Related Research Articles

Hindi cinema, popularly known as Bollywood and formerly as Bombay cinema, is the Indian Hindi-language film industry based in Mumbai. The popular term Bollywood, used to refer to mainstream Hindi cinema, is a portmanteau of "Bombay" and "Hollywood". The industry is part of the larger Indian cinema—the world's largest by number of feature films produced, along with the Cinema of South India and other Indian film industries.

The Cleveland Guardians are an American professional baseball team based in Cleveland. The Guardians compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the American League (AL) Central division. Since 1994, they have played at Progressive Field. Since their establishment as a Major League franchise in 1901, the team has won 10 Central division titles, six American League pennants, and two World Series championships,. The team's World Series championship drought since 1948 is the longest active among all 30 current Major League teams. The team's name references the Guardians of Traffic, eight monolithic 1932 Art Deco sculptures by Henry Hering on the city's Hope Memorial Bridge, which is adjacent to Progressive Field. The team's mascot is named "Slider." The team's spring training facility is at Goodyear Ballpark in Goodyear, Arizona.

India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar and Indonesia.
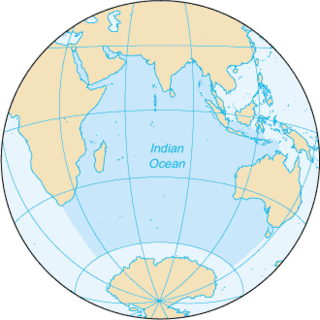
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering 70,560,000 km2 (27,240,000 sq mi) or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by the Southern Ocean or Antarctica, depending on the definition in use. Along its core, the Indian Ocean has some large marginal or regional seas such as the Arabian Sea, the Laccadive Sea, the Somali Sea, Bay of Bengal, and the Andaman Sea.

Jawaharlal Nehru was an Indian anti-colonial nationalist, secular humanist, social democrat and author who was a central figure in India during the middle of the 20th century. Nehru was a principal leader of the Indian nationalist movement in the 1930s and 1940s. Upon India's independence in 1947, he served as the country's prime minister for 17 years. Nehru promoted parliamentary democracy, secularism, and science and technology during the 1950s, powerfully influencing India's arc as a modern nation. In international affairs, he steered India clear of the two blocs of the Cold War. A well-regarded author, his books written in prison, such as Letters from a Father to His Daughter (1929), An Autobiography (1936) and The Discovery of India (1946), have been read around the world.

Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi was an Indian lawyer, anti-colonial nationalist and political ethicist who employed nonviolent resistance to lead the successful campaign for India's independence from British rule, and to later inspire movements for civil rights and freedom across the world. The honorific Mahātmā, first applied to him in 1914 in South Africa, is now used throughout the world.

Native Americans, also known as First Americans, Indigenous Americans, American Indians, and other terms, are the Indigenous peoples of the United States, including Hawaii and territories of the United States, and other times limited to the mainland. There are 574 federally recognized tribes living within the US, about half of which are associated with Indian reservations. "Native Americans" are Indigenous tribes that are originally from the contiguous United States, along with Alaska Natives.

The Bharatiya Janata Party is one of two major political parties in India, along with the Indian National Congress. It has been the ruling political party of the Republic of India since 2014 under its prime minister, Narendra Modi. The BJP is a right-wing party, and its policy has historically reflected Hindu nationalist positions. It has close ideological and organisational links to the much older Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh (RSS). As of 17 February 2022, it is the country's largest political party in terms of representation in the national parliament and state legislatures.

The Indian National Congress (INC), colloquially the Congress Party but often simply the Congress, is a political party in India with widespread roots. Founded in 1885, it was the first modern nationalist movement to emerge in the British Empire in Asia and Africa. From the late 19th century, and especially after 1920, under the leadership of Mahatma Gandhi, the Congress became the principal leader of the Indian independence movement. The Congress led India to independence from the United Kingdom, and powerfully influenced other anti-colonial nationalist movements in the British Empire. Due to its enduring history, the Congress is often called the "grand old party".

The Indian independence movement was a series of historic events with the ultimate aim of ending British rule in India. It lasted from 1857 to 1947.

The partition of India in 1947 divided British India into two independent dominions: India and Pakistan. The Dominion of India is today the Republic of India, and the Dominion of Pakistan is the Islamic Republic of Pakistan and the People's Republic of Bangladesh. The partition involved the division of two provinces, Bengal and Punjab, based on district-wide non-Muslim or Muslim majorities. The partition also saw the division of the British Indian Army, the Royal Indian Navy, the Royal Indian Air Force, the Indian Civil Service, the railways, and the central treasury. The partition was outlined in the Indian Independence Act 1947 and resulted in the dissolution of the British Raj, i.e. Crown rule in India. The two self-governing independent Dominions of India and Pakistan legally came into existence at midnight on 15 August 1947.

The Indian Army is the land-based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Army, and its professional head is the Chief of Army Staff (COAS), who is a four-star general. Two officers have been conferred with the rank of field marshal, a five-star rank, which is a ceremonial position of great honour. The Indian Army originated from the armies of the East India Company, which eventually became the British Indian Army, and the armies of the princely states, which were merged into the national army after independence. The units and regiments of the Indian Army have diverse histories and have participated in several battles and campaigns around the world, earning many battle and theatre honours before and after Independence.

