A hidden ball trick is a play in which a player deceives the opposing team about the location of the ball. Hidden ball tricks are most commonly observed in baseball, where the defence deceives the runner about the location of the ball, to tag out the runner. In goal-based sports (e.g., American football and lacrosse), the offence deceives the defence about the location of the ball, in an attempt to get the defence running the wrong way, such as in a fumblerooski.
In the sports of baseball and softball, the hidden ball trick usually involves a fielder using sleight of hand or misdirection to confuse a baserunner as to the location of the ball, allowing the fielder to tag out the runner unawares. Though several variations of the play exist, they usually involve a fielder keeping the ball without the runner's knowledge, waiting for the runner to step off a base, and then quickly tagging the runner out. For the trick to work, the fielder (generally an infielder) must get the ball while the ball is still in play, and the runner must either not know that the fielder has the ball or think that the play is over. [ citation needed ]
Fielders usually try to fool the runner by miming a throw to the pitcher or another defender while keeping the baseball out of sight, often in his glove. If the runner is not paying attention and assumes that the closest fielder no longer has the ball, he may stray off the base and be tagged out. [1] A related tactic is to quickly re-tag the runner after an unsuccessful tag in the hope that his hand or foot has lost contact with the base after a slide but before time has been called. [2]
In most situations, the balk rule precludes a pitcher from performing a hidden ball trick. [3] In high school and college baseball, a balk is called (NFHS R6-S2-A5) if a runner or runners are on base and the pitcher, while he is not touching the pitcher's plate, makes any motion naturally associated with his pitch, or he places his feet on or astride the pitcher's plate or positions himself within approximately five feet of the pitcher's plate without having the ball. In professional baseball, under Rule 6.02(a)(9), a balk occurs if the pitcher is standing on or astride of the pitching rubber without the ball. [4] As play after a foul ball, hit batsman, or time out, must not resume until the pitcher is on the pitcher's mound, the infielder cannot use these times to obtain the ball.
While variations exist, the use of the play in major league baseball is somewhat rare. Some say that the hidden-ball trick has been pulled fewer than 300 times in over 100 years of major league baseball. [1]
A first baseman may attempt the play after a pitcher, in an attempt to pick off a runner, throws to first. The first baseman then fakes the throwback to the pitcher while keeping the ball in his glove, and if and when the runner leaves the base, tags the runner. [1] Dave Bergman is a former first baseman who pulled this off on multiple occasions. [1] A second baseman could attempt a similar play after a successful steal of second base, having received a throw from the catcher.
Third baseman Bill Coughlin was reputed to have been the master of the hidden ball trick. Although not verified, Coughlin reportedly pulled it off seven times. [5] [6] The first known recorded and successful example of Coughlin's hidden ball trick was against the Detroit Tigers on September 24, 1901, as seen from a contemporary description of the game:
In returning the sphere to the infield the ball was thrown to our tricky third baseman and he promptly did a little sleight-o'-hand work, his hands moving faster than coachers' eyes, and shoved the ball up under his arm and assumed his position as it there were nothing wrong. Carrick was standing in the box as if he were about to toss the globule over, and Cronin eased off the ottoman slightly, but enough to get him caught, and he returned to the bench amidst the jeers and howls of the populace. [7]
He did it again on September 3, 1906, catching George Stone in the first inning. In Game 2 of the 1907 World Series, Coughlin caught Jimmy Slagle with a hidden ball trick, the only one in World Series history. The play went from Germany Schaefer to Coughlin. [8]
Former second baseman Marty Barrett also successfully performed the trick more than once. [1] After a runner reached second base on a ball hit to the outfield, and after receiving the throw-in from the outfield, he faked a throw to the pitcher while retaining the ball. [1] To aid the deception, Barrett took the throw with his back to the runner, then placed the ball between the back of his glove and one of his fingers: this way, he exposed his glove to the runner without the ball in the pocket, suggesting that he did not have the ball. [1] Other players have hidden the ball in their armpits. [1]
Former third baseman Matt Williams used a different technique which asked the runner to step off the base so that Williams could sweep the dirt off it, then tagged out the runner when the runner complied. [9] This worked twice. [10]
Former third baseman Mike Lowell also made the trick work twice, each time after a throw-in from the outfield. The key to Lowell's success was acting, placement, and waiting: acting as if nothing was on, standing away from the bag but not too far from it, and waiting, at least 10 seconds, until the runner on third took a few steps. [1]
Willie Kamm was considered another master of the trick. [11] On April 30, 1929, in a game against the Cleveland Indians, Kamm was involved in a rare triple play involving a hidden-ball trick. [12] The Indians had baserunners on first and second bases when Carl Lind grounded out to the shortstop. Johnny Hodapp, who had been on second base, tried to score but got caught in a rundown between third and home. Charlie Jamieson advanced to third. Kamm retrieved the ball and tagged both runners, whereupon the umpire ruled Hodapp out. Kamm then hid the ball under his arm and waited for Jamieson to step off the base. When he did so, Kamm tagged him out to complete the triple play. [13]
