
A figurehead is a carved wooden decoration found at the bow of ships, generally of a design related to the name or role of a ship. They were predominant between the 16th and 20th centuries, and modern ships' badges fulfil a similar role.
The phrase "power behind the throne" refers to a person or group that informally exercises the real power of a high-ranking office, such as a head of state. In politics, it most commonly refers to a relative, aide, or nominal subordinate of a political leader who serves as de facto leader, setting policy through possessing great influence and/or skillful manipulation.

New Georgia, with an area of 2,037 km2 (786 sq mi), is the largest of the islands in Western Province, Solomon Islands, and the 224th-largest island in the world.
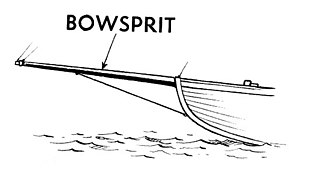
The bowsprit of a sailing vessel is a spar extending forward from the vessel's prow. The bowsprit is typically held down by a bobstay that counteracts the forces from the forestays. The word bowsprit is thought to originate from the Middle Low German word bōchsprēt – bōch meaning "bow" and sprēt meaning "pole".

The KNVB Beker, branded as the TOTO KNVB Beker for sponsorship reasons, is a competition in the Netherlands organized by the Royal Dutch Football Association (KNVB) since 1898. It was based on the format of the English FA Cup. Outside the Netherlands, it is often referred to as the Dutch Cup. The tournament consists of all teams from the top four tiers of Dutch league football, as well as the 24 semi-finalists of the six KNVB District Cups. The finals of the tournament traditionally takes place in De Kuip, and has been held there every season since the 1989 final. The winners of the cup compete against the winners of the Eredivisie for the Johan Cruyff Shield, which acts as the curtain raiser for the following season.

Waka are Māori watercraft, usually canoes ranging in size from small, unornamented canoes used for fishing and river travel to large, decorated war canoes up to 40 metres (130 ft) long.

A carranca is a type of figurehead attached to river craft which is attributed with power to protect the boatmen from the river's evil spirits. The culture in Brazil incorporated elements of the indigenous culture, so that the idea of river spirits and forest spirits can help or hinder a crossing is also natural of the Amerindian imaginary. They were once commonly found on the lower Rio São Francisco in Brazil's Northeast Region (Nordeste). The carranca is most commonly a figure of a human or an animal. They were used to identify traders operating on the São Francisco and, as with ancient figureheads, serve the superstitious as guardians on the river.

Underboss is a position within the leadership structure of certain organized crime groups, particularly in Sicilian, Greek, and Italian-American Mafia crime families. The underboss is second in command to the boss. The underboss is also person-in-charge of all capos and its soldiers. The underboss is sometimes a family member, such as a son, who will take over the family if the boss is sick, killed, or imprisoned. However the position of street boss has somewhat challenged the rank of underboss in the modern era. The position was installed within the Genovese crime family since at least the mid-1960s. It has also been used in the Detroit crime family and the Chicago Outfit.

A Duluth pack, is a traditional portage pack used in canoe travel, particularly in the Boundary Waters region of northern Minnesota and the Quetico Provincial Park of Ontario. It is a specialized type of backpack that is designed to fit in the bottom of canoes. Originally known as the "Poirier pack" or "Poirier pack-sack", the pack style later became known as the "Duluth pack", as its original, eponymous manufacturing company is located in Duluth, Minnesota.
The ISU Grand Prix of Figure Skating is a series of senior international figure skating competitions organized by the International Skating Union. The invitational series was inaugurated in 1995, incorporating several previously existing events. Medals are awarded in the disciplines of men's singles, ladies' singles, pair skating, and ice dancing. The junior-level equivalent is the ISU Junior Grand Prix.
A figure skating competition is a judged sports competition in figure skating.
The 1999 European Figure Skating Championships were an international figure skating competition in the 1998–99 season. Elite senior-level figure skaters from European ISU member nations competed for the title of European Champion. Skaters competed in the disciplines of men's singles, ladies' singles, pair skating, and ice dancing. The corresponding competition for non-European skaters was the 1999 Four Continents Figure Skating Championships.
Eddalands is an entire local government area in Ebonyi State, Nigeria. It is the most homogeneous LGA in Nigeria with people of one language, one culture and one tradition across the entire LGA.
The Grand Prix International St. Gervais was an annual senior-level international figure skating competition held in Saint-Gervais-les-Bains, France. For many years, beginning in 1969, it was paired with a similar competition in Germany, the Nebelhorn Trophy, to form a series called the Coupe des Alpes. Sometimes the "Coupe des Alpes" name was applied to the French event only, but in fact it was a team trophy awarded based on combined results of both competitions. The official name of the competition was unrelated to and predated the use of "Grand Prix" in the ISU Grand Prix of Figure Skating.

Toto and Marcellino is a 1958 Italian-French comedy film directed by Antonio Musu.

Camakau are a traditional watercraft of Fiji. Part of the broader Austronesian tradition, they are similar to catamarans, outrigger canoes, or smaller versions of the drua, but are larger than a takia. These vessels were built primarily for the purposes of travelling between islands and for trade. These canoes are single hulled, with an outrigger and a cama, a float, with both ends of the hull being symmetrical. They were very large, capable of travelling open ocean, and have been recorded as being up to 70 ft in length.
The 1986–87 Toto Cup Leumit was the third season of the third most important football tournament in Israel since its introduction.

Geriten, or "head-house", is the skull-house of the Karo people of North Sumatra, Indonesia. It is a pavilion-like structure with a distinctively shaped roof that acted as an ossuary where skulls of chiefs and important individuals are preserved after their deaths.

A canoe pack, also known as a portage pack, is a specialized type of backpack used primarily where travel is largely by water punctuated by portages where the gear needs to be carried over land.

Tomako or tomoko is a large war canoe from the Solomon Islands. The name "tomako" is used in New Georgia in the Roviana language. It is also known as magoru in Marovo, niabara in Vella Lavella, mon in Bougainville, ora in Makira, and iola or ola in Malaita and Ulawa. Tomako were narrow and usually between 12 and 18 m in length. They did not possess outriggers or sails and were propelled solely by paddling. They were built by fitting planks edge-to-edge which are then "sewn" together and caulked with a paste made from the nut of the tree Parinarium laurinum. They could carry 30 to 50 warriors, and were used in raiding expeditions for slaves or for headhunting. They were characteristically crescent-shaped, with sharply upturned prows and sterns that were decorated with fringes of cowrie shells, nautilus shells, and mother-of-pearl, as well as intricate carvings. These carvings are usually of spirit animals or warriors like the kesoko and Tiolo. The body is commonly blackened to contrast with the decorations.













