
The economy of Switzerland is one of the world's most advanced free market economies. The service sector has come to play a significant economic role, particularly the Swiss banking industry and tourism. The economy of Switzerland ranks first in the world in the 2015 Global Innovation Index and third in the 2020 Global Competitiveness Report. According to United Nations data for 2016, Switzerland is the third richest landlocked country in the world after Liechtenstein and Luxembourg, and together with the latter and Norway the only three countries in the world with a GDP per capita (nominal) above US$70,000 that are neither island nations nor ministates.

The four national languages of Switzerland are German, French, Italian and Romansh. German, French and Italian maintain equal status as official languages at the national level within the Federal Administration of the Swiss Confederation, while Romansh is used in dealings with people who speak it. In some situations, Latin is used, particularly as a single language to denote the country.

The eurozone, officially called the euro area, is a monetary union of 19 member states of the European Union (EU) that have adopted the euro (€) as their primary currency and sole legal tender. The monetary authority of the eurozone is the Eurosystem. Eight members of the European Union continue to use their own national currencies, although most of them will be obliged to adopt the euro in the future.

The Green Party of Switzerland is the fourth-largest party in the National Council of Switzerland and the largest party that is not represented on the Federal Council.

The Ticino League is a regionalist, national-conservative political party in Switzerland active in the canton of Ticino.
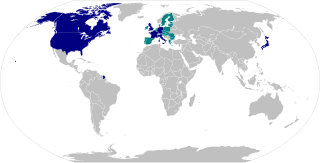
The Group of Seven (G7) is an intergovernmental organization consisting of Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom and the United States. The heads of government of the member states, as well as the representatives of the European Union, meet at the annual G7 Summit.

The economy of the European Union is the joint economy of the member states of the European Union (EU). It is the second largest economy in the world in nominal terms, after the United States, and the third one in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms, after China and the United States. The European Union's GDP was estimated to be around $15 trillion (nominal) in 2020, representing around 1/6 of the global economy.

The education system in Switzerland is very diverse, because the constitution of Switzerland delegates the authority for the school system mainly to the cantons. The Swiss constitution sets the foundations, namely that primary school is obligatory for every child and is free in public schools and that the confederation can run or support universities.

Islam in Switzerland has mostly arrived via immigration since the late 20th century. Numbering below 1% of total population in 1980, the fraction of Muslims in the population of permanent residents in Switzerland has quintupled in thirty years, estimated at just above 5% as of 2013. A majority is from Former Yugoslavia ; an additional 20% is from Turkey. This is due to the fact that in the 1960s and 1970s Switzerland encouraged young men from Yugoslavia and Turkey to come as guest workers. Initially these young men were only planning on staying in Switzerland temporarily, however, revised Swiss immigration laws in the 1970s permitted family regrouping. Consequently, these men ended up staying in Switzerland as these new laws allowed the wives and children of these young men into the country. Since this time period, most of the Muslim immigration to Switzerland stems from asylum seekers arriving primarily from Eastern Europe.

The Christ Catholic Church is the Old Catholic Church in Switzerland. With about 9,184 members nationwide, the Christ Catholic Church has the official status of a national church in various cantons.
Swiss Standard German, or Swiss High German, referred to by the Swiss as Schriftdeutsch, or Hochdeutsch, is the written form of one of four official languages in Switzerland, besides French, Italian and Romansh. It is a variety of Standard German, used in the German-speaking part of Switzerland and Liechtenstein. It is mainly written, and rather less often spoken.

Christianity is the predominant religion of Switzerland, its presence going back to the Roman era. Since the 16th century, Switzerland has been traditionally divided into Roman Catholic and Reformed confessions. However, adherence to Christian churches has declined considerably since the late 20th century, from close to 94% in 1980 to about 64% as of 2018.
Turks in Switzerland or Swiss Turks are Swiss residents of Turkish origin. The majority of Swiss Turks descend from the Republic of Turkey; however there has also been Turkish migration waves from other post-Ottoman countries including ethnic Turkish communities which have come to Switzerland from the Balkans, the island of Cyprus, and more recently Iraq and Syria.

This article includes a list of China's historical gross domestic product (GDP) values, the market value of all final goods and services produced by a nation in a given year. The GDP dollar estimates presented here are either calculated at market or government official exchange rates (nominal), or derived from purchasing power parity (PPP) calculations. This article also includes historical GDP growth.
The country of Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, has a comparatively meager public welfare system. As such, Switzerland is often classified as the model liberal-market economy of continental Europe, and stands out amongst other continental European states due to its small, means-tested welfare program. The OECD cites Switzerland's social expenditure as 19.6% of their gross domestic product, a rate that parallels other liberal-market states' spending rates.











