Related Research Articles

Alternating current (AC) is an electric current that periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time, in contrast to direct current (DC), which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in which electric power is delivered to businesses and residences, and it is the form of electrical energy that consumers typically use when they plug kitchen appliances, televisions, fans and electric lamps into a wall socket. The abbreviations AC and DC are often used to mean simply alternating and direct, respectively, as when they modify current or voltage.
Mains electricity or utility power, grid power, domestic power, and wall power, or, in some parts of Canada, hydro, is a general-purpose alternating-current (AC) electric power supply. It is the form of electrical power that is delivered to homes and businesses through the electrical grid in many parts of the world. People use this electricity to power everyday items by plugging them into a wall outlet.

Electric power distribution is the final stage in the delivery of electricity. Electricity is carried from the transmission system to individual consumers. Distribution substations connect to the transmission system and lower the transmission voltage to medium voltage ranging between 2 kV and 33 kV with the use of transformers. Primary distribution lines carry this medium voltage power to distribution transformers located near the customer's premises. Distribution transformers again lower the voltage to the utilization voltage used by lighting, industrial equipment and household appliances. Often several customers are supplied from one transformer through secondary distribution lines. Commercial and residential customers are connected to the secondary distribution lines through service drops. Customers demanding a much larger amount of power may be connected directly to the primary distribution level or the subtransmission level.

A circuit breaker is an electrical safety device designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by current in excess of that which the equipment can safely carry (overcurrent). Its basic function is to interrupt current flow to protect equipment and to prevent fire. Unlike a fuse, which operates once and then must be replaced, a circuit breaker can be reset to resume normal operation.

A substation is a part of an electrical generation, transmission, and distribution system. Substations transform voltage from high to low, or the reverse, or perform any of several other important functions. Between the generating station and consumer, electric power may flow through several substations at different voltage levels. A substation may include transformers to change voltage levels between high transmission voltages and lower distribution voltages, or at the interconnection of two different transmission voltages. They are a common component of the infrastructure. There are 55,000 substations in the United States.

A surge protector (or spike suppressor, surge suppressor, surge diverter, surge protection device or transient voltage surge suppressor is an appliance or device intended to protect electrical devices in alternating current circuits from voltage spikes with very short duration measured in microseconds, which can arise from a variety of causes including lightning strikes in the vicinity.
In electrical engineering, partial discharge (PD) is a localized dielectric breakdown (DB) of a small portion of a solid or fluid electrical insulation (EI) system under high voltage (HV) stress. While a corona discharge (CD) is usually revealed by a relatively steady glow or brush discharge (BD) in air, partial discharges within solid insulation system are not visible.

In electrical engineering, ground and neutral are circuit conductors used in alternating current (AC) electrical systems. The neutral conductor returns current to the supply. To limit the effects of leakage current from higher-voltage systems, the neutral conductor is often connected to earth ground at the point of supply. A ground conductor is not intended to carry current for normal operation of the circuit, but instead connects exposed metallic components to earth ground. A ground conductor only carries significant current if there is a circuit fault that would otherwise energize exposed conductive parts and present a shock hazard. Circuit protection devices may detect a fault to a grounded metal enclosure and automatically de-energize the circuit, or may provide a warning of a ground fault.

High voltage electricity refers to electrical potential large enough to cause injury or damage. In certain industries, high voltage refers to voltage above a certain threshold. Equipment and conductors that carry high voltage warrant special safety requirements and procedures.

An electric arc is an electrical breakdown of a gas that produces a prolonged electrical discharge. The current through a normally nonconductive medium such as air produces a plasma, which may produce visible light. An arc discharge is initiated either by thermionic emission or by field emission. After initiation, the arc relies on thermionic emission of electrons from the electrodes supporting the arc. An arc discharge is characterized by a lower voltage than a glow discharge. An archaic term is voltaic arc, as used in the phrase "voltaic arc lamp".

In an electric power system, a switchgear is composed of electrical disconnect switches, fuses or circuit breakers used to control, protect and isolate electrical equipment. Switchgear is used both to de-energize equipment to allow work to be done and to clear faults downstream. This type of equipment is directly linked to the reliability of the electricity supply.

A variable-frequency drive is a type of AC motor drive that controls speed and torque by varying the frequency of the input electricity. Depending on its topology, it controls the associated voltage or current variation.
An earthing system or grounding system (US) connects specific parts of an electric power system with the ground, typically the equipments conductive surface, for safety and functional purposes. The choice of earthing system can affect the safety and electromagnetic compatibility of the installation. Regulations for earthing systems vary among countries, though most follow the recommendations of the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). Regulations may identify special cases for earthing in mines, in patient care areas, or in hazardous areas of industrial plants.
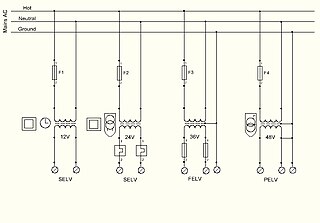
Extra-low voltage (ELV) is an electricity supply voltage and is a part of the low-voltage band in a range which carries a low risk of dangerous electrical shock. There are various standards that define extra-low voltage. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the UK IET define an ELV device or circuit as one in which the electrical potential between two conductors or between an electrical conductor and earth (ground) does not exceed 120 volts (V) for ripple-free direct current (DC) or 50 VRMS for alternating current (AC).
NFPA 70E(Standard for Electrical Safety in the Workplace) is a standard of the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA). The document covers electrical safety requirements for employees. The NFPA is best known for publishing the National Electrical Code.

An arc flash is the light and heat produced as part of an arc fault, a type of electrical explosion or discharge that results from a connection through air to ground or another voltage phase in an electrical system.
In an electric power system, a fault or fault current is any abnormal electric current. For example, a short circuit is a fault in which a live wire touches a neutral or ground wire. An open-circuit fault occurs if a circuit is interrupted by a failure of a current-carrying wire or a blown fuse or circuit breaker. In three-phase systems, a fault may involve one or more phases and ground, or may occur only between phases. In a "ground fault" or "earth fault", current flows into the earth. The prospective short-circuit current of a predictable fault can be calculated for most situations. In power systems, protective devices can detect fault conditions and operate circuit breakers and other devices to limit the loss of service due to a failure.

In electrical engineering, earth potential rise (EPR), also called ground potential rise (GPR), occurs when a large current flows to earth through an earth grid impedance. The potential relative to a distant point on the Earth is highest at the point where current enters the ground, and declines with distance from the source. Ground potential rise is a concern in the design of electrical substations because the high potential may be a hazard to people or equipment.

An electric power system is a network of electrical components deployed to supply, transfer, and use electric power. An example of a power system is the electrical grid that provides power to homes and industries within an extended area. The electrical grid can be broadly divided into the generators that supply the power, the transmission system that carries the power from the generating centers to the load centers, and the distribution system that feeds the power to nearby homes and industries.
References
- ↑ "IEEE 1584-2018 - IEEE Guide for Performing Arc-Flash Hazard Calculations". Archived from the original on March 21, 2019.
- ↑ http://ecmweb.com/mag/electric_calculating_arc_flash here
- ↑ "IEEE 1584.1-2022". IEEE Standards Sale. IEEE Petroleum and Chemical Industry Committee. Retrieved 16 November 2022.