Related Research Articles

In ancient times, Maldives were renowned for cowries, coir rope, dried tuna fish, ambergris (maavaharu) and coco de mer (tavakkaashi). Local and foreign trading ships used to load these products in the Maldives and bring them abroad.

The economy of Timor-Leste is a low-income economy as ranked by the World Bank. It is placed 140th on the Human Development Index, indicating a medium level of human development. 20% of the population is unemployed, and 52.9% live on less than $1.25 a day. About half of the population is illiterate. At 27%, East Timor's urbanisation rate is one of the lowest in the world.

International development or global development is a broad concept denoting the idea that societies and countries have differing levels of economic or human development on an international scale. It is the basis for international classifications such as developed country, developing country and least developed country, and for a field of practice and research that in various ways engages with international development processes. There are, however, many schools of thought and conventions regarding which are the exact features constituting the "development" of a country.

In the United Nations, the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) were eight international development goals for the year 2015 created following the Millennium Summit, following the adoption of the United Nations Millennium Declaration. These were based on the OECD DAC International Development Goals agreed by Development Ministers in the "Shaping the 21st Century Strategy". The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) succeeded the MDGs in 2016.

The Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI) is an index that scores and ranks countries by their perceived levels of public sector corruption, as assessed by experts and business executives. The CPI generally defines corruption as an "abuse of entrusted power for private gain". The index is published annually by the non-governmental organisation Transparency International since 1995.

The Millennium Challenge Corporation (MCC) is a bilateral United States foreign aid agency established by the U.S. Congress in 2004. It is an independent agency separate from the State Department and USAID. It provides grants to countries that have been determined to have good economic policies and potential for economic growth. The country qualification process is objective, involving scores provided by third parties in 20 different areas. An eligible country must apply for a grant with a specific project in mind.
Poverty in Pakistan has been recorded by the World Bank at 39.3% using the lower middle-income poverty rate of US$3.2 per day for the fiscal year 2020–21. In September 2021, the government stated that 22% percent of its population lives below the national poverty line set at Rs. 3030 (US$10) per month.
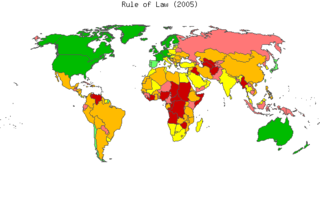
Based on a long-standing research program of the World Bank, the Worldwide Governance Indicators capture six key dimensions of governance between 1996 and present. They measure the quality of governance in over 200 countries, based on close to 40 data sources produced by over 30 organizations worldwide and are updated annually since 2002.
Poverty in South America is prevalent in most of its countries. Those that have the highest rates of poverty per population are Suriname, Bolivia and Venezuela. Recent political shifts in the region have led to improvements in some of these countries. In general, most South American economies have attempted to tackle poverty with stronger economic regulations, foreign direct investments and implementation of microeconomic policies to reduce poverty.
The concept of human development expands upon the notion of economic development to include social, political and even ethical dimensions. Since the mid-twentieth century, international organisations such as the United Nations and the World Bank have adopted human development as a holistic approach to evaluating a country’s progress that considers living conditions, social relations, individual freedoms and political institutions that contribute to freedom and well-being, in addition to standard measures of income growth.
This is a list of key international rankings of Costa Rica
The East Asia Climate Partnership (EACP) is Korea's international initiative for global cooperative development. Led by the Korea International Cooperation Agency (KOICA), a Korean government agency responsible for providing overseas grant aid, the EACP helps tackle climate change in developing countries and promotes green growth in Asia.

Poverty in Haiti is a long lasting issue that affects the residents on a daily basis playing a significant role in their everyday lives. Issues including housing, nutrition, education, healthcare, infant mortality rates, and environmental factors are very common amongst the poorest communities in the nation. Haiti has long struggled with poor living conditions in the more rural areas of the country causing many Haitians to migrate towards the capital city of Port-au-Prince. Poverty in Haiti is regarded as among the most severe in the Western hemisphere.

