
Ethernet is a family of wired computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN) and wide area networks (WAN). It was commercially introduced in 1980 and first standardized in 1983 as IEEE 802.3. Ethernet has since been refined to support higher bit rates, a greater number of nodes, and longer link distances, but retains much backward compatibility. Over time, Ethernet has largely replaced competing wired LAN technologies such as Token Ring, FDDI and ARCNET.
IEEE 802.2 is the original name of the ISO/IEC 8802-2 standard which defines logical link control (LLC) as the upper portion of the data link layer of the OSI Model. The original standard developed by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) in collaboration with the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) was adopted by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in 1998, but it still remains an integral part of the family of IEEE 802 standards for local and metropolitan networks.

Ethernet over twisted-pair technologies use twisted-pair cables for the physical layer of an Ethernet computer network. They are a subset of all Ethernet physical layers.

A cable modem is a type of network bridge that provides bi-directional data communication via radio frequency channels on a hybrid fibre-coaxial (HFC), radio frequency over glass (RFoG) and coaxial cable infrastructure. Cable modems are primarily used to deliver broadband Internet access in the form of cable Internet, taking advantage of the high bandwidth of a HFC and RFoG network. They are commonly deployed in the Americas, Asia, Australia, and Europe.

In computer networking, Gigabit Ethernet is the term applied to transmitting Ethernet frames at a rate of a gigabit per second. The most popular variant 1000BASE-T is defined by the IEEE 802.3ab standard. It came into use in 1999, and has replaced Fast Ethernet in wired local networks due to its considerable speed improvement over Fast Ethernet, as well as its use of cables and equipment that are widely available, economical, and similar to previous standards.
10BROAD36 is an obsolete computer network standard in the Ethernet family. It was developed during the 1980s and specified in IEEE 802.3b-1985.

IEEE 802.20 or Mobile Broadband Wireless Access (MBWA) was a specification by the standard association of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) for mobile wireless Internet access networks. The main standard was published in 2008. MBWA is no longer being actively developed.

Power over Ethernet, or PoE, describes any of several standards or ad hoc systems that pass electric power along with data on twisted pair Ethernet cabling. This allows a single cable to provide both data connection and electric power to devices such as Wireless Access Points (WAPs), Internet Protocol (IP) cameras, and Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) phones.
Resilient Packet Ring (RPR), also known as IEEE 802.17, is a protocol standard designed for the optimized transport of data traffic over optical fiber ring networks. The standard began development in November 2000 and has undergone several amendments since its initial standard was completed in June 2004. The amended standards are 802.17a through 802.17d, the last of which was adopted in May 2011. It is designed to provide the resilience found in SONET/SDH networks but, instead of setting up circuit oriented connections, provides a packet based transmission, in order to increase the efficiency of Ethernet and IP services.
IEEE 802.10 is a former standard for security functions that could be used in both local area networks and metropolitan area networks based on IEEE 802 protocols.

In computer networking, the term link aggregation refers to various methods of combining (aggregating) multiple network connections in parallel in order to increase throughput beyond what a single connection could sustain, and to provide redundancy in case one of the links should fail. A link aggregation group (LAG) is the collection of physical ports combined together.

The Ethernet physical layer is the physical layer functionality of the Ethernet family of computer network standards. The physical layer defines the electrical or optical properties and the transfer speed of the physical connection between a device and the network or between network devices. It is complemented by the MAC layer and the logical link layer.
Ethernet in the first mile (EFM) refers to using one of the Ethernet family of computer network technologies between a telecommunications company and a customer's premises. From the customer's point of view, it is their first mile, although from the access network's point of view it is known as the last mile.
IEEE 802.1AE is a network security standard that operates at the medium access control layer and defines connectionless data confidentiality and integrity for media access independent protocols. It is standardized by the IEEE 802.1 working group.
In computer networking, an Ethernet frame is a data link layer protocol data unit and uses the underlying Ethernet physical layer transport mechanisms. In other words, a data unit on an Ethernet link transports an Ethernet frame as its payload.
Data center bridging (DCB) is a set of enhancements to the Ethernet local area network communication protocol for use in data center environments, in particular for use with clustering and storage area networks.

The Ethernet Alliance was incorporated in the US state of California in August 2005 and officially launched in January 2006 as a non-profit industry consortium to promote and support Ethernet. The objectives were to provide an unbiased, industry-based source of educational information; to ensure interoperability among disparate, standards-based components and systems; to support the development of standards that support Ethernet technology; and to bring together the Ethernet industry to collaborate on the future of the technology.
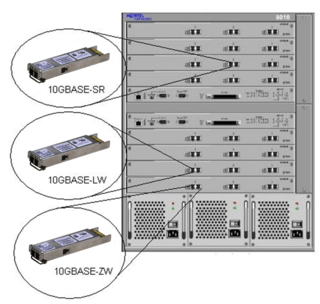
10 Gigabit Ethernet is a group of computer networking technologies for transmitting Ethernet frames at a rate of 10 gigabits per second. It was first defined by the IEEE 802.3ae-2002 standard. Unlike previous Ethernet standards, 10 Gigabit Ethernet defines only full-duplex point-to-point links which are generally connected by network switches; shared-medium CSMA/CD operation has not been carried over from the previous generations Ethernet standards so half-duplex operation and repeater hubs do not exist in 10GbE.
Terabit Ethernet or TbE is Ethernet with speeds above 100 Gbit/s. 400 Gigabit Ethernet and 200 Gigabit Ethernet standards developed by the IEEE P802.3bs Task Force using broadly similar technology to 100 Gigabit Ethernet were approved on December 6, 2017. In 2016, several networking equipment suppliers were already offering proprietary solutions for 200G and 400G.

Audio Video Bridging (AVB) is a common name for the set of technical standards which provide improved synchronization, low-latency, and reliability for switched Ethernet networks. AVB embodies the following technologies and standards:










