| Place | Province | Accessible | Condition | Image | Notes |
|---|
| 's-Hertogenbosch | North Brabant | Yes | Sizable parts of the fortifications remain intact. |  | Of the first city wall, built in the 13th century, one tower, belonging to one of the city gates, remains incorporated in a house on the Hinthamerstraat. Another remnant of the first city wall is formed by a gate over one of the arms of the Binnendieze River near the Korte Waterstraat. Sizable sections of the second, 13th-century city walls, and 17th- and 18th-century bastions remain intact as they serve as flood prevention measures. Of special note is the 17th-century pentagonal citadel. |
| Aardenburg | Zeeland | | Vestiges of the fortifications are visible in the landscape. |  | In 1625 AD, a new trace of earthen ramparts was built. These defenses were demolished between 1688 and 1701 AD. One city gate, the Westpoort, survives. Additionally, remnants of bastions, ravelins, and other outworks are clearly distinguishable in the fields surrounding the town. The foundations of a Roman gatehouse with 2 towers can be found at the Burchtstraat. The foundations of a Roman tower are now incorporated in the playground of a local school. |
| Amersfoort | Utrecht | Yes | Sizable parts of the fortifications remain intact. |  | Of the first 13th-century city wall, one tower and the barbican of one gate, the Kamperbinnenpoort, remain. After the enlargement of the city in 1450 AD, houses were built on the location of the first wall, and occasionally incorporating fragments of that wall in their structure. Of the 15th-century wall, several stretches remain to the north-east of the old town, while the foundations of the wall have been made visible on the south-eastern side. Two 15th-century gates remain as well; the koppelpoort, a combined land and water gate, and the Monnickendam, a water gate. |
| Amsterdam | North Holland | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | Of the medieval walls, the Sint Antoniuspoort is the most important remnant. Other remnants of the same wall are the Schreierstoren and the lower part of one of the towers of the former Regulierspoort. Of the later Baroque defenses, only the Muiderpoort remains intact, while some of the bastions can still be recognizable in the bendy course of the outer moat that still surrounds the old town. The most recent defensive structure around the city is the Stelling van Amsterdam, a 135 km long ring of fortifications around Amsterdam, consisting of 42 forts and other works. |
| Arnhem | Gelderland | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | Only the 14th-century Sabelspoort remains. |
| Asperen | Gelderland | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | On the side of the Linge River, a stone wall, incorporating the bases of several towers, remains. The water gate, giving access to the old harbor, is partially reconstructed. On the land side, parts of earthen ramparts and moats remain. |
| Bad Nieuweschans | Groningen | | Vestiges of the fortifications are visible in the landscape. |  | The walls of the tiny fortified village have been partially demolished, although a small section remains. |
| Bergen op Zoom | North Brabant | Yes | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | Of the medieval fortifications, only the 14th-century Gevangenpoort remains. Of the extensive 17th-century fortifications, only one single ravelin remains. |
| Bolsward | Friesland | Yes | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | A moat still encloses the town center. |
| Bourtange | Groningen | Yes | The fortifications were recently reconstructed. |  | The original fortifications were demolished in the 19th century, but have been reconstructed from 1960 onwards, in a successful effort to revitalize the village. |
| Breda | North Brabant | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | The only notable remnant of the city walls is the Spanjaardsgat gate; a water gate defended by two multiangular towers. It forms part of the defenses around Breda Castle, which in turn formed an integral part of the city walls. |
| Bredevoort | Gelderland | Yes | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | Part of the ramparts, located on the north-east of the town, have been reshaped into a park. To the south-west, a windmill stands on top of a remnant of one of the bastions. |
| Brielle | South Holland | Yes | The city wall remains intact. |  | The old town is completely enclosed by earth ramparts, featuring nine bastions, as well as multiple outer works. |
| Brouwershaven | Zeeland | Yes | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | Part of the ramparts, located on the east and north of the town, remain intact. |
| Buren | Gelderland | Yes | Sizable parts of the fortifications remain intact. |  | On the east side of town, facing the river, an impressive wall remains. On the north-west side of the town, a city gate remains, flanked by a row of houses built against the old town wall. |
| Culemborg | Gelderland | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | The old town, its medieval extensions, and the site of the old castle, are still surrounded by a moat. Of the oldest, the 14th-century city wall, one city gate remains, while several fragments of the city wall stand on the south and east sides of the old town. |
| Delft | South Holland | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | The old town is for the most part still surrounded by a moat. Along this moat stand two towers belonging to the medieval wall. On the eastern end of the old town stands the Oostpoort, a 15th-century combined land and water gate. |
| Doesburg | Gelderland | Yes | Sizable parts of the fortifications remain intact. | | The fortifications around the old city have been demolished, but the advanced line of defenses to the east of the city remains intact as part of a nature reserve. |
| Dokkum | Friesland | Yes | The city wall remains intact. |  | The old city is completely enclosed by a line of earth ramparts, featuring five bastions. |
| Dordrecht | South Holland | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | The old city is completely enclosed by a moat, while the old harbor is guarded by the Groothoofdspoort, a late medieval city gate, later rebuilt in a Renaissance style. |
| Elburg | Gelderland | Yes | Sizable parts of the fortifications remain intact. |  | The old city is completely enclosed by a moat and a 16th-century rectangular earthen rampart with a bastion at each corner. The rampart was changed into a park in the 19th century, but the defenses are still easily recognizable. Several of the old gates were defended by a barbican, the lower parts of which have been excavated and the casemates of one of the barbicans can be visited. Several sections of the medieval city wall still stand behind the 16th-century rampart. One tower of the medieval wall had been changed into a gate in the 16th century. This structure forms the last remaining city gate of the old town. |
| Enkhuizen | North Holland | Yes | Sizable parts of the fortifications remain intact. |  | The landward side of the old town is still completely surrounded by an earthen rampart with five bastions. The last remaining gate facing the landward side of the city is the 17th-century Koepoort. The most impressive remnant of the fortifications is the 16th-century 'Drommedaris' gate, which stands near the harbor. |
| Franeker | Friesland | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | The old city is completely enclosed by a moat. The locations of the old bastions and bulwarks are still recognizable in the shape of the moat. |
| Gennep | Limburg | | Sizable parts of the fortifications remain intact. |  | Lowered remnants of the old city walls surround the west and north sides of the old town. |
| Geertruidenberg | North Brabant | Yes | Sizable parts of the fortifications remain intact. |  | Most of the fortifications were demolished, but restored sections of the bastioned trace remains to the north and east sides of the old town. |
| Goes | Zeeland | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | The old city is completely enclosed by a moat. The locations of the old bastions and bulwarks are still recognizable in the shape of the moat. |
| Gorinchem | South Holland | Yes | The city wall remains intact. |  | The old city is completely enclosed by an intact city wall. To the west of the city, the bastioned trace was demolished in order to accommodate the construction of a canal. The defences on that side were subsequently replaced by a Caponier. |
| Gouda | South Holland | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | The old city is completely enclosed by a moat. The remains of a town gate are located near a street named Bogen, meaning 'Arcs', named after the arcs built in the medieval town wall which its trace once ran alongside the Turfsingel side of the street. A part of the town wall is located at the corner Oosthaven with Nieuwe Veerstal. This part of the walls itself once was a part of Gouda castle. Other remains of the castle include subterraneans, cellars and fundaments of walls and towers located in the Houtmanplantsoen, behind the nearby windmill. The lower part of this windmill is a remnant of one of the castle's towers. |
| Grave | North Brabant | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | Fragments of the double system of moats remain, as well as one city gate. The lower portions of several round medieval towers can be seen at the old harbor. The water gate, leading down to the river Maas, is a recent reconstruction. |
| Groenlo | Gelderland | Yes | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | The old town is partially surrounded by an old moat, which clearly shows the locations of the old bastions. Part of the bastion trace has been reconstructed. |
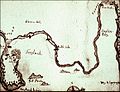
| Groningen | Groningen | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. | 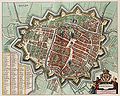 | The old town is surrounded by a moat. |
| Haarlem | North Holland | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | The old city centre is still partially surrounded by a moat. To the north of the city, the moat clearly shows the locations of the old bastions, which have been changed into a park. One city gate remains; the 14th-century Amsterdamse Poort. |
| Hardenberg | Overijssel | | Vestiges. | | The only remnant of the medieval town walls is a small lower part of a wall at the western end of the Wilhelminaplein, next to an old water pump. |
| Harderwijk | Gelderland | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | Several sections of the old medieval wall remains, the most sizable parts being located to the north of the old city, facing the former Zuiderzee. Two gates, the Vischpoort and the Smeepoort, still remain. The Vischpoort has a lighthouse installed on the roof. |
| Harlingen | Friesland | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. | | Several sections of the moat, indicating the presence of three of the old bastions, remain on the east side of the city. |
| Hasselt | Overijssel | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. | | On the landside of the city, remnants of the ramparts, featuring four sizable bastions, remain incorporated in a park. |
| Hattem | Gelderland | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | On the landside of the old town center some remnants of the city walls remain. On the side of the old town facing the river IJssel, the Dijkpoort can be found. |
| Hellevoetsluis | South Holland | Yes | The city wall remains intact. |  | The old navy harbor is still entirely surrounded by a bastion trace, which is outfitted with a brick revetment on the side of the walls facing the river. |
| Heukelum | Gelderland | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. | | The town is still enclosed by a moat on the three sides facing away from the river Linge. |
| Heusden | North Brabant | | The fortifications were recently reconstructed. |  | The city walls had been slighted in the 19th century, but have been extensively reconstructed during the middle of the 20th century. |
| Hoorn | North Holland | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | The old town is still surrounded by a moat. One city gate remains, the 16th-century Oosterpoort. The most notable remnant of the city defenses, however, is the Hoofdtoren, an impressive 16th-century tower, built to defend the harbor. |
| Hulst | Zeeland | Yes | The city wall remains intact. |  | The old town is still surrounded by a rampart and a moat. Several remnants of outer works, such as ravelins and an outer wall, remain. |
| IJzendijke | Zeeland | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | Some fragments of the old moat remain. One ravelin belonging to the old fortifications has been restored |
| IJsselstein | Utrecht | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | The old moat remains, while some remnants of the town wall remain on the south and east side of the old town. |
| Kampen | Overijssel | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | The old moat remains, while the old earthen ramparts remain incorporated in a park. Three medieval city gates remain, two of which have been rebuilt in a renaissance style. The largest gate, the Kroonmarktpoort, retained its medieval appearance. |
| Klundert | North Brabant | Yes | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | Several sections of the ramparts and bastions remain intact to the north and south of the old town. |
| Leerdam | Utrecht | Yes | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | The city wall remains intact on the side of the town facing the river Linge. |
| Leeuwarden | Friesland | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | The old town is still entirely surrounded by a moat. Several bastions to the north of the old town have been changed into a park. |
| Leiden | South Holland | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | The old city is still surrounded by a moat. Of the city defenses, two city gates remain and one medieval tower stand to the south of the old town. Part of a bastion on the east side of the city has been reconstructed. |
| Maastricht | Limburg | Yes | Sizable parts of the fortifications remain intact. |  | Important parts of all major fortification systems remain intact. Of the first city wall, the Helpoort [ nl ] gate remains, as well as several important sections of the oldest 13th-century city wall. Important parts of the second medieval city wall remain on the east side of the old town, while extensive remnants of the complicated system of baroque fortifications can be found to the north. Additionally, a large network of communication tunnels, casemates, and countermines remain underneath the present outskirts of the city, which were built on top of the old city walls. |
| Megen | North Brabant | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | Only a single 14th-century tower, known as the Gevangenpoort, remains. |
| Middelburg | Zeeland | Yes | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | The bastioned trace of the city wall has been changed into a park and is still surrounded by a moat. Only one city gate remains, the 18th-century Koepoort. |
| Montfoort | Utrecht | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | One of the medieval city gates has been incorporated into the town hall. Another remaining portion of the town wall remains to the south west of the old town. |
| Muiden | North Holland | Yes | Sizable parts of the fortifications remain intact. |  | The 16th-century town walls were greatly adapted in the 19th century, when the town became part of the advanced defenses of Amsterdam. The city walls located to the west of the river Vecht remain intact, as do the walls around the Muiderslot castle. |
| Naarden | North Holland | Yes | The city wall remains intact. |  | Naarden is one of the best preserved fortified cities in Europe, featuring a double system of moats and walls, built in the 17th century. The inner wall features numerous tunnels, casemates, and barracks. |
| Nieuwpoort, South Holland | South Holland | Yes | The city wall remains intact. |  | The tiny town is entirely surrounded by an earth rampart featuring six bastions and a false bray in front of the curtain walls. The town hall is built over a canal running through the center of town and defends a system of locks with which the land surrounding the fortress could be inundated. |
| Nijmegen | Gelderland | | Sizable parts of the fortifications remain intact. |  | Sizable parts of the medieval city walls remain to the west and east of the old city. The most notable remnant is the wall, and three towers, located in the Kronenburger park. Of the three towers, the Kronenburger tower is arguable one of the most impressive medieval towers in the Netherlands. |
| Ootmarsum | Overijssel | | Vestiges. | | The old town is still fully enclosed bij two ringroads, called the Westwal (Western wall) and the Oostwal (Eastern wall), indicating the trace of the medieval walls. |
| Oudeschans | Groningen | Yes | Sizable parts of the fortifications remain intact. |  | The walls of the tiny fortified village have been partially demolished, but remain very recognizable. Part of the city walls have subsequently been reconstructed in the 20th century. |
| Oudewater | Utrecht | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. | 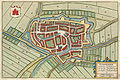 | The old city is enclosed by a moat. The locations of some of the old bastions and bulwarks are still recognizable in the shape of the moat. |
| Philippine, Netherlands | Zeeland | | Vestiges of the fortifications are visible in the landscape. |  | Remnants of bastions, ravelins, and other outworks are clearly distinguishable in the fields surrounding the town. |
| Ravenstein | North Brabant | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | A moat surrounds much of the old town, clearly showing the location of bastions and ravelins. The remnants of two hornworks are visible to the north and south of the old town. The side of the town facing the river Maas features the remnants of two bastions, excavated from the body of the dyke, as well as the single remaining city gate. |
| Retranchement | Zeeland | Yes | The city wall remains intact. | 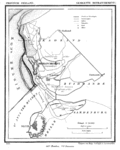 | Retranchement was built in 1604 AD as an entrenched camp, consisting of two small, square forts, connected by a wall with three bastions. The northern fort no longer exists as it was destroyed in a flood in 1682 AD. |
| Rhenen | Utrecht | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | Lowered fragments of the 14th-century city wall can be found to the south of the old town. To the north, a windmill stands on top of a remnant of the wall. On the eastern entrance of the old town, the remnants of a sizable barracane can be found. |
| Roermond | Limburg | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | Several fragments of the medieval city wall remain. The most notable and best preserved remnant is the Rattentoren, a 14th-century round tower standing on the north side of the old town. |
| Sas van Gent | Zeeland | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | Of the once powerful and strategic fortress, very little remains. Most of the fortifications were demolished in 1930. What remains are the remnants of one bastion, upon which the base of an old windmill stands, and the remnants of an old late 17th-century tidal mill, which was built into the fortifications. |
| Schiedam | South Holland | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. | | Parts of the moat remain, including the northern and western part. The famous Schiedam windmills are built on top of the bases of wall towers. |
| Schoonhoven | South Holland | Yes | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | Only a fragment of the old moat remains on the landward side of the town. On the riverside stands the Waterpoort, the last remaining city gate, with some adjacent stretches of the old town walls. |
| Sittard | Limburg | Yes | Sizable parts of the fortifications remain intact. |  | The powerful fortress town was destroyed by French forces in 1677 AD. Sizable remnants of the medieval city wall remain, buried underneath a later earthen rampart which still surrounds most of the old town. |
| Sluis | Zeeland | Yes | The city wall remains intact. |  | The old town of Sluis was completely destroyed in the second world war, but the extensive fortification system remained intact and can still be visited today. |
| Sloten | Zeeland | Yes | Sizable parts of the fortifications remain intact. |  | The tiny fortress town of Sloten is still mostly surrounded by its ramparts, while the moat still completely encircles the town. Two water gates remain intact at the places where an old canal dissects the town. |
| Steenbergen | North Brabant | | Vestiges of the fortifications are visible in the landscape. |  | Some fragments of the old moat remain. The locations of the old bastions can be recognized by the course of the moat and the street pattern. Remnants of the outer works are distinguishable in the surrounding landscape. |
| Steenwijk | Overijssel | Yes | Sizable parts of the fortifications remain intact. |  | Sizable parts of the moats and ramparts remain. |
| Stevensweert | Limburg | | Vestiges of the fortifications are visible in the landscape. |  | Although the walls themselves have been demolished, the town was built as an ideal fortress, and features the characteristic spider web street pattern that many such towns were built with. Part of the city walls have been reconstructed from 2007 AD onwards. |
| Tholen | Zeeland | Yes | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | The ramparts were changed into a park, but the moat is still present and four bastions are still recognizable. |
| Tiel | Gelderland | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | Fragments of the moat remain, as well as one city gate. |
| Utrecht | Utrecht | Yes | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | The medieval city wall has been completely demolished. Remnants of three of the 16th-century Italian style bastions remain. The most complete bastion is Sonnenborgh. Most of the old city fortifications were changed into an English style landscape park in the 19th century. The Dutch Water Line forms a double ring of fortresses where it passes east of the city. |
| Valkenburg aan de Geul | Limburg | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | Two city gates remain at the foot of the ruined castle. Part of the city wall remains to the west side of the old town. The small Den Halder castle was built around an old tower of the city wall. |
| Veere | Zeeland | Yes | Sizable parts of the fortifications remain intact. |  | The Campveerse toren is a large medieval tower that still guards the entrance to the old harbor today. The later earth ramparts remain mostly intact, especially the enlargements built by order of Napoleon |
| Venlo | Limburg | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | Nearly nothing remains of the once extensive fortifications of Venlo. The most extensive remnant being a stretch of 14th-century wall known as the "Luif" |
| Vianen | Utrecht | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | The Lekpoort is the last remaining city gate of the little town of Vianen. Apart from the gate, a large part of the town is still enclosed by a moat, while a sizable length of (lowered) city wall still stands on the south side of the town. |
| Vlissingen | Zeeland | Yes | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | Several remnants of bastions, curtain walls and a tower of a medieval city gate, still stand on the waterside. The landward facing defenses have all been demolished. |
| Wageningen | Gelderland | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | The foundations of a small stretch of the medieval city wall have been unearthed and restored. Of the later ramparts, the moat remains, its trace clearly showing the locations of the old bastions. |
| Weesp | North Holland | Yes | The city wall remains intact. |  | Only four of the planned eight bastions were constructed. All four remain intact and surrounded by a moat. In the 19th century, a circular fort was constructed on an island in the river Vecht. |
| Willemstad | North Brabant | Yes | The city wall remains intact. |  | In 1583 AD, prince William of Orange orders the construction of a fortified city on the location of the village of Ruigenhil. The city, called Willemstad, is still entirely surrounded by its seven sided city wall. |
| Wijk bij Duurstede | Utrecht | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | A portion of the moat remains, as do several fragments of the city wall facing the riverside. One city gate still stands as a windmill has been built on top of it. The ramparts that surround the ruins of Duurstede castle have been reshaped into a landscape style park. |
| Woerden | Utrecht | Yes | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | Sizable sections of the inner and outer moats still remain and several of the bastions are still recognizable as such. The medieval castle still stands on the south eastern side of the old town. |
| Woudrichem | North Brabant | Yes | The city wall remains intact. |  | The city received a set of strong ramparts with seven bastions in 1580 AD. Only one of the gates, the Gevangenpoort, now remains |
| Zaltbommel | Gelderland | Yes | Sizable parts of the fortifications remain intact. |  | The earthen ramparts and its bastions were made into an English landscape park in the 19th century, but the structures remain intact up to a significant height and are easily recognizable. The outer moat still encloses the landward side of the city. Behind the earthen ramparts stand several sizable fragments of the medieval city wall. |
| Zierikzee | Zeeland | Yes | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | A moat still surrounds the old town. While the walls have been demolished, three medieval gates remain. Of these gates, the ensemble of the Noordhavenpoort and Zuidhavenpoort, which guard the entrance to the old harbor, form one of the most impressive remaining medieval defensive structures in the Netherlands |
| Zutphen | Gelderland | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | Remnants of moats from the medieval and post-medieval fortifications are still visible around the old town. The remnants of the medieval fortifications include several towers, the impressive Drogenapstoren gate, the Bourgonjetoren bastion, a water gate named Berkel gate, and a sizable stretch of the old city wall to the south of the old town. |
| Zwolle | Overijssel | | One or more individual structures (Bastions, gates, towers, etc.) remain. |  | The moat, still clearly showing the remnants of the old bastions, still encloses the old town. The Sassenpoort is the sole remaining city gate, but is one of the largest and most impressive gates of the Netherlands. A number of fragments of the medieval city wall, including two strong towers, still stand along the waterside of the Thorbeckegracht |