Related Research Articles

Anammox, an abbreviation for "anaerobic ammonium oxidation", is a globally important microbial process of the nitrogen cycle that takes place in many natural environments. The bacteria mediating this process were identified in 1999, and were a great surprise for the scientific community. In the anammox reaction, nitrite and ammonium ions are converted directly into diatomic nitrogen and water.

Desulfobacterales are an order of sulfate-reducing bacteria within the phylum Thermodesulfobacteria. The order contains three families; Desulfobacteraceae, Desulfobulbaceae, and Nitrospinaceae. The bacterium in this order are strict anaerobic respirators, using sulfate or nitrate as the terminal electron acceptor instead of oxygen. Desulfobacterales can degrade ethanol, molecular hydrogen, organic acids, and small hydrocarbons. The bacterium of this order have a wide ecological range and play important environmental roles in symbiotic relationships and nutrient cycling.
Fibrobacterota is a small bacterial phylum which includes many of the major rumen bacteria, allowing for the degradation of plant-based cellulose in ruminant animals. Members of this phylum were categorized in other phyla. The genus Fibrobacter was removed from the genus Bacteroides in 1988.

Gammaproteobacteria is a class of bacteria in the phylum Pseudomonadota. It contains about 250 genera, which makes it the most genus-rich taxon of the Prokaryotes. Several medically, ecologically, and scientifically important groups of bacteria belong to this class. All members of this class are Gram-negative. It is the most phylogenetically and physiologically diverse class of the Pseudomonadota.
The Synergistota is a phylum of anaerobic bacteria that show Gram-negative staining and have rod/vibrioid cell shape. Although Synergistota have a diderm cell envelope, the genes for various proteins involved in lipopolysaccharides biosynthesis have not yet been detected in Synergistota, indicating that they may have an atypical outer cell envelope. The Synergistota inhabit a majority of anaerobic environments including animal gastrointestinal tracts, soil, oil wells, and wastewater treatment plants and they are also present in sites of human diseases such as cysts, abscesses, and areas of periodontal disease. Due to their presence at illness related sites, the Synergistota are suggested to be opportunistic pathogens but they can also be found in healthy individuals in the microbiome of the umbilicus and in normal vaginal flora. Species within this phylum have also been implicated in periodontal disease, gastrointestinal infections and soft tissue infections. Other species from this phylum have been identified as significant contributors in the degradation of sludge for production of biogas in anaerobic digesters and are potential candidates for use in renewable energy production through their production of hydrogen gas. All of the known Synergistota species and genera are presently part of a single class (Synergistia), order (Synergistiales), and family (Synergistaceae).
Lentisphaerota is a phylum of bacteria closely related to Chlamydiota and Verrucomicrobiota.

The FCB group is a superphylum of bacteria named after the main member phyla Fibrobacterota, Chlorobiota, and Bacteroidota. The members are considered to form a clade due to a number of conserved signature indels.
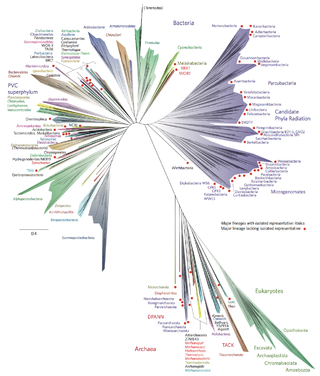
Bacterial phyla constitute the major lineages of the domain Bacteria. While the exact definition of a bacterial phylum is debated, a popular definition is that a bacterial phylum is a monophyletic lineage of bacteria whose 16S rRNA genes share a pairwise sequence identity of ~75% or less with those of the members of other bacterial phyla.
"Candidatus Scalindua" is a bacterial genus, and a proposed member of the order Planctomycetales. These bacteria lack peptidoglycan in their cell wall and have a compartmentalized cytoplasm. They are ammonium oxidizing bacteria found in marine environments.
Syntrophomonas wolfei is a bacterium. It is anaerobic, syntrophic and fatty acid-oxidizing. It has a multilayered cell wall of the gram-negative type.
Desulfatibacillum is a bacteria genus from the order Desulfobacterales.
Chitinivibrio is an extremely haloalkaliphilic genus of bacteria from the family of Chitinivibrionaceae with one known species. Chitinivibrio alkaliphilus has been isolated from hypersaline lake sediments from Wadi al Natrun in Egypt.
The candidate phyla radiation is a large evolutionary radiation of bacterial lineages whose members are mostly uncultivated and only known from metagenomics and single cell sequencing. They have been described as nanobacteria or ultra-small bacteria due to their reduced size (nanometric) compared to other bacteria.
Zixibacteria is a bacterial phylum with candidate status, meaning it had no cultured representatives. It is a member of the FCB group
Fermentibacteria is a bacterial phylum with candidate status. It is part of the FCB group.

NC10 is a bacterial phylum with candidate status, meaning its members remain uncultured to date. The difficulty in producing lab cultures may be linked to low growth rates and other limiting growth factors.
CandidatusWirthbacteria is a proposed bacterial phylum containing only one known sample from the Crystal Geyser aquifer, Ca. Wirthibacter wanneri. This bacterium stands out in a basal position in some trees of life as it is closely related to Candidate phyla radiation but is not considered part of that clade.
Ann Patricia Wood is a retired British biochemist and bacteriologist who specialized in the ecology, taxonomy and physiology of sulfur-oxidizing chemolithoautotrophic bacteria and how methylotrophic bacteria play a role in the degradation of odour causing compounds in the human mouth, vagina and skin. The bacterial genus Annwoodia was named to honor her contributions to microbial research in 2017.
The Ignavibacteriales are an order of obligately anaerobic, non-photosynthetic bacteria that are closely related to the green sulfur bacteria.
References
- ↑ Guermazi, Sonda; Daegelen, Patrick; Dauga, Catherine; Rivière, Delphine; Bouchez, Théodore; Godon, Jean Jacques; Gyapay, Gábor; Sghir, Abdelghani; Pelletier, Eric; Weissenbach, Jean; Le Paslier, Denis (August 2008). "Discovery and characterization of a new bacterial candidate division by an anaerobic sludge digester metagenomic approach". Environmental Microbiology. 10 (8): 2111–2123. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2008.01632.x. ISSN 1462-2920. PMC 2702496 . PMID 18459975.
- ↑ Hug, Laura A.; Baker, Brett J.; Anantharaman, Karthik; Brown, Christopher T.; Probst, Alexander J.; Castelle, Cindy J.; Butterfield, Cristina N.; Hernsdorf, Alex W.; Amano, Yuki; Ise, Kotaro; Suzuki, Yohey (2016-04-11). "A new view of the tree of life". Nature Microbiology. 1 (5): 16048. doi: 10.1038/nmicrobiol.2016.48 . ISSN 2058-5276. PMID 27572647.