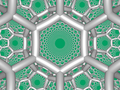
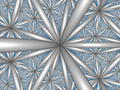
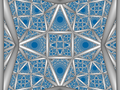
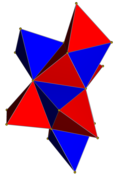
Order-4 hexagonal tiling honeycomb Perspective projection viewPoincaré disk model Type Hyperbolic regular honeycomb Paracompact uniform honeycomb Schläfli symbols {6,3,4}1,1 }0,1 {(3,6)2 } Coxeter diagrams ↔ Cells {6,3} Faces hexagon {6} Edge figure square {4} Vertex figure octahedron Dual Order-6 cubic honeycomb Coxeter groups B V ¯ 3 {\displaystyle {\overline {BV}}_{3}} D V ¯ 3 {\displaystyle {\overline {DV}}_{3}} 1,1 ]V V ^ 3 {\displaystyle {\widehat {VV}}_{3}} [2] ]Properties Regular, quasiregular
In the field of hyperbolic geometry , the order-4 hexagonal tiling honeycomb arises as one of 11 regular paracompact honeycombs in 3-dimensional hyperbolic space . It is paracompact because it has cells composed of an infinite number of faces. Each cell is a hexagonal tiling whose vertices lie on a horosphere : a flat plane in hyperbolic space that approaches a single ideal point at infinity.
A geometric honeycomb is a space-filling of polyhedral or higher-dimensional cells , so that there are no gaps. It is an example of the more general mathematical tiling or tessellation in any number of dimensions.
Honeycombs are usually constructed in ordinary Euclidean ("flat") space, like the convex uniform honeycombs . They may also be constructed in non-Euclidean spaces , such as hyperbolic uniform honeycombs . Any finite uniform polytope can be projected to its circumsphere to form a uniform honeycomb in spherical space.
The Schläfli symbol of the order-4 hexagonal tiling honeycomb is {6,3,4}. Since that of the hexagonal tiling is {6,3}, this honeycomb has four such hexagonal tilings meeting at each edge. Since the Schläfli symbol of the octahedron is {3,4}, the vertex figure of this honeycomb is an octahedron. Thus, eight hexagonal tilings meet at each vertex of this honeycomb, and the six edges meeting at each vertex lie along three orthogonal axes. [ 1]
Symmetry Subgroup relations The order-4 hexagonal tiling honeycomb has three reflective simplex symmetry constructions.
The half-symmetry uniform construction {6,31,1 } has two types (colors) of hexagonal tilings, with Coxeter diagram
An additional two reflective symmetries exist with non-simplectic fundamental domains: [6,3* ,4], which is index 6, with Coxeter diagram * ], which is index 48. The latter has a cubic fundamental domain, and an octahedral Coxeter diagram with three axial infinite branches: . It can be seen as using eight colors to color the hexagonal tilings of the honeycomb.
The order-4 hexagonal tiling honeycomb contains hypercycle surfaces and are similar to the truncated infinite-order triangular tiling ,
The order-4 hexagonal tiling honeycomb is a regular hyperbolic honeycomb in 3-space, and one of 11 which are paracompact.
11 paracompact regular honeycombs {6,3,3} {6,3,4} {6,3,5} {6,3,6} {4,4,3} {4,4,4} {3,3,6} {4,3,6} {5,3,6} {3,6,3} {3,4,4}
There are fifteen uniform honeycombs in the [6,3,4] Coxeter group family, including this regular form, and its dual , the order-6 cubic honeycomb .
[6,3,4] family honeycombs {6,3,4} r{6,3,4} t{6,3,4} rr{6,3,4} t0,3 {6,3,4} tr{6,3,4} t0,1,3 {6,3,4} t0,1,2,3 {6,3,4} {4,3,6} r{4,3,6} t{4,3,6} rr{4,3,6} 2t{4,3,6} tr{4,3,6} t0,1,3 {4,3,6} t0,1,2,3 {4,3,6}
The order-4 hexagonal tiling honeycomb has a related alternated honeycomb, triangular tiling and octahedron cells.
It is a part of sequence of regular honeycombs of the form {6,3,p}, all of which are composed of hexagonal tiling cells:
{6,3,p } honeycombs Space H3 Form Paracompact Noncompact Name {6,3,3} {6,3,4} {6,3,5} {6,3,6} {6,3,7} {6,3,8} ... {6,3,∞ } Coxeter Image Vertex {3,3} {3,4} {3,5} {3,6} {3,7} {3,8} {3,∞ }
This honeycomb is also related to the 16-cell , cubic honeycomb and order-4 dodecahedral honeycomb , all of which have octahedral vertex figures.
{p,3,4} regular honeycombs Space S3 E3 H3 Form Finite Affine Compact Paracompact Noncompact Name {3,3,4} {4,3,4} {5,3,4} {6,3,4} {7,3,4} {8,3,4} ... {∞ ,3,4} Image Cells {3,3} {4,3} {5,3} {6,3} {7,3} {8,3} {∞ ,3}
The aforementioned honeycombs are also quasiregular:
Regular and Quasiregular honeycombs: {p,3,4} and {p,31,1 } Space Euclidean 4-space Euclidean 3-space Hyperbolic 3-space Name {3,3,4}{3,31,1 } = { 3 , 3 3 } {\displaystyle \left\{3,{3 \atop 3}\right\}} {4,3,4}{4,31,1 } = { 4 , 3 3 } {\displaystyle \left\{4,{3 \atop 3}\right\}} {5,3,4}{5,31,1 } = { 5 , 3 3 } {\displaystyle \left\{5,{3 \atop 3}\right\}} {6,3,4}{6,31,1 } = { 6 , 3 3 } {\displaystyle \left\{6,{3 \atop 3}\right\}} Coxeter Image Cells
Rectified order-4 hexagonal tiling honeycomb Rectified order-4 hexagonal tiling honeycomb Type Paracompact uniform honeycomb Schläfli symbols r{6,3,4} or t1 {6,3,4} Coxeter diagrams Cells {3,4} r{6,3} Faces triangle {3}hexagon {6} Vertex figure square prism Coxeter groups B V ¯ 3 {\displaystyle {\overline {BV}}_{3}} B P ¯ 3 {\displaystyle {\overline {BP}}_{3}} [3] ]D V ¯ 3 {\displaystyle {\overline {DV}}_{3}} 1,1 ]D P ¯ 3 {\displaystyle {\overline {DP}}_{3}} []×[] ]Properties Vertex-transitive, edge-transitive
The rectified order-4 hexagonal tiling honeycomb , t1 {6,3,4}, octahedral and trihexagonal tiling facets, with a square prism vertex figure .
It is similar to the 2D hyperbolic tetraapeirogonal tiling, r{∞ ,4},
Truncated order-4 hexagonal tiling honeycomb Truncated order-4 hexagonal tiling honeycomb Type Paracompact uniform honeycomb Schläfli symbol t{6,3,4} or t0,1 {6,3,4} Coxeter diagram Cells {3,4} t{6,3} Faces triangle {3}dodecagon {12} Vertex figure square pyramid Coxeter groups B V ¯ 3 {\displaystyle {\overline {BV}}_{3}} D V ¯ 3 {\displaystyle {\overline {DV}}_{3}} 1,1 ]Properties Vertex-transitive
The truncated order-4 hexagonal tiling honeycomb , t0,1 {6,3,4}, octahedron and truncated hexagonal tiling facets, with a square pyramid vertex figure .
It is similar to the 2D hyperbolic truncated order-4 apeirogonal tiling , t{∞ ,4},
Bitruncated order-4 hexagonal tiling honeycomb Bitruncated order-4 hexagonal tiling honeycomb Type Paracompact uniform honeycomb Schläfli symbol 2t{6,3,4} or t1,2 {6,3,4} Coxeter diagram Cells t{4,3} t{3,6} Faces square {4}hexagon {6} Vertex figure digonal disphenoid Coxeter groups B V ¯ 3 {\displaystyle {\overline {BV}}_{3}} B P ¯ 3 {\displaystyle {\overline {BP}}_{3}} [3] ]D V ¯ 3 {\displaystyle {\overline {DV}}_{3}} 1,1 ]D P ¯ 3 {\displaystyle {\overline {DP}}_{3}} []×[] ]Properties Vertex-transitive
The bitruncated order-4 hexagonal tiling honeycomb , t1,2 {6,3,4}, truncated octahedron and hexagonal tiling cells, with a digonal disphenoid vertex figure .
Cantellated order-4 hexagonal tiling honeycomb Cantellated order-4 hexagonal tiling honeycomb Type Paracompact uniform honeycomb Schläfli symbol rr{6,3,4} or t0,2 {6,3,4} Coxeter diagram Cells r{3,4} {}x{4} rr{6,3} Faces triangle {3}square {4}hexagon {6} Vertex figure wedge Coxeter groups B V ¯ 3 {\displaystyle {\overline {BV}}_{3}} D V ¯ 3 {\displaystyle {\overline {DV}}_{3}} 1,1 ]Properties Vertex-transitive
The cantellated order-4 hexagonal tiling honeycomb , t0,2 {6,3,4}, cuboctahedron , cube , and rhombitrihexagonal tiling cells, with a wedge vertex figure .
Cantitruncated order-4 hexagonal tiling honeycomb Cantitruncated order-4 hexagonal tiling honeycomb Type Paracompact uniform honeycomb Schläfli symbol tr{6,3,4} or t0,1,2 {6,3,4} Coxeter diagram Cells t{3,4} {}x{4} tr{6,3} Faces square {4}hexagon {6}dodecagon {12} Vertex figure mirrored sphenoid Coxeter groups B V ¯ 3 {\displaystyle {\overline {BV}}_{3}} D V ¯ 3 {\displaystyle {\overline {DV}}_{3}} 1,1 ]Properties Vertex-transitive
The cantitruncated order-4 hexagonal tiling honeycomb , t0,1,2 {6,3,4}, truncated octahedron , cube , and truncated trihexagonal tiling cells, with a mirrored sphenoid vertex figure .
Runcinated order-4 hexagonal tiling honeycomb The runcinated order-4 hexagonal tiling honeycomb , t0,3 {6,3,4}, cube , hexagonal tiling and hexagonal prism cells, with an irregular triangular antiprism vertex figure .
It contains the 2D hyperbolic rhombitetrahexagonal tiling , rr{4,6},
Runcitruncated order-4 hexagonal tiling honeycomb The runcitruncated order-4 hexagonal tiling honeycomb , t0,1,3 {6,3,4}, rhombicuboctahedron , cube , dodecagonal prism , and truncated hexagonal tiling cells, with an isosceles-trapezoidal pyramid vertex figure .
Omnitruncated order-4 hexagonal tiling honeycomb Omnitruncated order-4 hexagonal tiling honeycomb Type Paracompact uniform honeycomb Schläfli symbol t0,1,2,3 {6,3,4} Coxeter diagram Cells tr{4,3} tr{6,3} {}x{12} {}x{8} Faces square {4}hexagon {6}octagon {8}dodecagon {12} Vertex figure tetrahedron Coxeter groups B V ¯ 3 {\displaystyle {\overline {BV}}_{3}} Properties Vertex-transitive
The omnitruncated order-4 hexagonal tiling honeycomb , t0,1,2,3 {6,3,4}, truncated cuboctahedron , truncated trihexagonal tiling , dodecagonal prism , and octagonal prism cells, with an irregular tetrahedron vertex figure .

 ↔
↔