On June 8, 2007, shortstop Julio Lugo of the Boston Red Sox caught Alberto Callaspo of the Arizona Diamondbacks. However, third baseman Lowell, Lugo's teammate, claimed it was not a true hidden ball trick since the pitcher did most of the work "selling" the trick. [14] Before Lugo caught Callaspo, Lowell laid claim to the last successful hidden ball trick and held that position for eight years to the day. Lowell's occurred on August 10, 2005, when he, then with the Florida Marlins, caught the Arizona Diamondbacks Luis Terrero, with reliever Todd Jones on the mound. Lowell also caught Brian Schneider of the Montreal Expos in 2004.
On July 12, 2013, San Diego Padres shortstop Everth Cabrera attempted to execute the hidden-ball trick on San Francisco Giants third baseman Pablo Sandoval after Sandoval hit a double. As pitcher Sean O'Sullivan walked onto the mound and Sandoval took his lead, Cabrera, while holding the ball, tagged Sandoval. However, Sandoval had requested and was granted time by second base umpire Laz Díaz immediately after his double. Because O'Sullivan never assumed his position on the pitcher's plate with the baseball, the umpires appropriately never called "Play" and Cabrera's tag of Sandoval was therefore not legal. The Umpire Ejection Fantasy League explains this is why a hidden-ball trick may never be executed after a base hit, mound visit, or other events in which "time" is called: to put the ball back into play, the pitcher must engage the rubber and if the pitcher engages the rubber without the ball, it is a balk under Rule 8.05(i). [3]
On August 10, 2013, in a Tampa Bay loss to the Los Angeles Dodgers, 5–0, Evan Longoria, Tampa Bay Rays's third baseman pulled the trick in the fourth inning on Juan Uribe. With the bases loaded and no outs, A.J. Ellis flew out to the center field, with Andre Ethier tagging to score, Uribe tagging to third and Skip Schumaker tagging to second. Tampa first baseman (and former Dodger) James Loney cut off-center fielder Wil Myers' throw at the mound, flipped to shortstop Yunel Escobar, who flipped to third baseman Longoria standing several feet behind third base, out of Uribe's line of sight. Longoria just stood behind the bar looking bored and kicking the dirt for several seconds before he got his chance. "I was watching it, and I didn't know what to do to stop it", said pitcher Zack Greinke, who was on deck. "I didn't want to yell at Uribe, because I might get him off [the bag]. I didn't know what to do. He just lifted his foot for a tenth of a second and Longoria was ready for it. As Uribe shifted his weight and took his foot off the third-base bag, Longoria sneaked from behind and slapped Uribe's thigh with a tag. Longoria looked over his shoulder at umpire Angel Hernández, who called Uribe out for an 8-3-6-5 double play. In an after-the-game stunt from his teammates, Uribe was presented with a baseball shoe taped to a base. [15]
On September 19, 2013, Colorado Rockies first baseman Todd Helton caught Matt Carpenter of the St. Louis Cardinals for the final out of the first inning in a day game at Coors Field. Helton, who days earlier had announced his retirement after 17 seasons with the Rockies, [16] tagged Carpenter after faking a throwback to pitcher Roy Oswalt following a pickoff attempt. Carpenter was dusting his hands after a head-first slide when he stepped off the backside of the first base towards 1B umpire Bill Miller. Cardinal's first base coach Chris Maloney was unable to help Carpenter before Helton got him with a poking tag. "I've been wanting to do that for 17 seasons. Now I can cross that off my bucket list", said the 40-year-old Helton, [17] who at the time was the oldest active professional athlete in Denver. [18] The Rockies went on to win 7-6 in a 15 inning game that was the second-longest in Coors Field history. [19]
In the minor leagues, on August 31, 1987, catcher Dave Bresnahan of the Williamsport Bills pulled an unusual hidden ball trick against the Reading Phillies in the Eastern League. With a runner on third base, Bresnahan switched catcher's mitts and put on a glove in which he had secreted a peeled potato. When the pitch came in, Bresnahan fired the white potato down the third-base line, enticing the runner to sprint home. Bresnahan then tagged the runner with the baseball which he kept in his mitt. The umpire awarded the runner home plate for Bresnahan's deception. Bresnahan was subsequently released from the Bills for the incident, but the fans of the Bills loved the play and the team eventually retired Bresnahan's number. [20] [21] [22]
In goal-based sports (e.g., American football and lacrosse), the offence deceives the defence about the location of the ball, in an attempt to get the defence running the wrong way.
A hidden ball trick is considered a trick play in American football. There are various executions of such plays, including the Statue of Liberty play and Fumblerooski.
On November 9, 1895 John Heisman executed a hidden ball trick utilizing quarterback Reynolds Tichenor to get Auburn's only touchdown in a 6 to 9 loss to Vanderbilt. During the play, the ball was snapped to a half-back who was able to slip it under the back of the quarterback's jersey and who in turn was able to trot in for the touchdown. This was also the first game in the south decided by a field goal. [23] Heisman later used the trick against Pop Warner's Georgia team. Warner picked up the trick and later used it at Cornell against Penn State in 1897. [24] He then used it in 1903 at Carlisle against Harvard and garnered national attention.
The hidden ball trick was famously parodied in the 1930s by the Marx Brothers in the film Horse Feathers and by the Three Stooges in the comedy short Three Little Pigskins , and was used in the final play of the football game in the 1970 film M*A*S*H .
Hidden ball tricks can be used in rugby [25] [26] [27] and lacrosse. [28] [29] [30]
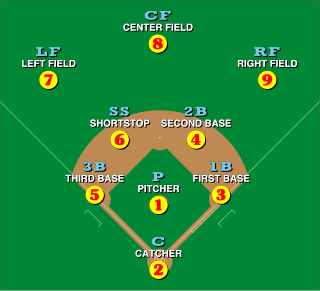
In the sport of baseball, each of the nine players on a team is assigned a particular fielding position when it is their turn to play defense. Each position conventionally has an associated number, for use in scorekeeping by the official scorer: 1 (pitcher), 2 (catcher), 3, 4, 5, 6 (shortstop), 7, 8, and 9. Collectively, these positions are usually grouped into three groups: the outfield, the infield, and the battery. Traditionally, players within each group will often be more able to exchange positions easily ; however, the pitcher and catcher are highly specialized positions and rarely will play at other positions.

