Related Research Articles

The Duala are a Bantu ethnic group of Cameroon. They primarily inhabit the littoral and southwest region of Cameroon and form a portion of the Sawabantu or "coastal people" of Cameroon. The Dualas readily welcomed German and French colonial policies. The number of German-speaking Africans increased in central African German colonies prior to 1914. The Duala leadership in 1884 placed the tribe under German rule. Most converted to Protestantism and were schooled along German lines. Colonial officials and businessmen preferred them as inexpensive clerks to German government offices and firms in Africa. They have historically played a highly influential role in Cameroon due to their long contact with Europeans, high rate of education, and wealth gained over centuries as slave traders and landowners.

The Subu are a Bantu ethnic group who inhabit part of the coast of Cameroon. Along with other coastal peoples, they belong to Cameroon's Sawa ethnic groups. They were one of the earliest Cameroonian peoples to make contact with Europeans, and over two centuries, they became influential traders and middlemen. Under the kings William I of Bimbia and Young King William, the Isubu formed a state called Bimbia.

A jengu is a water spirit in the traditional beliefs of the Sawabantu groups of Cameroon, like the Duala, Bakweri, Malimba, Subu, Bakoko, Oroko people. Among the Bakweri, the term used is liengu. Miengu are similar to bisimbi in the Bakongo spirituality and Mami Wata. The Bakoko people use the term Bisima.
Ewale a Mbedi was the eponymous ancestor of the Duala people of Cameroon. According to the oral histories of the Duala and related Sawa peoples of the Cameroon coast, Ewale hailed from a place called Piti. He and his followers migrated southwest to the coast and settled at the present-day location of Douala. The area was inhabited by the Bassa and/or Bakoko, who were driven inland by the new arrivals. Meanwhile, Ewale and his followers set up trade with European merchant ships.
Mbedi a Mbongo is the common ancestor of many of the Sawa coastal ethnic groups of Cameroon according to their oral traditions. Stories say that he lived at a place called Piti, northeast of present-day Douala. From there, his sons migrated south toward the coast in what are known as the Mbedine events. These movements may be mythical in many cases, but anthropologists and historians accept the plausibility of a migration of some Sawa ancestors to the coast during the 16th century.

Monneba, also spelled Moneba and other ways, was a local Duala leader on the Cameroon coast in the 1630s. Dutch sources from the 1660s say that Monneba ran a trading post on the Cameroons River at the present location of Douala. His people dealt primarily in ivory, with some slaves. Modern scholars equate Monneba with a Duala ruler named Mulobe a Ewale or Mulabe a Ewale. Assuming this is true, he is the earliest Duala leader of whom we have corroboration in written sources. It is quite possible that Monneba/Mulobe was the ruler who set into motion the transformation of the Duala into a trading people and the most influential ethnic group in early Cameroonian history.
George or Joss, born Doo a Makongo or Doo a Mukonga, was a king of the Duala people in the late 18th century. Doo a Makongo was the son of Makongo a Njo. He lived at Douala on the Wouri estuary on the coast of Cameroon. By 1788–1790, Doo was a powerful ruler in the area. During this time, the British slave trade was at its height, and Douala was the primary trading post in the region.
Kwane a Ngie, known in British records as Angua or Quan, was a Duala ruler from the Bonambela sublineage who flourished from 1788 to 1790 in Douala, Cameroon. The British slave trade was at its height at this time, and, although a rival ruler from the Bonanjo sublineage named George or Joss reigned simultaneously, British records point to Kwane as the more powerful or respected leader.
Elame a Doo was a ruler of the Bonapriso sublineage of the Duala people who lived on the Wouri estuary of Cameroon in the late 19th century. He was the son of Doo a Priso and the grandson of Priso a Doo. Elame signed the 1884 German-Duala treaty that granted the German Empire sovereignty over Cameroon.

Rudolf Duala Manga Bell was a Duala king and resistance leader in the German colony of Kamerun (Cameroon). After being educated in both Kamerun and Europe, he succeeded his father Manga Ndumbe Bell on 2 September 1908.
Ewonde a Kwane was a Duala ruler of the Bonambela/Akwa lineage who lived in Douala on the Wouri River. Ewonde was the son of the powerful chief Kwane a Ngie. Ewonde died early, causing a secession crisis in Bonambela. Ngando a Kwa claimed to be his heir and declared himself equal to Bele a Doo, leader of the Bonanjo/Bell lineage. Ewonde's daughter Kanya married Enjobe, an Aboh slave or immigrant in Douala. Their son would found the Bonambele/Deido sublineage. Duala tradition states that another of Ewonde's daughters, Lesenge, married into Isubu royalty and was the mother of King William of Bimbia.
Doo or DOO may refer to:

Douala is the largest city in Cameroon and its economic capital. It is also the capital of Cameroon's Littoral Region. Home to Central Africa's largest port and its major international airport, Douala International Airport (DLA), it is the commercial and economic capital of Cameroon and the entire CEMAC region comprising Gabon, Congo, Chad, Equatorial Guinea, Central African Republic and Cameroon. Consequently, it handles most of the country's major exports, such as oil, cocoa and coffee, timber, metals and fruits. As of 2015, the city and its surrounding area had an estimated population of 5,768,400. The city sits on the estuary of Wouri River and its climate is tropical.

The Mungo River is a large river in Cameroon that drains the mountains in the southern portion of the Cameroon line of active and extinct volcanoes.
Auguste Manga Ndumbe Bell was a leader of the Duala people of southern Cameroon from 1897 to 1908 during the period after the German colonialists assumed control of the region as the Kamerun colony.

Ndumbé Lobé Bell or King Bell was a leader of the Duala people in Southern Cameroon during the period when the Germans established their colony of Kamerun. He was an astute politician and a highly successful businessman.

Jantzen & Thormählen was a German firm based in Hamburg that was established to exploit the resources of Cameroon. The firm's commercial and political influence was a major factor in the establishment of the colony of Kamerun in 1884.

Bimbia was an independent state of the Isubu people of Cameroon. In 1884, it was annexed by the Germans and incorporated in the colony of Kamerun. It lies in Southwest Region, to the south of Mount Cameroon and to the west of the Wouri estuary. Is situated at the East coast of the Limbé sub-division.
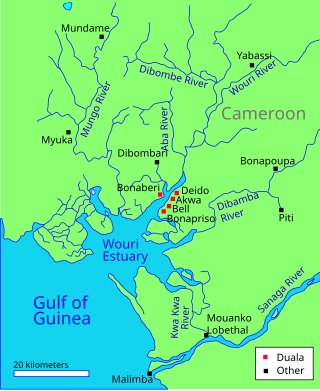
The Wouri estuary, or Cameroon estuary is a large tidal estuary in Cameroon where several rivers come together, emptying into the Bight of Biafra. Douala, the largest city in Cameroon, is at the mouth of the Wouri River where it enters the estuary. The estuary contains extensive mangrove forests, which are being damaged by pollution and population pressures.
References
- Austen, Ralph A., and Derrick, Jonathan (1999): Middlemen of the Cameroons Rivers: The Duala and their Hinterland, c. 1600–c.1960. Cambridge University Press.
