| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|
| Bald eagle  | Haliaeetus leucocephalus
(Linnaeus, 1766)
- H. l. leucocephalus(Linnaeus, 1766)
- H. l. washingtoniensis(Audubon, 1827)
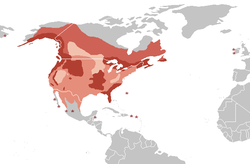
| Most of Canada and Alaska, all of the contiguous United States, and northern Mexico
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
|
|---|
| Pallas's fish eagle  | Haliaeetus leucoryphus
(Pallas, 1771) | Kazakhstan, Russia, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Mongolia, China, India, Nepal, Bangladesh, Myanmar and Bhutan. | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | EN
|
|---|
| White-tailed eagle  | Haliaeetus albicilla
(Linnaeus, 1758)
- H. a. albicilla - (Linnaeus, 1758)
- H. a. groenlandicus - Brehm, CL, 1831
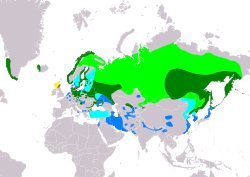
| Greenland and Iceland across Europe and Asia to as far east as Hokkaido, Japan
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
|
|---|
| Steller's sea eagle  | Haliaeetus pelagicus
(Pallas, 1811) | Russia, Korea, Japan, China, and Taiwan
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | VU
|
|---|