Softball is a popular variation of baseball, the difference being that it is played with a larger ball on a smaller field and with only underhand pitches permitted. Softball is played competitively at club levels, the college level, and the professional level. The game was first created in 1887 in Chicago by George Hancock.

In baseball and softball, a double play is the act of making two outs during the same continuous play. Double plays can occur any time there is at least one baserunner and fewer than two outs.
In baseball, a triple play is the act of making three outs during the same play. There have only been 736 triple plays in Major League Baseball (MLB) since 1876, an average of just over five per season.

Catcher is a position in baseball and softball. When a batter takes their turn to hit, the catcher crouches behind home plate, in front of the (home) umpire, and receives the ball from the pitcher. In addition to this primary duty, the catcher is also called upon to master many other skills in order to field the position well. The role of the catcher is similar to that of the wicket-keeper in cricket.

A first baseman, abbreviated 1B, is the player on a baseball or softball team who fields the area nearest first base, the first of four bases a baserunner must touch in succession to score a run. The first baseman is responsible for the majority of plays made at that base. In the numbering system used to record defensive plays, the first baseman is assigned the number 3.

In baseball, an out occurs when the umpire rules a batter or baserunner out. When a batter or runner is out, they lose their ability to score a run and must return to the dugout until their next turn at bat. When three outs are recorded in a half-inning, the batting team's turn expires.

