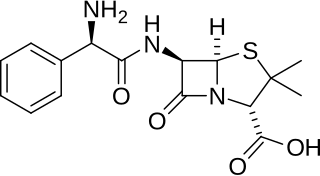
Ampicillin is an antibiotic belonging to the aminopenicillin class of the penicillin family. The drug is used to prevent and treat a number of bacterial infections, such as respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, meningitis, salmonellosis, and endocarditis. It may also be used to prevent group B streptococcal infection in newborns. It is used by mouth, by injection into a muscle, or intravenously.

Typhoid fever, also known as typhoid, is a disease caused by Salmonella serotype Typhi bacteria. Symptoms vary from mild to severe, and usually begin six to 30 days after exposure. Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over several days. This is commonly accompanied by weakness, abdominal pain, constipation, headaches, and mild vomiting. Some people develop a skin rash with rose colored spots. In severe cases, people may experience confusion. Without treatment, symptoms may last weeks or months. Diarrhea may be severe, but is uncommon. Other people may carry it without being affected, but are still contagious. Typhoid fever is a type of enteric fever, along with paratyphoid fever. S. enterica Typhi is believed to infect and replicate only within humans.
ATC code J07Vaccines is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup J07 is part of the anatomical group J Antiinfectives for systemic use.

The DPT vaccine or DTP vaccine is a class of combination vaccines against three infectious diseases in humans: diphtheria, pertussis, and tetanus. The vaccine components include diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and either killed whole cells of the bacterium that causes pertussis or pertussis antigens. The term toxoid refers to vaccines which use an inactivated toxin produced by the pathogen which they are targeted against to generate an immune response. In this way, the toxoid vaccine generates an immune response which is targeted against the toxin which is produced by the pathogen and causes disease, rather than a vaccine which is targeted against the pathogen itself. The whole cells or antigens will be depicted as either "DTwP" or "DTaP", where the lower-case "w" indicates whole-cell inactivated pertussis and the lower-case "a" stands for "acellular". In comparison to alternative vaccine types, such as live attenuated vaccines, the DTP vaccine does not contain any live pathogen, but rather uses inactivated toxoid to generate an immune response; therefore, there is not a risk of use in populations that are immune compromised since there is not any known risk of causing the disease itself. As a result, the DTP vaccine is considered a safe vaccine to use in anyone and it generates a much more targeted immune response specific for the pathogen of interest.

CSL Limited is an Australian multinational specialty biotechnology company that researches, develops, manufactures, and markets products to treat and prevent serious human medical conditions. CSL's product areas include blood plasma derivatives, vaccines, antivenom, and cell culture reagents used in various medical and genetic research and manufacturing applications. The company was established in 1916 as Commonwealth Serum Laboratories and was wholly owned by the Australian federal government until its privatisation in 1994.

A conjugate vaccine is a type of subunit vaccine which combines a weak antigen with a strong antigen as a carrier so that the immune system has a stronger response to the weak antigen.
Pegfilgrastim, sold under the brand name Neulasta among others, is a PEGylated form of the recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (GCSF) analog filgrastim. It serves to stimulate the production of white blood cells (neutrophils). Pegfilgrastim was developed by Amgen.
The MMRV vaccine combines the attenuated virus MMR vaccine with the addition of the varicella (chickenpox) vaccine. The MMRV vaccine is typically given to children between one and two years of age.

Combined hepatitis A and B vaccine, is used to provide protection against hepatitis A and hepatitis B. It is given by injection into muscle.
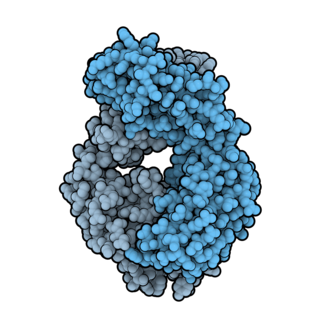
Ofatumumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody to CD20, which appears to provide rapid B-cell depletion. Under the brand name Kesimpta, it is approved for the treatment of multiple sclerosis in the United States as well as in the European Union and other regions. Under the brand name Arzerra, it is approved for the treatment of certain types of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in the United States. It is sold by Novartis under license from Genmab.

Hepatitis A vaccine is a vaccine that prevents hepatitis A. It is effective in around 95% of cases and lasts for at least twenty years and possibly a person's entire life. If given, two doses are recommended beginning after the age of one. It is given by injection into a muscle. The first hepatitis A vaccine was approved in Europe in 1991, and the United States in 1995. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.
The Vi capsular polysaccharide vaccine is a typhoid vaccine recommended by the World Health Organization for the prevention of typhoid. The vaccine was first licensed in the US in 1994 and is made from the purified Vi capsular polysaccharide from the Ty2 Salmonella Typhi strain; it is a subunit vaccine.

Ty21a is a live attenuated bacterial vaccine that protects against typhoid. First licensed in Europe in 1983 and in the United States in 1989, it is an orally administered, live-attenuated Ty2 strain of S. Typhi in which multiple genes, including the genes responsible for the production of Vi, have been deleted so as to render it harmless but nevertheless immunogenic. It is one of the three typhoid vaccines currently recommended by the World Health Organization.

Typhoid vaccines are vaccines that prevent typhoid fever. Several types are widely available: typhoid conjugate vaccine (TCV), Ty21a and Vi capsular polysaccharide vaccine (ViPS). They are about 30 to 70% effective in the first two years, depending on the specific vaccine in question. The Vi-rEPA vaccine has been shown to be efficacious in children.
A subunit vaccine is a vaccine that contains purified parts of the pathogen that are antigenic, or necessary to elicit a protective immune response. Subunit vaccine can be made from dissembled viral particles in cell culture or recombinant DNA expression, in which case it is a recombinant subunit vaccine.
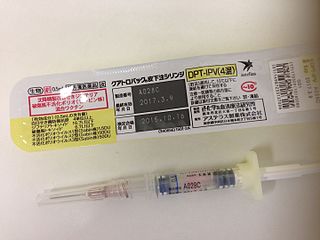
DTaP-IPV vaccine is a combination vaccine whose full generic name is diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and acellular pertussis adsorbed and inactivated poliovirus vaccine (IPV).

A hexavalent vaccine, or 6-in-1 vaccine, is a combination vaccine with six individual vaccines conjugated into one, intended to protect people from multiple diseases. The term usually refers to the children's vaccine that protects against diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, poliomyelitis, haemophilus B, and hepatitis B, which is used in more than 90 countries around the world including in Europe, Canada, Australia, Jordan, and New Zealand.

A vaccine dose contains many ingredients very little of which is the active ingredient, the immunogen. A single dose may have merely nanograms of virus particles, or micrograms of bacterial polysaccharides. A vaccine injection, oral drops or nasal spray is mostly water. Other ingredients are added to boost the immune response, to ensure safety or help with storage, and a tiny amount of material is left-over from the manufacturing process. Very rarely, these materials can cause an allergic reaction in people who are very sensitive to them.












