| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|
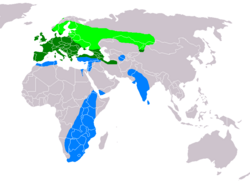
| Common buzzard  | Buteo buteo
(Linnaeus, 1758)
- B. b. buteo
- B. b. harterti
- B. b. insularum
- B. b. menetriesi
- B. b. pojana
- B. b. vulpinus
| northwestern China (Tian Shan), far western Siberia and northwestern Mongolia.
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
[24]
|
|---|
| Eastern buzzard  | Buteo japonicus
(Temminck & Schlegel, 1844)
- B. j. burmanicus - Hume, 1875
- B. j. japonicus - Temminck & Schlegel, 1845
- B. j. toyoshimai - Momiyama, 1927
- B. j. oshiroi - Kuroda, Nagahisa, 1971
| East Asia and some parts of Russia and South Asia
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
[25]
|
|---|
| Himalayan buzzard  | Buteo refectus
Portenko, 1935 | The Himalayas in Nepal, India and southern China.
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
[26]
|
|---|
| Cape Verde buzzard | Buteo bannermani
(Swann, 1919) | Cape Verde
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | |
|---|
| Socotra buzzard  | Buteo socotraensis
Porter & Kirwan, 2010 | Socotra, Yemen
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | VU
[27]
|
|---|
| Red-tailed hawk  | Buteo jamaicensis
(Gmelin, 1788)
| Alaska and northern Canada to as far south as Panama and the West Indies.
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
[28]
|
|---|
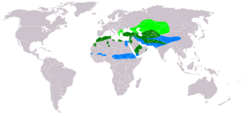
| Long-legged buzzard  | Buteo rufinus
(Cretzschmar, 1829)
- B. r. rufinus - (Cretzschmar, 1829)
- B. r. cirtensis - (Levaillant, J, 1850)
| Southeastern Europe down to East Africa to the northern part of the Indian subcontinent.
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
[29]
|
|---|
| Rough-legged buzzard  | Buteo lagopus
(Pontoppidan, 1763)
- B. l. lagopus - (Pontoppidan, 1763)
- B. l. menzbieri - Dementiev, 1951
- B. l. kamtschatkensis - Dementiev, 1931
- B. l. sanctijohannis - (Gmelin, JF, 1788)
| Arctic and Subarctic regions of North America, Europe, and Russia
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
[30]
|
|---|
| Ferruginous hawk  | Buteo regalis
(Gray, 1844) | North America
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
[31]
|
|---|
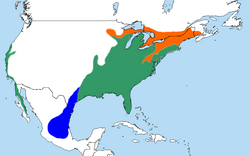
| Red-shouldered hawk  | Buteo lineatus
(Gmelin, 1788)
- B. l. lineatus (Gmelin, 1788)
- B. l. alleni Ridgway, 1885
- B. l. extimus Bangs, 1920
- B. l. texanus Bishop, 1912
- B. l. elegans Cassin, 1855
| Eastern North America and along the coast of California and northern to northeastern-central Mexico.
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
[32]
|
|---|
| Broad-winged hawk  | Buteo platypterus
(Vieillot, 1823)
- B. p. platypterus – (Vieillot, 1823)
- B. p. brunnescens – Danforth & Smyth, 1935
- B. p. cubanensis – Burns, 1911
- B. p. insulicola – Riley, 1908
- B. p. rivierei – Verrill, AH, 1905
- B. p. antillarum – Clark, AH, 1905
| Eastern North America, as far west as British Columbia and Texas, Neotropics from Mexico south to southern Brazil
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
[33]
|
|---|
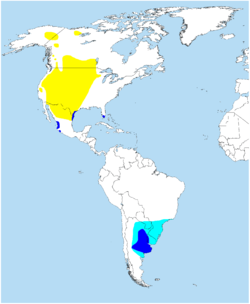
| Swainson's hawk  | Buteo swainsoni
Bonaparte, 1838 | Western North America, Chile, Argentina, Dominican Republic, and Trinidad and Tobago, and in Norway.
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
[34]
|
|---|
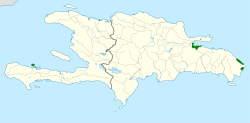
| Ridgway's hawk  | Buteo ridgwayi
(Cory, 1883) | Hispaniola
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | CR
[35]
|
|---|
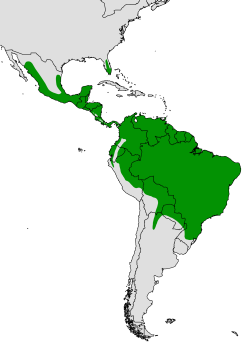
| Short-tailed hawk  | Buteo brachyurus
(Vieillot, 1816)
- B. b. fuliginosus - Sclater, PL, 1858
- B. b. brachyurus - Vieillot, 1816
| From southeastern Brazil and northern Argentina north through Central America to the mountains of the Mexico-Arizona border area, as well as in southern Florida, United States
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
[36]
|
|---|
| White-throated hawk  | Buteo albigula
Philippi, 1899 | South America
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
[37]
|
|---|
| Galapagos hawk  | Buteo galapagoensis
(Gould, 1837) | Galápagos Islands
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | VU
[38]
|
|---|
| Gray-lined hawk  | Buteo nitidus
Latham, 1790
- B. n. blakei - Hellmayr & Conover, 1949
- B. n. nitidus - (Latham, 1790)
- B. n. pallidus - (Todd, 1915)
| El Salvador to Argentina, as well as on the Caribbean island of Trinidad.
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
[39]
|
|---|
| Gray hawk  | Buteo plagiatus
(Schlegel, 1862) | From Costa Rica north into the southwestern United States
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
[40]
|
|---|
| Zone-tailed hawk  | Buteo albonotatus
(Kaup, 1847) | Southern Arizona, New Mexico, and western Texas almost throughout inland Mexico and the central portions of Central America down into eastern Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru, southern Brazil, Paraguay, Bolivia, and northern Argentina.
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
[41]
|
|---|
| Hawaiian hawk  | Buteo solitarius
(Peale, 1848) | Hawaii | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | NT
[42]
|
|---|
| Rufous-tailed hawk  | Buteo ventralis
Gould, 1837 | Argentina, Chile
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | VU
[43]
|
|---|
| Mountain buzzard  | Buteo oreophilus
Hartert and Neumann, 1914 | East Africa | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | NT
[44]
|
|---|
| Forest buzzard  | Buteo trizonatus
Rudebeck, 1957 | South Africa, Lesotho and Eswatini | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | NT
[45]
|
|---|
| Madagascar buzzard  | Buteo brachypterus
Hartlaub, 1860 | Madagascar
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
[46]
|
|---|
| Upland buzzard  | Buteo hemilasius
Temminck & Schlegel, 1844 | Central and East Asia | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
[47]
|
|---|
| Red-necked buzzard  | Buteo auguralis
Salvadori, 1865 | The Sahel and Central Africa | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
[48]
|
|---|
| Jackal buzzard  | Buteo rufofuscus
(Forster, 1798) | Southern Africa | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
[49]
|
|---|
| Augur buzzard  | Buteo augur
(Rüppell, 1836)
| From Ethiopia to southern Angola and central Namibia.
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
[50]
|
|---|




















































