
In organic chemistry, hydrocarbons are divided into two classes: aromatic compounds and aliphatic compounds. Aliphatic compounds can be saturated, like hexane, or unsaturated, like hexene and hexyne. Open-chain compounds, whether straight or branched, and which contain no rings of any type, are always aliphatic. Cyclic compounds can be aliphatic if they are not aromatic.

In chemistry, an alkene is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond.

Carbon is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon makes up only about 0.025 percent of Earth's crust. Three isotopes occur naturally, 12C and 13C being stable, while 14C is a radionuclide, decaying with a half-life of about 5,730 years. Carbon is one of the few elements known since antiquity.
A chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and plus (+) and minus (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name, and it contains no words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae.
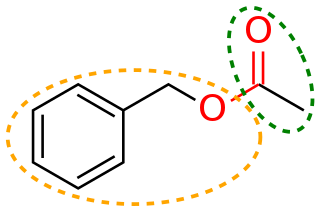
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a substituent or moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the rest of the molecule's composition. This enables systematic prediction of chemical reactions and behavior of chemical compounds and the design of chemical synthesis. The reactivity of a functional group can be modified by other functional groups nearby. Functional group interconversion can be used in retrosynthetic analysis to plan organic synthesis.
Carbon compounds are defined as chemical substances containing carbon. More compounds of carbon exist than any other chemical element except for hydrogen. Organic carbon compounds are far more numerous than inorganic carbon compounds. In general bonds of carbon with other elements are covalent bonds. Carbon is tetravalent but carbon free radicals and carbenes occur as short-lived intermediates. Ions of carbon are carbocations and carbanions are also short-lived. An important carbon property is catenation as the ability to form long carbon chains and rings.

In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate, millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds, along with a few other exceptions, are not classified as organic compounds and are considered inorganic. Other than those just named, little consensus exists among chemists on precisely which carbon-containing compounds are excluded, making any rigorous definition of an organic compound elusive.
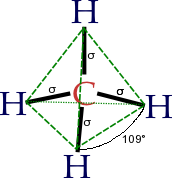
Organic chemistry is a branch of chemistry that studies the structure, properties and reactions of organic compounds, which contain carbon-carbon covalent bonds. Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes physical and chemical properties, and evaluation of chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical study.

Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkaline, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and sometimes broadened to include metalloids like boron, silicon, and selenium, as well. Aside from bonds to organyl fragments or molecules, bonds to 'inorganic' carbon, like carbon monoxide, cyanide, or carbide, are generally considered to be organometallic as well. Some related compounds such as transition metal hydrides and metal phosphine complexes are often included in discussions of organometallic compounds, though strictly speaking, they are not necessarily organometallic. The related but distinct term "metalorganic compound" refers to metal-containing compounds lacking direct metal-carbon bonds but which contain organic ligands. Metal β-diketonates, alkoxides, dialkylamides, and metal phosphine complexes are representative members of this class. The field of organometallic chemistry combines aspects of traditional inorganic and organic chemistry.
A period 2 element is one of the chemical elements in the second row of the periodic table of the chemical elements. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behavior of the elements as their atomic number increases; a new row is started when chemical behavior begins to repeat, creating columns of elements with similar properties.
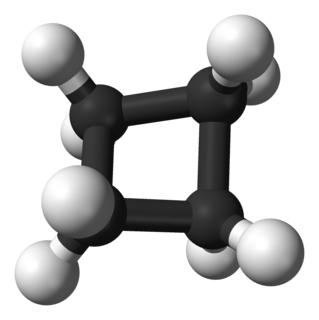
In organic chemistry, the cycloalkanes are the monocyclic saturated hydrocarbons. In other words, a cycloalkane consists only of hydrogen and carbon atoms arranged in a structure containing a single ring, and all of the carbon-carbon bonds are single. The larger cycloalkanes, with more than 20 carbon atoms are typically called cycloparaffins. All cycloalkanes are isomer of Alkene.

In chemistry, aromaticity is a property of cyclic (ring-shaped), typically planar (flat) molecular structures with pi bonds in resonance that gives increased stability compared with other geometric or connective arrangements with the same set of atoms. Aromatic rings are very stable and do not break apart easily. Organic compounds that are not aromatic are classified as aliphatic compounds—they might be cyclic, but only aromatic rings have enhanced stability.
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. However, the distinction is not clearly defined; authorities have differing views on the subject. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as inorganic chemistry.
In chemical nomenclature, the IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry is a method of naming organic chemical compounds as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). It is published in the Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry. Ideally, every possible organic compound should have a name from which an unambiguous structural formula can be created. There is also an IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry.
Butene, also known as butylene, is an alkene with the formula C4H8. The word butene may refer to any of the individual compounds. They are colourless gases that are present in crude oil as a minor constituent in quantities that are too small for viable extraction. Butene is therefore obtained by catalytic cracking of long-chain hydrocarbons left during refining of crude oil. Cracking produces a mixture of products, and the butene is extracted from this by fractional distillation.
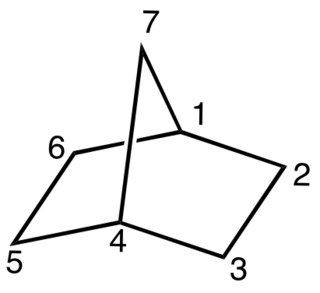
A bicyclic molecule is a molecule that features two joined rings. Bicyclic structures occur widely, for example in many biologically important molecules like α-thujene and camphor. A bicyclic compound can be carbocyclic, or heterocyclic, like DABCO. Moreover, the two rings can both be aliphatic, or can be aromatic, or a combination of aliphatic and aromatic.
In chemical nomenclature, a preferred IUPAC name (PIN) is a unique name, assigned to a chemical substance and preferred among the possible names generated by IUPAC nomenclature. The "preferred IUPAC nomenclature" provides a set of rules for choosing between multiple possibilities in situations where it is important to decide on a unique name. It is intended for use in legal and regulatory situations.
In organic chemistry, the carbon number of a compound is the number of carbon atoms in each molecule. The properties of hydrocarbons can be correlated with the carbon number, although the carbon number alone does not give an indication of the saturation of the organic compound. When describing a particular molecule, the "carbon number" is also the ordinal position of a particular carbon atom in a chain.
This is an index of lists of molecules. Millions of molecules have existed in the universe since before the formation of Earth. Three of them, carbon dioxide, water and oxygen were necessary for the growth of life. Though we have always been surrounded by these substances, we have not always known what they were composed of.