
Mendocino is an unincorporated community in Mendocino County, California, United States. Mendocino is located 9.5 miles (15 km) south of Fort Bragg, at an elevation of 154 feet. The population of the census-designated place (CDP) was 894 at the 2010 census, up from 824 at the 2000 census. The town's name comes from Cape Mendocino, named by early Spanish navigators in honor of Antonio de Mendoza, Viceroy of New Spain. In turn, the etymology of Mendoza is "cold mountain."

The Yuki are an indigenous people of California, whose traditional territory is around Round Valley, Mendocino County. Today they are enrolled members of the Round Valley Indian Tribes of the Round Valley Reservation.
The Guidiville Rancheria of California are a Pomo tribe located in Mendocino County, California.

State Route 162 runs roughly west–east from U.S. Route 101 near Longvale, in Mendocino County, to Oroville, in Butte County. For most of its length, it is a two lane, undivided highway. The highway is broken into two pieces; the state's sponsorship of the road ends where it enters the Mendocino National Forest in Mendocino County where it becomes an unimproved dirt road maintained by the U.S. Forest Service as Forest Highway 7 (FH 7). State Route 162 begins again at the eastern boundary of the National Forest in Glenn County, some 30 miles (48 km) west of Willows.

The 70-acre (280,000 m2) Coyote Valley Reservation in Redwood Valley, California is home to about 170 members of the Coyote Valley tribe of the Native American Pomo people, who descend from the Shodakai Pomo. They are a federally recognized tribe, who were formerly known as the Coyote Valley Band of Pomo Indians of California.

Montgomery Woods State Natural Reserve is a 1,323-acre state-owned park located in the Coastal Range in Mendocino County, California, United States. The Reserve occupies the headwaters of Montgomery Creek, a tributary of Big River, which flows into the Pacific Ocean at Mendocino Headlands State Park. The virgin groves of Coast Redwood in Montgomery Woods are examples of a now rare upland riparian meadow habitat; most other preserved redwood groves are on broad alluvial plains. The Reserve is accessed from a parking area along Orr Springs Road 13 miles (21 km) west of Ukiah, California, or 15 miles (24 km) east of Comptche, California. A moderately steep trail from the parking area climbs uphill along Montgomery Creek about three-quarters of a mile. Once in the grove, the trail makes a meandering three mile (5 km) loop, with substantial use of boardwalks to protect the fragile forest floor. The reserve was initiated by a 9-acre donation from Robert Orr in 1945, with 765 acres donated since 1947 by the Save the Redwoods League.
The Sherwood Valley Rancheria of Pomo Indians of California is a federally recognized tribe of Pomo Indians in California.
Indian Springs, California may refer to:

Bell Springs was a town and stage coach stop on Bell Springs Road in Mendocino County, California. It was located 9 miles (14 km) northeast of Leggett, at an elevation of 3622 feet . A post office operated at Bell Springs from 1920 to 1961. The place was named in 1861 by Jim Graham for the cowbells he found at the site. What was once Bell Springs is now the location of the Bell Springs Ranch. Bell Springs Road, 28 miles of steep narrow unpaved mountain road, was originally called Mail Ridge, and was the only through road connecting Mendocino County and Humboldt County before Highway 101 was built.

Nacomis Indian Rancheria is an unincorporated community in Mendocino County, California. It lies at an elevation of 768 feet.

Old Ornbaun Hot Springs is on private property in Mendocino County, California. It is not open to the public and does not have springs to see or visit. It lies at an elevation of 1227 feet.

Soda Springs is an unincorporated community in Mendocino County, California. It is located 5 miles (8 km) northeast of Boonville, at an elevation of 1388 feet.
Soda Springs, California may refer to:

Vichy Springs is an unincorporated community in Mendocino County, California. It is located on Sulphur Creek 3 miles (4.8 km) east-northeast of Ukiah, at an elevation of 801 feet.
Cahto is a former settlement in Mendocino County, California. It was located 3 miles (4.8 km) southwest of Laytonville.

The North Fork Eel River is the smallest of four major tributaries of the Eel River in northwestern California in the United States. It drains a rugged wilderness area of about 286 square miles (740 km2) in the California Coast Ranges, and flows through national forests for much of its length. Very few people inhabit the relatively pristine watershed of the river; there are no operational stream gauges and only one bridge that crosses the river, near the boundary between Trinity and Mendocino Counties.

Crabtree Hot Springs is a geological phenomenon in Lake County, California about 25 miles (40 km) north of Upper Lake. It is located on private property and closed to the public. It lies at an elevation of 2,257 feet. There is a cluster of four natural hot springs at this location, in an isolated narrow winding steep walled canyon on the north bank of the Rice Fork of the Eel River, about one fourth mile downriver from its junction with Salt Creek. Three of the hot springs are aligned in one area at a large swimming hole, while the fourth hot spring is about 60 feet back upriver. The temperature of the hottest spring is 106 °F (41 °C), with a flow rate of about 10 US gallons (38 L) per minute.
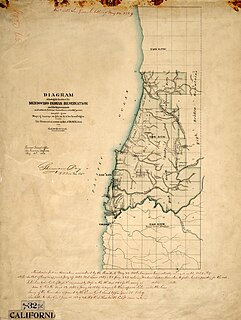
Mendocino Indian Reservation, a former Indian reservation in Mendocino County, one of the early Indian reservations to be established in California by the Federal Government for the resettlement of California Indians. It was established in the spring of 1856, in the vicinity of modern Noyo. Its area was 25,000 acres and its boundary extended north from what is now Simpson Lane at 39°24′43″N123°48′30″W to Abalobadiah Creek and east from the Pacific Ocean to a north–south line passing through the summit of Bald Hill.

The Mendocino Complex Fire was the largest recorded fire complex in California history. It was a large complex of two wildfires, the River Fire and Ranch Fire, which burned in Mendocino, Lake, Colusa, and Glenn Counties in the U.S. State of California, with the Ranch Fire being California's single-largest recorded wildfire. The Ranch Fire burned eight miles northeast of Ukiah, and the River Fire burned six miles north of Hopland, to the south of the larger Ranch Fire. First reported on July 27, 2018, both fires burned a combined total of 459,123 acres (1,858 km2), before they were collectively 100% contained on September 18; the Ranch Fire alone burned 410,203 acres (1,660 km2), surpassing the Thomas Fire to become the single-largest modern California wildfire. The Ranch Fire also surpassed the size of the 315,577-acre Rush Fire, which burned across California and Nevada, as well as the Santiago Canyon Fire of 1889, which was previously believed to have been California's all-time largest wildfire. The fires collectively destroyed 280 structures while damaging 37 others; causing at least $267 million in damages, including $56 million in insured property damage and $201 million in fire suppression costs. The city of Lakeport, communities of Kelseyville, Lucerne, Upper Lake, Nice, Saratoga Springs, Witter Springs, Potter Valley, and Finley, parts of Hopland, and the tribal communities of Hopland Rancheria and Big Valley Rancheria were evacuated.














