ranks with the help of his influential father.

Shyamala Gopalan was a biomedical scientist at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, whose work in isolating and characterizing the progesterone receptor gene has stimulated advances in breast biology and oncology. She was the mother of Kamala Harris and Maya Harris, a lawyer and political commentator.

Painganadu Venkataraman "P. V." Gopalan was an Indian career civil servant who served with the Government of Zambia and the Government of India.

MeenakshiAshley Harris is an American lawyer, author, and theater producer. In theatre production, Harris won a Tony Award for producing A Strange Loop and was also nominated for producing Suffs. Harris's first children's picture book, Kamala and Maya's Big Idea (2020), was released by HarperCollins' imprint Balzer + Bray; it was based on the story of her mother, Maya Harris, and aunt, Kamala Harris, the 49th vice president of the United States.

Donald Jasper Harris, is a Jamaican-American economist and emeritus professor at Stanford University, known for applying post-Keynesian ideas to development economics. He was the first Black scholar granted tenure in the Stanford Department of Economics, and he is the father of Kamala Harris, the incumbent vice president of the United States and 2024 Democratic presidential nominee, and of Maya Harris, a lawyer, advocate and writer.

Kamala Harris is the 49th vice president of the United States. Harris was formerly the junior United States senator from California, and prior to her election to the Senate, she served as the 32nd attorney general of California. Her family includes several members who are notable in politics and academia.

Slavery is noted in the area later known as Algeria since antiquity. Algeria was a center of the Trans-Saharan slave trade route of enslaved Black Africans from sub-Saharan Africa, as well as a center of the slave trade of Barbary slave trade of Europeans captured by the barbary pirates.
















