Eagle is the common name for the golden eagle, bald eagle, and other birds of prey in the family Accipitridae. Eagles belong to several groups of genera, some of which are closely related. True eagles comprise the genus Aquila. Most of the 68 species of eagles are from Eurasia and Africa. Outside this area, just 14 species can be found—two in North America, nine in Central and South America, and three in Australia.

Hawks are birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. They are very widely distributed and are found on all continents except Antarctica.

A harrier is any of the several species of diurnal hawks sometimes placed in the subfamily Circinae of the bird of prey family Accipitridae. Harriers characteristically hunt by flying low over open ground, feeding on small mammals, reptiles, or birds. The young of the species are sometimes referred to as ring-tail harriers. They are distinctive with long wings, a long narrow tail, the slow and low flight over grasslands and skull peculiarities. The harriers are thought to have diversified with the expansion of grasslands and the emergence of C4 grasses about 6 to 8 million years ago during the Late Miocene and Pliocene.

The Accipitridae is one of the three families within the order Accipitriformes, and is a family of small to large birds of prey with strongly hooked bills and variable morphology based on diet. They feed on a range of prey items from insects to medium-sized mammals, with a number feeding on carrion and a few feeding on fruit. The Accipitridae have a cosmopolitan distribution, being found on all the world's continents and a number of oceanic island groups. Some species are migratory. The family contains 255 species which are divided into 70 genera.

The buntings are a group of Old World passerine birds forming the genus Emberiza, the only genus in the family Emberizidae. The family contains 44 species. They are seed-eating birds with stubby, conical bills.

The Accipitriformes are an order of birds that includes most of the diurnal birds of prey, including hawks, eagles, vultures, and kites, but not falcons.

The Buteoninae are a subfamily of birds of prey which consists of medium to large, broad-winged species.

Circaetinae is a bird of prey subfamily which consists of a group of medium to large broad-winged species. The group is sometimes treated as tribe Circaetini. These birds mainly specialise in feeding on snakes and other reptiles, which is the reason most are referred to as "snake-eagles" or "serpent-eagles". The exceptions are the bateleur, a more generalised hunter, and the Philippine eagle, which preys on mammals and birds.

An elanine kite is any of several small, lightly-built raptors with long, pointed wings.

The white hawk is a bird of prey breeding in the tropical New World of the family Accipitridae. Though it is commonly placed in the subfamily Buteoninae, the validity of this group is doubtful and currently under review.

Setophaga is a genus of birds of the New World warbler family Parulidae. It contains at least 34 species. For example, the males in breeding plumage are often highly colorful. The Setophaga warblers are an example of adaptive radiation with the various species using different feeding techniques and often feeding in different parts of the same tree.

Chlorophonia is a genus of finches in the family Fringillidae. The Chlorophonias are endemic to the Neotropics. They are small, mostly bright green birds that inhabit humid forests and nearby habitats, especially in highlands.

The black-chested buzzard-eagle is a bird of prey of the hawk and eagle family (Accipitridae). It lives in open regions of South America. This species is also known as the black buzzard-eagle, the gray buzzard-eagle, or analogously with "eagle" or "eagle-buzzard" replacing "buzzard-eagle", or as the Chilean blue eagle. It is sometimes placed in the genus Buteo.

The solitary eagle or montane solitary eagle is a large Neotropical eagle. It is also known as the black solitary eagle.

Buteogallus is a genus of birds of prey in the family Accipitridae. All members of this genus are essentially neotropical, but the distribution of a single species extends slightly into the extreme southwestern United States. Many of the species are fond of large crustaceans and even patrol long stretches of shore or riverbank on foot where such prey abounds, but some have a rather different lifestyle. Unlike many other genera of raptor, some members are referred to as "hawks", and others as "eagles".

The black-faced hawk is a species of bird of prey in the family Accipitridae. This low-density species has traditionally been believed to be restricted to Amazon Basin north of the Amazon River, but there are several records south of this river, in, for example, the Brazilian states of Pará and Acre, and southeastern Peru. It is closely related to the white-browed hawk and individuals showing a level of intermediacy between the two species are known, suggesting that they rarely hybridize

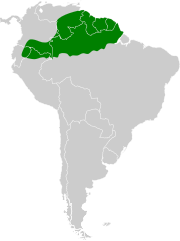
The grey-backed hawk is an Endangered species of bird of prey in subfamily Accipitrinae, the "true" hawks, of family Accipitridae. It is found in Ecuador and far northern Peru.

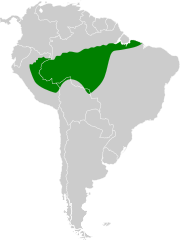
The barred hawk is a species of bird of prey in the family Accipitridae. It has also been known as the black-chested hawk.

Paraclaravis is a genus that contains two species of doves that live in the Neotropics, with ranges in Middle America and South America. Paraclaravis doves have red eyes and pink legs, and the plumages of the males are primarily light grey-blue, and the females are primarily brown. Both sexes have a series of distinctive spots or bands on the wings. They are fairly arboreal for ground doves. Paraclaravis doves have a distinct fast and rocking flight pattern. They are found alone, in pairs or in small flocks in forests. Both species are generally local and rare, and appears to be associated with flowering bamboo.

Pseudastur is a genus of bird of prey in the family Accipitridae. It contains the following species: