
Petermann Island is a small, low and rounded island, lying off the northwest coast of Kyiv Peninsula in Graham Land, Antarctica, a short distance south of Booth Island and the Lemaire Channel. It is a popular tourist destination.

Booth Island is a rugged, Y-shaped island, 8 kilometres (5 mi) long and rising to 980 m (3,215 ft) off the northwest coast of Kyiv Peninsula in Graham Land, Antarctica in the northeastern part of the Wilhelm Archipelago. The narrow passage between the island and the mainland is the Lemaire Channel.

The Fildes Peninsula is a 7 km (4.3 mi) long peninsula that forms the south-western end of King George Island in the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica. It was named from association with nearby Fildes Strait by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1960; the strait was likely named for Robert Fildes, a British sealer of the 1800s.

Stonington Island is a rocky island lying 1.8 km (1.1 mi) northeast of Neny Island in the eastern part of Marguerite Bay off the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. It is 0.75 km (0.47 mi) long from north-west to south-east and 0.37 km (0.23 mi) wide, yielding an area of 20 ha. It was formerly connected by a drifted snow slope to Northeast Glacier on the mainland. Highest elevation is Anemometer Hill which rises to 25 m (82 ft).
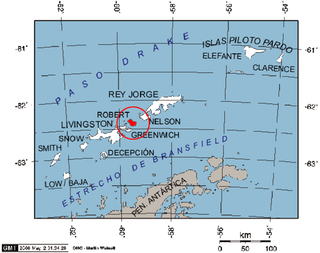
Robert Island or Mitchells Island or Polotsk Island or Roberts Island is an island 11 miles (18 km) long and 8 miles (13 km) wide, situated between Nelson Island and Greenwich Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Robert Island is located at 62°24′S59°30′W. Surface area 132 km2 (51 sq mi). The name "Robert Island" dates back to around 1821 and is now established in international usage.

Henryk Arctowski Polish Antarctic Station is a Polish research station on King George Island, off the coast of Antarctica.

Base Presidente Eduardo Frei Montalva is the most important Antarctic base of Chile. It is located at Fildes Peninsula, an ice-free area, in front of Fildes Bay, west of King George Island, South Shetland Islands. Situated alongside the Escudero Station and only 200 metres (660 ft) from the Russian Bellingshausen Station, it is at an altitude of 10 metres (33 ft) above sea-level. The base is located in the Chilean commune of Antártica, which is the Antarctic territory claimed by Chile.

Inexpressible Island is a small, rocky island in Terra Nova Bay, Victoria Land, Antarctica.

Cape Evans is a rocky cape on the west side of Ross Island, Antarctica, forming the north side of the entrance to Erebus Bay.
Pendulum Cove is a cove at the north-east side of Port Foster, Deception Island, in the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica. The name of the cove derives from the pendulum and magnetic observations made there by the British expedition under Henry Foster in 1829.

Yankee Harbour is a small inner harbour entered from Shopski Cove between Glacier Bluff and Spit Point, indenting the south-west side of Greenwich Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. It is 2.35 km (1.46 mi) long in west-south-west to east-north-east direction, and 1.6 km (0.99 mi) wide, and is bounded by Provadiya Hook to the south-west, Parvomay Neck to the north and east, and Kladara Beach to the south.

Cámara Base is an Argentine Antarctic base and scientific research station named after Frigate Lieutenant Naval Aviator Juan Ramón Cámara. It is located in the northern foothills of La Morenita Hill, at Menguante Cove in Half Moon Island off the east coast of Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica.

Fort William Point is the conspicuous flat-topped rocky headland forming the northwest extremity of Coppermine Peninsula and Robert Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The point is a northwest entrance point of English Strait and forms the west side of the entrance to Carlota Cove.
Lambda Island is an island lying immediately north-west of Delta Island in the Melchior Islands, of the Palmer Archipelago in Antarctica. The island, the largest in the north-western part of the island group, was first roughly charted and named "Île Sourrieu" by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1903–05 under Jean-Baptiste Charcot, but that name has not survived in usage. The current name, derived from lambda, the 11th letter of the Greek alphabet, was given by Discovery Investigations personnel who roughly charted the island in 1927. The island was surveyed by Argentine expeditions in 1942, 1943 and 1948.

Ardley Island is an island 1.9 kilometres (1 nmi) long, lying in Maxwell Bay close off the south-west end of King George Island, in the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica. It was charted as a peninsula in 1935 by Discovery Investigations personnel of the Discovery II and named for Lieutenant R.A.B. Ardley, Royal Naval Reserve, an officer on the ship in 1929–31 and 1931–33. Aerial photography has since shown that the feature is an island with Braillard Point being the headland forming the northeast end of Ardley Island. It has been designated an Antarctic Specially Protected Area because of the importance of its seabird colonies.
Collins Point is a small but prominent headland 1.4 km (0.87 mi) west-south-west of Fildes Point, on the south side of Port Foster, Deception Island, in the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica. It was charted by a British expedition under Foster, 1828–31. It was named by Lieutenant Commander D.N. Penfold, Royal Navy, following his survey of the island in 1948–49, for Rear Admiral Kenneth Collins of the Hydrographic Department of the Admiralty.
Suffield Point is the south-west entrance point of Norma Cove, Fildes Peninsula, on King George Island in the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica. It was charted in the course of the Discovery Investigations, 1933–35, and named after boatswain William E. Suffield. The site is part of the Fildes Peninsula Antarctic Specially Protected Area, designated as such because of its paleontological values.

Martel Inlet is an inlet forming the northeast head of Admiralty Bay, King George Island, in the South Shetland Islands off Antarctica. The inlet and most of its constituent features were charted in December 1909 by the Fourth French Antarctic Expedition under Jean-Baptiste Charcot and named "Fiord Martel" after J.L. Martel, a French politician. The mountain ridge Ullmann Spur is located at the head of the inlet.
Maxwell Bay, also called Fildes Bay and Guardia Nacional Bay is a bay 19 km (12 mi) long, lying between King George Island and Nelson Island, in the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica. The main entrance to the bay is at the south-east side and is wide open; Fildes Strait on the north-west side is encumbered by rocks and is only navigable by boats. The name "Maxwells Straits" was given to this bay and to Fildes Strait by British sealing captain James Weddell in 1822–24, for Lieutenant Francis Maxwell who had served with Weddell in 1813–14. The name was altered and limited to the feature here described by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1960.

Whalers Bay is a small bay entered between Fildes Point and Penfold Point at the east side of Port Foster, Deception Island, in the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica. The bay was so named by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1908–10, under Charcot, because of its use at that time by whalers.