The Indian Air Force (IAF) is the air arm of the Indian Armed Forces. Its complement of personnel and aircraft assets ranks third amongst the air forces of the world. Its primary mission is to secure Indian airspace and to conduct aerial warfare during armed conflict. It was officially established on 8 October 1932 as an auxiliary air force of the British Empire which honoured India's aviation service during World War II with the prefix Royal. After India gained independence from United Kingdom in 1947, the name Royal Indian Air Force was kept and served in the name of Dominion of India. With the government's transition to a Republic in 1950, the prefix Royal was removed.

The Indian Rebellion of 1857 was a major uprising in India in 1857–58 against the rule of the British East India Company, which functioned as a sovereign power on behalf of the British Crown. The rebellion began on 10 May 1857 in the form of a mutiny of sepoys of the Company's army in the garrison town of Meerut, 40 mi (64 km) northeast of Delhi. It then erupted into other mutinies and civilian rebellions chiefly in the upper Gangetic plain and central India, though incidents of revolt also occurred farther north and east. The rebellion posed a considerable threat to British power in that region, and was contained only with the rebels' defeat in Gwalior on 20 June 1858. On 1 November 1858, the British granted amnesty to all rebels not involved in murder, though they did not declare the hostilities to have formally ended until 8 July 1859. Its name is contested, and it is variously described as the Sepoy Mutiny, the Indian Mutiny, the Great Rebellion, the Revolt of 1857, the Indian Insurrection, and the First War of Independence.

The Indian Navy is the naval branch of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Navy. The Chief of Naval Staff, a four-star admiral, commands the navy. As a blue-water navy, it operates significantly in Persian Gulf Region and the Horn of Africa to the Strait of Malacca, and routinely conducts anti-piracy operations and partners with other navies in the region. It also conducts routine two to three month-long deployments in the South and East China seas as well as the western Mediterranean sea simultaneously.

An Indian reservation is an area of land held and governed by a federally recognized Native American tribal nation whose government is accountable to the U.S. Bureau of Indian Affairs and not to the state government in which it is located. Some of the country's 574 federally recognized tribes govern more than one of the 326 Indian reservations in the United States, while some share reservations, and others have no reservation at all. Historical piecemeal land allocations under the Dawes Act facilitated sales to non–Native Americans, resulting in some reservations becoming severely fragmented, with pieces of tribal and privately held land being treated as separate enclaves. This jumble of private and public real estate creates significant administrative, political and legal difficulties.
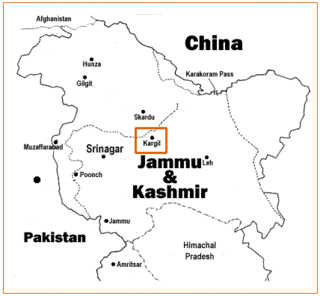
The Kargil War, also known as the Kargil conflict, was an armed conflict fought between India and Pakistan from May to July 1999 in the Kargil district of Jammu and Kashmir and elsewhere along the Line of Control (LoC). In India, the conflict is also referred to as Operation Vijay, which was the name of the Indian military operation to clear out the Kargil sector. The Indian Air Force's role in acting jointly with Indian Army ground troops during the war was aimed at flushing out regular and irregular troops of the Pakistan Army from vacated Indian positions along the LoC. This particular operation was given the codename Operation Safed Sagar.

The British Raj was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent; it is also called Crown rule in India, or Direct rule in India, and lasted from 1858 to 1947. The region under British control was commonly called India in contemporaneous usage and included areas directly administered by the United Kingdom, which were collectively called British India, and areas ruled by indigenous rulers, but under British paramountcy, called the princely states. The region was sometimes called the Indian Empire, though not officially.

Indians are the citizens and nationals of the Republic of India. According to the 2011 Indian national census, the population of India stood at over 1.2 billion people, making it the world's second-most populous country that contains 17.50 percent of the global population. In India, the term "Indian" refers to nationality, rather than a particular ethnicity or language; the Indian nationality consists of dozens of regional ethnolinguistic groups, reflecting the population's rich and complex history. The Indian diaspora is significantly large and present throughout the world, notably in other parts of Asia as well as in North America, Europe, the Caribbean, Oceania, and Africa. The demonym Indian applies to nationals of the present-day Republic of India; however, before the partition of India in 1947, the demonym applied to all people residing in the entirety of British India, which included what is now Pakistan and Bangladesh.

The Indian subcontinent, or simply the subcontinent, is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka. The terms Indian subcontinent and South Asia are often used interchangeably to denote the region, although the geopolitical term of South Asia frequently includes Afghanistan, which may otherwise be classified as Central Asian.
References
- ↑ Dharwadker, Vinay; Ramanujan, A. K. (1994). The Oxford Anthology of Modern Indian Poetry . OUP. p. 249. ISBN 978-0-19-562865-4.