
Eglin Air Force Base (AFB) is a United States Air Force base in the western Florida Panhandle, located about three miles (5 km) southwest of Valparaiso in Okaloosa County.
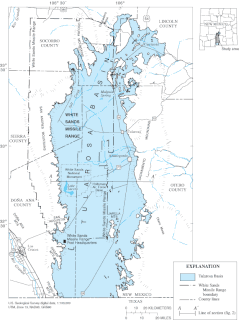
White Sands Missile Range (WSMR) is a military testing area operated by the United States Army. The range was originally established as the White Sands Proving Ground on 9 July 1945. White Sands National Park is located within the range.

Hurlburt Field is a United States Air Force installation located in Okaloosa County, Florida, immediately west of the town of Mary Esther. It is part of the greater Eglin Air Force Base reservation and is home to Headquarters Air Force Special Operations Command (AFSOC), the 1st Special Operations Wing (1 SOW), the USAF Special Operations School (USAFSOS) and the Air Combat Command's (ACC) 505th Command and Control Wing. It was named for First Lieutenant Donald Wilson Hurlburt, who died in a crash at Eglin. The installation is nearly 6,700 acres (27 km2) and employs nearly 8,000 military personnel.

Holloman Air Force Base is a United States Air Force base established in 1942 located six miles (10 km) southwest of the central business district of Alamogordo, and a census-designated place in Otero County, New Mexico, United States. The base was named in honor of Col. George V. Holloman, a pioneer in guided missile research. It is the home of the 49th Wing of the Air Education and Training Command (AETC).

Crossbow was the code name in World War II for Anglo-American operations against the German long range reprisal weapons (V-weapons) programme. The main V-weapons were the V-1 flying bomb and V-2 rocket – these were launched against Britain from 1944 to 1945 and used against continental European targets as well.

Wendover Air Force Base is a former United States Air Force base in Utah now known as Wendover Airport. During World War II, it was a training base for B-17 and B-24 bomber crews. It was the training site of the 509th Composite Group, the B-29 unit that carried out the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.

Duke Field, also known as Eglin AFB Auxiliary Field #3, is a military airport located three miles (5 km) south of the central business district of Crestview, in Okaloosa County, Florida, United States.

The Blockhaus d'Éperlecques is a Second World War bunker, now part of a museum, near Saint-Omer in the northern Pas-de-Calais département of France, and only some 14.4 kilometers north-northwest from the more developed La Coupole V-2 launch facility, in the same general area.

The McKinley Climatic Laboratory is both an active laboratory and a historic site located in Building 440 on Eglin Air Force Base, Florida. The laboratory is part of the 96th Test Wing. In addition to Air Force testing, it can be used by other US government agencies and private industry.

Duxford Aerodrome is located 8 nautical miles south of Cambridge, within the Parish of Duxford, Cambridgeshire, England and nearly 1-mile (1.6 km) west of the village.

The Republic-Ford JB-2, also known as the Thunderbug, KGW and LTV-N-2 Loon, was a United States copy of the German V-1 flying bomb. Developed in 1944, and planned to be used in the United States invasion of Japan, the JB-2 was never used in combat. It was the most successful of the United States Army Air Forces Jet Bomb (JB) projects during World War II. Postwar, the JB-2 played a significant role in the development of more advanced surface-to-surface tactical missile systems such as the MGM-1 Matador and later MGM-13 Mace.

To carry out the planned V-1 "flying bomb" attacks on the United Kingdom, Germany built a number of military installations including launching sites and depots. Some of the installations were huge concrete fortifications.

The Siracourt V-1 bunker is a Second World War bunker built in 1943–44 by the forces of Nazi Germany at Siracourt, a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in the Nord-Pas-de-Calais region of France. Codenamed Wasserwerk St. Pol, it was intended for use as a bomb-proof storage facility and launch site for V-1 flying bombs. However it never went into operation due to intensive Allied bombing that made it the most heavily attacked of all the German V-weapon sites, and also of all military targets in Europe during World War II.

Wagner Field,, is a component of Eglin Air Force Base, Florida. It is located northeast of the main base, 13.9 miles northeast of Valparaiso, Florida.
This is a partial list of accidents and incidents involving the Boeing-designed B-17 Flying Fortress. Combat losses are not included except for a very few cases denoted by singular circumstances. A few documented drone attrition cases are also included.

The 1st Experimental Guided Missiles Group is an inactive United States Air Force unit. It was last assigned to the Air Proving Ground Command and stationed at Eglin Air Force Base, Florida. It was inactivated on 22 July 1949.
Eglin Air Force Base, a United States Air Force base located southwest of Valparaiso, Florida, was established in 1935 as the Valparaiso Bombing and Gunnery Base. It is named in honor of Lieutenant Colonel Frederick I. Eglin (1891–1937), who was killed in a crash of his Northrop A-17 pursuit aircraft on a flight from Langley to Maxwell Field, Alabama.

The Santa Rosa Island Range Complex is a component of the Eglin AFB testing range, located 17.5 miles west-southwest of the main base, on Santa Rosa Island, sitting between the communities of Navarre and Okaloosa Island.

B-17G-95-DL Flying Fortress No. 44-83690 is a B-17 Flying Fortress heavy bomber located at the Museum of Aviation, Robins Air Force Base in Georgia undergoing restoration. It was built by the Douglas Aircraft Company and delivered for use on May 9, 1945. It was flown to Grissom Air Force Base for display as a museum piece in 1961, and subsequently restored.


















