IEEE 802.15 is a working group of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) IEEE 802 standards committee which specifies Wireless Specialty Networks (WSN) standards. The working group was formerly known as Working Group for Wireless Personal Area Networks.

IEEE 802 is a family of Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) standards for local area networks (LANs), personal area networks (PANs), and metropolitan area networks (MANs). The IEEE 802 LAN/MAN Standards Committee (LMSC) maintains these standards. The IEEE 802 family of standards has had twenty-four members, numbered 802.1 through 802.24, with a working group of the LMSC devoted to each. However, not all of these working groups are currently active.
IEEE 802.2 is the original name of the ISO/IEC 8802-2 standard which defines logical link control (LLC) as the upper portion of the data link layer of the OSI Model. The original standard developed by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) in collaboration with the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) was adopted by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in 1998, but it remains an integral part of the family of IEEE 802 standards for local and metropolitan networks.

Synchronous Optical Networking (SONET) and Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) are standardized protocols that transfer multiple digital bit streams synchronously over optical fiber using lasers or highly coherent light from light-emitting diodes (LEDs). At low transmission rates data can also be transferred via an electrical interface. The method was developed to replace the plesiochronous digital hierarchy (PDH) system for transporting large amounts of telephone calls and data traffic over the same fiber without the problems of synchronization.
In telecommunication, a distributed-queue dual-bus network (DQDB) is a distributed multi-access network that (a) supports integrated communications using a dual bus and distributed queuing, (b) provides access to local or metropolitan area networks, and (c) supports connectionless data transfer, connection-oriented data transfer, and isochronous communications, such as voice communications.

Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) is a standard for data transmission in a local area network. It uses optical fiber as its standard underlying physical medium, although it was also later specified to use copper cable, in which case it may be called CDDI, standardized as TP-PMD, also referred to as TP-DDI.

In computer networking, Fast Ethernet physical layers carry traffic at the nominal rate of 100 Mbit/s. The prior Ethernet speed was 10 Mbit/s. Of the Fast Ethernet physical layers, 100BASE-TX is by far the most common.
In telecommunications and computer networks, a channel access method or multiple access method allows more than two terminals connected to the same transmission medium to transmit over it and to share its capacity. Examples of shared physical media are wireless networks, bus networks, ring networks and point-to-point links operating in half-duplex mode.
The data link layer, or layer 2, is the second layer of the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking. This layer is the protocol layer that transfers data between nodes on a network segment across the physical layer. The data link layer provides the functional and procedural means to transfer data between network entities and may also provide the means to detect and possibly correct errors that can occur in the physical layer.

In IEEE 802 LAN/MAN standards, the medium access control (MAC), also called media access control, is the layer that controls the hardware responsible for interaction with the wired or wireless transmission medium. The MAC sublayer and the logical link control (LLC) sublayer together make up the data link layer. The LLC provides flow control and multiplexing for the logical link, while the MAC provides flow control and multiplexing for the transmission medium.
Resilient Packet Ring (RPR), as defined by IEEE standard 802.17, is a protocol designed for the transport of data traffic over optical fiber ring networks. The standard began development in November 2000 and has undergone several amendments since its initial standard was completed in June 2004. The amended standards are 802.17a through 802.17d, the last of which was adopted in May 2011. It is designed to provide the resilience found in SONET and Synchronous Digital Hierarchy networks but, instead of setting up circuit oriented connections, provides a packet based transmission, in order to increase the efficiency of Ethernet and IP services.
Switched Multi-megabit Data Service (SMDS) was a connectionless service used to connect LANs, MANs and WANs to exchange data, in early 1990s. In Europe, the service was known as Connectionless Broadband Data Service (CBDS).

A metropolitan-area Ethernet, Ethernet MAN, carrier Ethernet or metro Ethernet network is a metropolitan area network (MAN) that is based on Ethernet standards. It is commonly used to connect subscribers to a larger service network or for internet access. Businesses can also use metropolitan-area Ethernet to connect their own offices to each other.

A computer network is a set of computers sharing resources located on or provided by network nodes. Computers use common communication protocols over digital interconnections to communicate with each other. These interconnections are made up of telecommunication network technologies based on physically wired, optical, and wireless radio-frequency methods that may be arranged in a variety of network topologies.

The physical-layer specifications of the Ethernet family of computer network standards are published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), which defines the electrical or optical properties and the transfer speed of the physical connection between a device and the network or between network devices. It is complemented by the MAC layer and the logical link layer. An implementation of a specific physical layer is commonly referred to as PHY.
Ethernet in the first mile (EFM) refers to using one of the Ethernet family of computer network technologies between a telecommunications company and a customer's premises. From the customer's point of view, it is their first mile, although from the access network's point of view it is known as the last mile.
The Time-Triggered Ethernet standard defines a fault-tolerant synchronization strategy for building and maintaining synchronized time in Ethernet networks, and outlines mechanisms required for synchronous time-triggered packet switching for critical integrated applications and integrated modular avionics (IMA) architectures. SAE International released SAE AS6802 in November 2011.
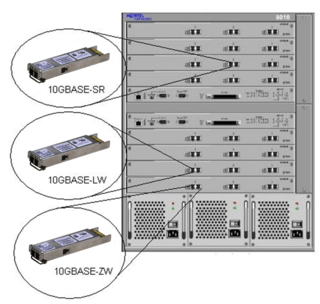
10 Gigabit Ethernet is a group of computer networking technologies for transmitting Ethernet frames at a rate of 10 gigabits per second. It was first defined by the IEEE 802.3ae-2002 standard. Unlike previous Ethernet standards, 10GbE defines only full-duplex point-to-point links which are generally connected by network switches; shared-medium CSMA/CD operation has not been carried over from the previous generations of Ethernet standards so half-duplex operation and repeater hubs do not exist in 10GbE. The first standard for faster 100 Gigabit Ethernet links was approved in 2010.
Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) is a set of standards under development by the Time-Sensitive Networking task group of the IEEE 802.1 working group. The TSN task group was formed in November 2012 by renaming the existing Audio Video Bridging Task Group and continuing its work. The name changed as a result of the extension of the working area of the standardization group. The standards define mechanisms for the time-sensitive transmission of data over deterministic Ethernet networks.
Classic Ethernet is a family of 10 Mbit/s Ethernet standards, which is the first generation of Ethernet standards. In 10BASE-X, the 10 represents its maximum throughput of 10 Mbit/s, BASE indicates its use of baseband transmission, and X indicates the type of medium used. Classic Ethernet includes coax, twisted pair and optical variants. The first Ethernet standard was published in 1983 and classic Ethernet operating at 10 Mbit/s was the dominant form of Ethernet until the first standard for Fast Ethernet was approved in 1995.








