The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to geophysics:
Contents
- Nature of geophysics
- Branches of geophysics
- History of geophysics
- General geophysics concepts
- Gravity
- Heat flow
- Electricity
- Electromagnetic waves
- Fluid dynamics
- Magnetism
- Radioactivity
- Mineral physics
- Vibration
- Closely allied sciences
- Atmospheric sciences
- Geology
- Engineering
- Water on the Earth
- Society
- Influential persons
- Organizations
- Publications
- Geophysics lists
- See also
- External links
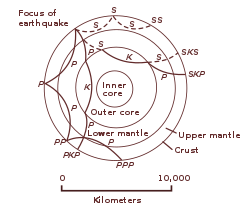
Geophysics – the physics of the Earth and its environment in space; also the study of the Earth using quantitative physical methods. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations have a broader definition that includes the hydrological cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial relations; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.