
A moat is a deep, broad ditch dug around a castle, fortification, building, or town, historically to provide it with a preliminary line of defence. Moats can be dry or filled with water. In some places, moats evolved into more extensive water defences, including natural or artificial lakes, dams and sluices. In older fortifications, such as hillforts, they are usually referred to simply as ditches, although the function is similar. In later periods, moats or water defences may be largely ornamental. They could also act as a sewer.

A water castle, sometimes water-castle, is a castle where natural or artificial water is part of its defences. It can be entirely surrounded by water-filled moats or natural waterbodies such as island castles in a river or offshore. The term comes from European castle studies, mainly German Burgenkunde. When stately homes were built in such a location, or a Wasserburg was later rebuilt as a residential manor, the German term becomes Wasserschloss, lit. "water palace/manor".

In military engineering, a ditch is an obstacle designed to slow down or break up an attacking force, while a trench is intended to provide cover to the defenders. In military fortifications the side of a ditch farthest from the enemy and closest to the next line of defence is known as the scarp while the side of a ditch closest to the enemy is known as the counterscarp.

A circular rampart is an embankment built in the shape of a circle that was used as part of the defences for a military fortification, hill fort or refuge, or was built for religious purposes or as a place of gathering.

Hodenhagen Castle is the site of a former lowland castle (Niederungsburg) built in the 13th century in the vicinity of Hodenhagen in the German state of Lower Saxony. This medieval manor house only lasted just under 100 years and was destroyed in 1289.

Uhlenburg is the site (Burgstall) of a lowland castle that was built in the 14th century close to the River Aller near Essel in the German state of Lower Saxony. This Late Middle Ages aristocratic seat only existed for a few decades towards the end of the 14th century and was destroyed by force in 1393/94.

Blankenhagen Castle was a lowland castle (Niederungsburg), whose ruins are located by the River Aller near Grethem in Lower Saxony, Germany. The motte-and-bailey castle is believed to have been built around 1200. It is supposed that there used to be fortified buildings on the two low mounds or mottes, and that a bailey was constructed on an outer island-like area.

Calenberg Castle was a medieval lowland castle in central Germany, near Schulenburg in the borough of Pattensen, 13 kilometres (8.1 mi) west of the city of Hildesheim. It was built as a water castle in 1292 by the Welf duke, Otto the Strict, in der Leine river meadows between two branches of the Leine river on the southern part of the chalk marl hill of the Calenberg. At the start of the 16th century it was converted into a fort (Feste). In the 15th century, Fort Calenberg gave its name to the Welf Principality of Calenberg. Following the Thirty Years' War it lost its military importance and was slighted. Today it is a ruin with underground vaults that are surrounded by high ramparts.

A hill castle or mountain castle is a castle built on a natural feature that stands above the surrounding terrain. It is a term derived from the German Höhenburg used in categorising castle sites by their topographical location. Hill castles are thus distinguished from lowland castles (Niederungsburgen).

Frohberg Castle is a medieval castle ruin in the Swiss municipality of Aesch in the canton of canton of Basel-Land.
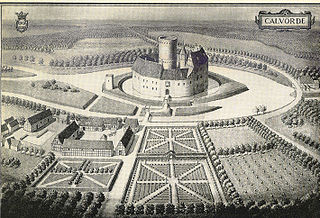
A marsh or marshland castle is a type of lowland castle that is situated in marshy or boggy countryside. It uses the natural inaccessibility of the terrain to its defensive advantage.

