
The politics of Bulgaria take place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic republic, whereby the Prime minister is the head of government, and of a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the National Assembly. The Judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature.

Petar Stefanov Stojanov is a Bulgarian politician who was President of Bulgaria from 1997 to 2002. He was elected as a candidate of the Union of Democratic Forces (UDF). He did not succeed in the next presidential elections and after leaving office refrained from politics for a while, but, later became an MP in 2005 and was Chairman of UDF from 1 October 2005 to 22 May 2007.

Sergei Dmitrievich Stanishev is a Bulgarian politician who has served as President of the Party of European Socialists since November 2011 and Member of the European Parliament (MEP) from Bulgaria. He previously served as Prime Minister of Bulgaria from 2005 to 2009, Leader of the Socialist Party from 2001 to 2014 and Member of the National Assembly from 1997 to 2014.

This article describes the party affiliations of the leaders of each member-state represented in the European Council during the year 2005. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belongs to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belongs. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the system of Qualified Majority Voting.

Prior to 1 May 2004 the European Union had fifteen members. On that date ten new member states were admitted. This article describes the party affiliations of the leaders of each member-state represented in the European Council from the beginning of 2004 until 1 May. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belonged to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belonged. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the system of Qualified Majority Voting.

This article describes the party affiliations of the leaders of each member-state represented in the European Council during the year 2003. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belonged to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belonged. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the system of Qualified Majority Voting.

This article describes the party affiliations of leaders of each member-state represented in the European Council during the year 2007. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belongs to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belongs. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the system of Qualified Majority Voting.

This article describes the party affiliations of the leaders of each member-state represented in the European Council during the year 2002. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belonged to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belonged. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the system of Qualified Majority Voting.

This article describes the party affiliations of the leaders of each member-state represented in the European Council during the year 2001. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belonged to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belonged. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the system of Qualified Majority Voting.

This article describes the party affiliations of leaders of each member-state represented in the European Council during the year 2008. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belongs to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belongs. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the system of Qualified Majority Voting.
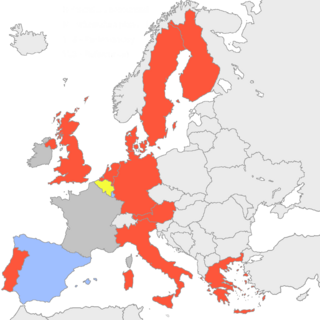
This article describes the party affiliations of the leaders of each member-state represented in the European Council during the year 2000. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belonged to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belonged. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the system of Qualified Majority Voting.

This article describes the party affiliations of the leaders of each member-state represented in the European Council during the year 1999. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belonged to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belonged. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the system of Qualified Majority Voting.

This article describes the party affiliations of leaders of each member-state represented in the European Council during the year 2009. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belongs to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belongs. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the system of Qualified Majority Voting.

This article describes the party affiliations of leaders of each member-state represented in the European Council during the year 2010. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belongs to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belongs. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the system of Qualified Majority Voting.

This article describes the party affiliations of leaders of each member-state represented in the European Council during the year 2011. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belongs to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belongs. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the system of Qualified Majority Voting.

This article describes the party affiliations of leaders of each member-state represented in the European Council during the year 2012. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belongs to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belongs. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the system of Qualified Majority Voting.
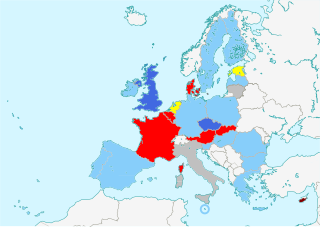
Until 1 July 2013 the European Union will have twenty-seven members. On that date, Croatia is expected to join the Union, therefore forcing a change of the influence each member-state has, as well as its Qualified Majority Voting. This article describes the party affiliations of leaders of each member-state represented in the European Council during the year 20133. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belongs to at the national level, as well as the national level to which that national party belongs. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the system of Qualified Majority Voting.
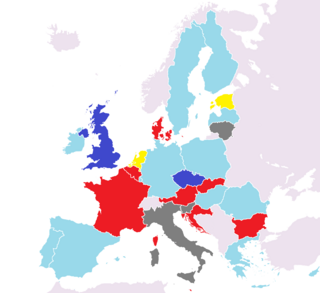
Since 1 July 2013 the European Union have twenty-eight members. Croatia joined the Union, therefore forcing a change of the influence each member-state has, as well as its Qualified Majority Voting. This article describes the party affiliations of leaders of each member-state represented in the European Council during the year 2013. The list below gives the political party that each head of government, or head of state, belongs to at the national level, as well as the European political alliance to which that national party belongs. The states are listed from most to least populous. More populous states have greater influence in the council, in accordance with the system of Qualified Majority Voting.

Miroslav Cerar Jr. (Slovene pronunciation: [ˈmíːɾɔslaw ˈtsɛ̀ːɾaɾ], known as Miro Cerar[ˈmíːrɔ -]; is a Slovenian law professor and politician. He was the eight Prime Minister of Slovenia, leading the 12th Government. He served as Deputy Prime Minister and Minister of Foreign Affairs in the 13th Government. He is a full professor at the Chair of Theory and Sociology of Law at the University of Ljubljana Faculty of Law.

European Parliament elections were held in Slovenia on 25 May 2014. It was the first in the series of three elections held in the 2014, and the major test leading up to the parliamentary elections in July. The political atmosphere was in a crisis that started with the fall of Borut Pahor's government, then Janez Janša's government in 2013, the latter coming after Janša was accused of corruption. The cabinet of Alenka Bratušek was breaking up, as the former leader of the Positive Slovenia Zoran Janković, who was under the suspicion of corruption, announced his candidature for party president, even though the coalition parties threatened to leave the government if he was to be elected, which later he was.




