Emília Pires was East Timor's Minister of Finance from April 2007 until 16 February 2015. Ms. Pires was sworn in as the Minister of Finance of the V Constitutional Government of East Timor on August 8, 2012 under the leadership of Prime Minister Xanana Gusmão.
Tanzania has a current population of 55.57 million people. Current statistics form the World Bank show that in 2011, 49.1% of Tanzanians lived below US$1.90 per day. This figure is an improvement over 2007's report indicating a poverty rate of 55.1%. Tanzania has seen annual GDP gains of 7% since 2010 and this economic growth is attributed to this positive trends for poverty alleviation in Tanzania. The 2019 World Bank report showed that in the last 10 years, poverty has reduced by 8 percent, from 34.4% in 2007 to 26.4% in 2018.

In the United Nations, the Post-2015 Development Agenda was a set of talks and discussions that led to the creation of the 2016 Sustainable Development Goals. This replaced the 2015 Millennium Development Goals.
Extreme poverty is defined as living on less than US$2.50 purchasing power parity. Uganda has made significant progress in eradicating poverty and achieved the first millennium development goal of halving the number of people in extreme poverty. Uganda was listed as the 9th most successful country in Africa as regards poverty eradication. The percentage of Ugandans living in absolute poverty has been on a substantial decline, and the finance ministry in the country projected that the extreme poverty level will be reduced to 10% in the future. This success has been attributed to the deliberate efforts to combat poverty in the country by numerous national strategies that are explained below.
Synergy International Systems, Inc. (SIS) is an information technology and consulting company based in Washington, D.C. that provides web-based software to international development agencies, country governments, NGOs and private sector partners. Their key products are focused on monitoring and evaluation (M&E), national development effectiveness, aid management, judicial system modernization, social protection, public financial management, disaster relief and reconstruction, environment, education, and public health. There is a company-maintained global learning center in Yerevan, Armenia. The company's services include software development and customization, IT strategy consulting, systems integration, capacity development and technical support. Synergy has developed management information systems for public and private sector clients in 65 countries.
The coffee industry of Timor Leste is the largest non-oil export. Since the introduction of coffee by the Portuguese in the 1800s, the industry contributes a sizeable portion of the country's employment and investment and is a major source of income for rural communities. The industry is vulnerable to global coffee price fluctuation, deficient infrastructure, and lack of capital.
Sustainable Development Goals and Lebanon explains major contributions launched in Lebanon towards the advancement of the Sustainable Development Goals SDGs and the 2030 agenda.
References
- ↑ "World Economic Outlook Database, April 2012". International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 5 October 2012.
- 1 2 "Timor Leste: Human Development Indicators". International Human Development Indicators. United Nations Development Program. Archived from the original on 9 November 2010. Retrieved 11 June 2012.
- ↑ Asian Development Bank. (2016, April). Basic Statistics 2016. Retrieved 21, November 2016, from https://www.adb.org/publications/basic-statistics-2016
- ↑ Asian Development Bank. (n.d.). Poverty in Timor-Leste. Retrieved 21 November 2016 from https://www.adb.org/countries/timor-leste/poverty
- ↑ "2010 Corruption Perceptions Index". Transparency International. Retrieved 5 October 2012.
- 1 2 Dionisio Da Cruz Pereira (19 March 2009). "The challenges for East Timor". On Line Opinion. Retrieved 5 October 2012.
- ↑ "The National Development Plan – Part 1". The National Development Plan. Prime Minister and Cabinet, Timor-Leste Government. Retrieved 5 October 2012.
- ↑ "Millennium Development Goals". United Nations Development Programme. Retrieved 5 October 2012.
- ↑ "Poverty Reduction and Achievement of the MDGs". UNPD Timor Leste. United Nations Development Programme, Timor-Leste Country Office. Retrieved 11 June 2012.
