The topic of this article may not meet Wikipedia's general notability guideline .(January 2022) |

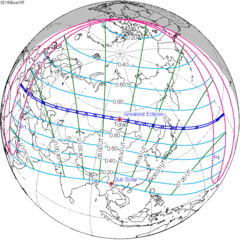
A partial lunar eclipse took place on Monday, June 25, 1945.
The topic of this article may not meet Wikipedia's general notability guideline .(January 2022) |

A partial lunar eclipse took place on Monday, June 25, 1945.
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saros | Date Viewing | Type Chart | Saros | Date Viewing | Type Chart | |
| 109 | 1944 Jul 06  | Penumbral | 114 | 1944 Dec 29  | Penumbral | |
| 119 | 1945 Jun 25  | Partial | 124 | 1945 Dec 19  | Total | |
| 129 | 1946 Jun 14  | Total | 134 | 1946 Dec 08  | Total | |
| 139 | 1947 Jun 03  | Partial | 144 | 1947 Nov 28  | Penumbral | |
A lunar eclipse will be preceded and followed by solar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a half saros). [1] This lunar eclipse is related to two total solar eclipses of Solar Saros 126.
| June 19, 1936 | June 30, 1954 |
|---|---|
 |  |

A total lunar eclipse took place on Friday 21 January 2000, the first of two total lunar eclipses in 2000.

A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on 18–19 October 2013, the last of three lunar eclipses in 2013.
A total lunar eclipse took place on Tuesday, July 6, 1982, the second of three total lunar eclipses in 1982, and the only one that was in the descending node. A dramatic total eclipse lasting 1 hour and 46 minutes plunged the full Moon into deep darkness, as it passed right through the centre of the Earth's umbral shadow. While the visual effect of a total eclipse is variable, the Moon may have been stained a deep orange or red colour at maximum eclipse. This was a great spectacle for everyone who saw it. The partial eclipse lasted for 3 hours and 56 minutes in total.
A total lunar eclipse took place on Saturday, May 24 and Sunday, May 25, 1975, the first of two total lunar eclipses in 1975. The Moon was plunged into darkness for 1 hour and 28 minutes in a deep total eclipse which saw the Moon 43% of its diameter inside the Earth's umbral shadow. The visual effect of an eclipse depends on the state of the Earth's atmosphere, but the Moon may have been stained a deep red colour. The partial eclipse lasted for 3 hours and 35 minutes in total. Occurring only 4.4 days after perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was 0.7% larger than average. The moon was 377,010 km from the Earth at greatest eclipse.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Thursday, June 25, 1964. The moon passed through the center of the Earth's shadow.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Thursday, December 30, 1982. A shallow total eclipse saw the Moon in relative darkness for 1 hour 3 seconds. The Moon was 18% of its diameter into the Earth's umbral shadow, and should have been significantly darkened. The partial eclipse lasted for 3 hours and 16 minutes in total. This was a supermoon since perigee was on the same day. It was also a blue moon, the second full moon of December for the eastern hemisphere where the previous full moon was on December 1. Since total lunar eclipses are also known as blood moons, this combination is known as a super blue blood moon.
A total lunar eclipse took place on Thursday, April 24, 1986, the first of two total lunar eclipses in 1986, the second being on October 17, 1986. The Moon was plunged into darkness for 1 hour, 3 minutes and 34.8 seconds, in a deep total eclipse which saw the Moon 20.217% of its diameter inside the Earth's umbral shadow. The visual effect of this depends on the state of the Earth's atmosphere, but the Moon may have been stained a deep red colour. The partial eclipse lasted for 3 hours, 18 minutes and 46.8 seconds in total. The Moon was just 1.2 days before perigee, making it 5.3% larger than average.

A partial lunar eclipse took place on Wednesday, May 25, 1994, the first of two lunar eclipses in 1994, the second being with a penumbral lunar eclipse on Friday, November 18.

A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on Friday, November 18, 1994, the second of two lunar eclipses in 1994, the first was a partial lunar eclipse on Wednesday, May 25.

A partial lunar eclipse occurred on the 16 and 17 July 2019. The Moon was covered 65.31% by the Earth's umbral shadow at maximum eclipse.

A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on 5 June 2020. It was the second of four penumbral lunar eclipses in 2020.
A penumbral lunar eclipse will take place on Monday, March 25, 2024. It will be visible to the naked eye as 95.57% of the Moon will be immersed in Earth's penumbral shadow.
A partial lunar eclipse will take place on Wednesday, 18 September 2024, the second of two lunar eclipses in 2024 and the final partial lunar eclipse of Lunar Saros 118.

A penumbral lunar eclipse will take place on May 7, 2031.
A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on Saturday, November 6, 1976, the second of two lunar eclipses in 1976, the first being on May 13. This subtle penumbral eclipse may have been visible to a skilled observer at maximum eclipse. 83.827% of the Moon's disc was partially shaded by the Earth, which caused a gentle shadow gradient across its disc at maximum; the eclipse as a whole lasted 4 hours, 25 minutes and 52.1 seconds. Occurring only 0.3 days after apogee, the moon's apparent diameter was 6.5% smaller than average.

A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on Thursday, September 25, 1969, the last of three penumbral lunar eclipses in 1969, the first being on Wednesday, April 2, and the second being on Wednesday, August 27. At maximum eclipse, 90% of the Moon's disc was partially shaded by the Earth, which caused a slight shadow gradient across its disc; this subtle effect may have been visible to careful observers. No part of the Moon was in complete shadow. The eclipse lasted 4 hours and 5 minutes overall.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Sunday, July 26, 1953.

A total lunar eclipse will take place on March 25, 2043.

A penumbral lunar eclipse will take place on August 27, 2045. It will be noticeably visible as 68.25% of the Moon will cross within Earth's penumbral shadow.
A partial lunar eclipse will take place on June 28, 2075.