Throughout the history of baseball, the rules have frequently changed as the game continues to evolve. A few common rules most professional leagues have in common is that four balls is a base on balls, three strikes is a strikeout, and three outs end a half-inning.

In baseball and softball, a tag out, sometimes just called a tag, is a play in which a baserunner is out because a fielder touches him with the ball or with the hand or glove holding the ball, while the ball is live and the runner is in jeopardy of being put out – usually when he is not touching a base.

In baseball, an assist is a defensive statistic, baseball being one of the few sports in which the defensive team controls the ball. An assist is credited to every defensive player who fields or touches the ball prior to the recording of a putout, even if the contact was unintentional. For example, if a ball strikes a player's leg and bounces off him to another fielder, who tags the baserunner, the first player is credited with an assist. A fielder can receive a maximum of one assist per out recorded. An assist is also credited if a putout would have occurred, had another fielder not committed an error. For example, a shortstop might field a ground ball cleanly, but the first baseman might drop his throw. In this case, an error would be charged to the first baseman, and the shortstop would be credited with an assist.

In baseball, a pitcher may commit illegal motions or actions that constitute a balk. Most of these violations involve pitchers pretending to pitch when they have no intention of doing so. In games played under the Official Baseball Rules that govern professional play in the United States and Canada, a balk results in a dead ball or delayed dead ball. In certain other circumstances, a balk may be wholly or partially disregarded. In the United States, under the National Federation of State High School Associations, a balk results in an immediate dead ball. In the event a balk is enforced, the pitch is generally nullified, each runner is awarded one base, and the batter (generally) remains at bat with the previous count. The balk rule in Major League Baseball was introduced in 1898.

William Edward Kamm was an American professional baseball player. He played as a third baseman in Major League Baseball from 1923 to 1935. Kamm played most of his career for the Chicago White Sox before finishing his playing days with the Cleveland Indians. He was the dominant defensive third baseman in the American League for most of his career.
In baseball, a fourth out is a legal out made by the defense after three outs in a half-inning have already been made. According to the rules, the third out does not cause the ball to become dead; if the fielders make a subsequent out that prevents a run from scoring, this out will supersede the apparent third out, thus becoming the recorded third out. The defense successfully makes an appeal while the ball is still live, and the umpire calls a temporary fourth out that (usually) replaces the existing third out. For statistical purposes, the apparent third out is "undone" and the fourth out's result is recorded instead. With the advent of video replay appeals, a new rationale for making extra out(s) has emerged: insurance against a prior out being undone on appeal. These fourth-out situations are not the same as four strikeouts in an inning.

William Paul Coughlin, nicknamed "Scranton Bill", was an American Major League Baseball third baseman for the Washington Senators (1901–1904) and Detroit Tigers (1904–1908). Coughlin spent his entire adult life (1899–1943) playing and coaching baseball, as a major league player, minor league coach, and spending his last 23 years as the head baseball coach at Lafayette College, in Easton, Pennsylvania.
This is an alphabetical list of selected unofficial and specialized terms, phrases, and other jargon used in baseball, along with their definitions, including illustrative examples for many entries.

In baseball, a neighborhood play is a force play in which a fielder receiving the ball in attempting to force out a runner at second base, catches and quickly throws the ball to first base in a double play attempt without actually touching second base, or by touching second base well before catching the ball. By every rules code, such a play is not an out, because to record a force out, the fielder with the ball must actually touch a force base before the forced runner arrives.

The 1907 Detroit Tigers won the American League pennant with a record of 92–58, but lost to the Chicago Cubs in the 1907 World Series, four games to none. The season was their seventh since they entered the American League in 1901.

The 2010 National League Championship Series (NLCS) was a best-of-seven game Major League Baseball playoff series that pitted the winners of the 2010 National League Division Series—the Philadelphia Phillies and San Francisco Giants—against each other for the National League Championship. The Giants would defeat the Phillies, four games to two, to advance to their first World Series since 2002. The series, the 41st NLCS in league history, began on October 16 and ended on October 23. The Phillies had home field advantage as a result of their better regular-season record. The Phillies hosted Games 1, 2 and 6, while the Giants were at home for Games 3, 4 and 5.