A hillside castle is a castle built on the side of a hill above much of the surrounding terrain but below the summit itself. It is thus a type of hill castle and emerged in Europe in the second half of the 11th century. As a result of the particular danger to the site from attacks on the castle from the rising ground above it, this weak point is usually strongly protected by a shield wall or a Bergfried. Often a combination of these two passive defensive works were used.
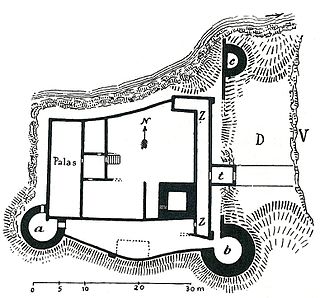
A neck ditch, sometimes called a throat ditch, is a dry moat that does not fully surround a castle, but only bars the side that is not protected by natural obstacles. It is often an important element in the defensive system of hill castles, especially in Germany and other parts of Central Europe.

An outer bailey or outer ward is the defended outer enclosure of a castle. It protects the inner bailey and usually contains those ancillary buildings used for the management of the castle or the supply of its occupants. These domestic buildings could include workshops, livestock stalls and stables; storage facilities such as barns, sheds and granaries, as well as quarters for servants such as maids, farm workers, and even the castle governors or castellans. In many cases there was also a brewery, a bakehouse and a kitchen, if the latter was not located in the hall or palas. An outer bailey was often called a base court in England. Depending on topography it could also be referred to as a lower bailey or lower ward, the keep being in the upper bailey or ward. Chepstow Castle has lower, middle and upper baileys.

A Zwinger is an open kill zone area between two defensive walls that is used for defensive purposes. Zwingers were built in the post-classical and early modern periods to improve the defence of castles and town walls. The term is usually left untranslated, but is sometimes rendered as "outer courtyard", presumably referring to the subsequent role of a Zwinger as a castle's defences became redundant and it was converted into a palace or schloss; however, this belies its original purpose as a form of killing ground for the defence. The word is linked with zwingen, "to force", perhaps because the Zwinger forced an enemy to negotiate it before assaulting the main defensive line. Essenwein states that the "main purpose of this feature was so that the besieging force could not reach the actual castle wall very easily with battering rams or belfries, but had to stop at the lower, outer wall; also that two ranks of archers, behind and above one another, could fire upon the approaching enemy".
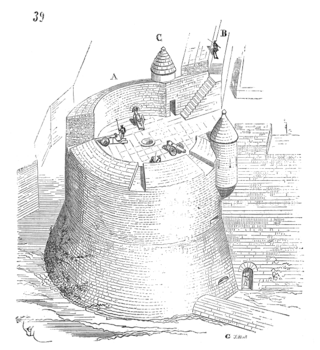
The roundel is an artillery fortification with a rounded or circular plan of a similar height to the adjacent defensive walls. If the fortification is clearly higher than the walls it is called a battery tower.

Schauenburg Castle is a ruined hilltop castle located in Oberkirch, Germany, atop a 367-metre-high (1,204 ft) (NN) hill spur overlooking the Rench river valley above the town of Gaisbach, Baden-Württemberg. The castle was built by Duke Berthold II of Zähringen.

Neideck Castle is a former high mediaeval nobleman's castle above the village of Streitberg, in the municipality of Wiesenttal in the Upper Franconian county of Forchheim in the German state of Bavaria. As a result of its exposed location above the valley of the Wiesent, it has become a symbol of Franconian Switzerland.
The burgstall of Dietrichstein Castle, also called the Diederichstein Ruins, is the site of an old, probably high mediaeval, aristocratic, castle, situated high above the valley of the River Trubach in the municipality of Pretzfeld in the Upper Franconian county of Forchheim in Bavaria, Germany.
The Altenburg fortification near Heroldsbach is a levelled early medieval fortified position at a height of 362 m above sea level (NHN), about 850 metres northwest of the church in Heroldsbach in the Upper Franconian county of Forchheim in the south German state of Bavaria. No historical or archaeological information is available for this sector fortification, but pottery finds from the interior of the site date to the Early Middle Ages. All that has survived is a double rampart system with a ditch. The site is protected by the state of Bavaria as monument number D-4-6331-0001: Frühmittelalterliche Abschnittsbefestigung "Altenburg".




















