The Polynesian languages form a genealogical group of languages, itself part of the Oceanic branch of the Austronesian family.
Tapu is a Polynesian traditional concept denoting something holy or sacred, with "spiritual restriction" or "implied prohibition"; it involves rules and prohibitions. The English word taboo derives from this later meaning and dates from Captain James Cook's visit to Tonga in 1777.

Pākehā is a Māori-language word used in English, particularly in New Zealand. It generally means a non-Polynesian New Zealander or more specifically a European New Zealander. It is not a legal term and has no definition under New Zealand law. Papa'a has a similar meaning in Cook Islands Māori.
In Polynesian mythology, Hawaiki is the original home of the Polynesians, before dispersal across Polynesia. It also features as the underworld in many Māori stories.

Samoan is a Polynesian language spoken by Samoans of the Samoan Islands. Administratively, the islands are split between the sovereign country of Samoa and the United States territory of American Samoa. It is an official language, alongside English, in both jurisdictions. It is widely spoken across the Pacific region, heavily so in New Zealand and also in Australia and the United States. Among the Polynesian languages, Samoan is the most widely spoken by number of native speakers.
Polynesians are an ethnolinguistic group comprising closely related ethnic groups native to Polynesia, which encompasses the islands within the Polynesian Triangle in the Pacific Ocean. They trace their early prehistoric origins to Island Southeast Asia and are part of the larger Austronesian ethnolinguistic group, with an Urheimat in Taiwan. They speak the Polynesian languages, a branch of the Oceanic subfamily within the Austronesian language family. The Indigenous Māori people form the largest Polynesian population, followed by Samoans, Native Hawaiians, Tahitians, Tongans, and Cook Islands Māori.
Tongan is an Austronesian language of the Polynesian branch native to the island nation of Tonga. It has around 187,000 speakers. It uses the word order verb–subject–object.

Kapa is a fabric made by native Hawaiians from the bast fibres of certain species of trees and shrubs in the orders Rosales and Malvales. The bark is beaten and felted to achieve a soft texture and dye stamped in geometric patterns.

A lavalava, sometimes written as lava-lava, also known as an 'ie, short for 'ie lavalava, is an article of daily clothing traditionally worn by Polynesians and other Oceanic peoples. It consists of a single rectangular cloth worn similarly to a wraparound skirt or kilt. The term lavalava is both singular and plural in the Samoan language.

Polynesian culture is the culture of the indigenous peoples of Polynesia who share common traits in language, customs and society. The development of Polynesian culture is typically divided into four different historical eras:
Cook Islands Māori is an Eastern Polynesian language that is the official language of the Cook Islands. Cook Islands Māori is closely related to, but distinct from, New Zealand Māori. Cook Islands Māori is called just Māori when there is no need to distinguish it from New Zealand Māori. It is also known as Māori Kūki ʻĀirani, or as Rarotongan Many Cook Islanders also call it Te reo Ipukarea, which translates as "the language of the ancestral homeland".

Tapa cloth is a barkcloth made in the islands of the Pacific Ocean, primarily in Tonga, Samoa and Fiji, but as far afield as Niue, Cook Islands, Futuna, Solomon Islands, Java, New Zealand, Vanuatu, Papua New Guinea and Hawaii. In French Polynesia it has nearly disappeared, except for some villages in the Marquesas.

The paper mulberry is a species of flowering plant in the family Moraceae. It is native to Asia, where its range includes mainland China, Taiwan, Japan, Korea, Southeast Asia, Myanmar, and India. It is widely cultivated elsewhere and it grows as an introduced species in New Zealand, parts of Europe, the United States, and Africa. Other common names include tapa cloth tree.
Palagi or papalagi (plural) is a term in Samoan culture of uncertain etymology, sometimes used to describe foreigners.
Tuamotuan, Paʻumotu or Paumotu is a Polynesian language spoken by 4,000 people in the Tuamotu archipelago, with an additional 2,000 speakers in Tahiti.
Mangareva, Mangarevan is a Polynesian language spoken by about 600 people in the Gambier Islands of French Polynesia and by Mangarevians emigrants on the islands of Tahiti and Moorea, located 1,650 kilometres (1,030 mi) to the North-West of the Gambier Islands.
The Penrhyn language is a Cook Islands Maori dialectal variant belonging to the Polynesian language family. It is spoken by about 200 people on Penrhyn Island and other islands in the Northern Cook Islands. It is considered to be an endangered language as many of its users are shifting to Cook Islands Māori and English.
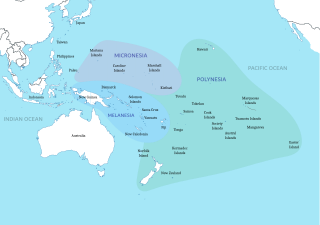
Polynesia is a subregion of Oceania, made up of more than 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are called Polynesians. They have many things in common, including linguistic relations, cultural practices, and traditional beliefs. In centuries past, they had a strong shared tradition of sailing and using stars to navigate at night.
Bible translations into Oceanic languages have a relatively closely related and recent history.

The Tahitian Dog is an extinct breed of dog from Tahiti and the Society Islands. Similar to other strains of Polynesian dogs, it was introduced to the Society Islands and Tahiti by the ancestors of the Tahitian (Mā’ohi) people during their migrations to Polynesia.









