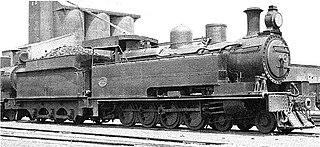
The South African Railways Class 17 4-8-0TT of 1926 was a steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in the Natal Colony.

The South African Railways Class A 4-8-2T of 1888 is a steam locomotive class from the pre-Union era in the Colony of Natal.

The South African Railways Class 13 4-8-0TT of 1905 was a steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in Transvaal.

The South African Railways Class H 4-10-2T, introduced in 1899, was a steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in the Colony of Natal.
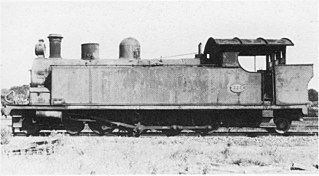
The South African Railways Class H1 4-8-2T of 1903 was a steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in Transvaal.

The South African Railways Class H2 4-8-2T of 1909 was a steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in the Colony of Natal.
The South African Railways Class 1 4-8-0 of 1904 was a steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in the Colony of Natal.
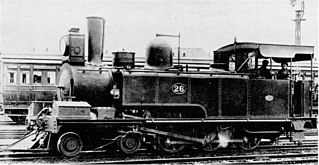
The South African Railways Class C 4-6-0T of 1879 was a steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in the Colony of Natal.

The South African Railways Class C2 4-6-4T of 1896 was a steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in the Colony of Natal.

The South African Railways Class G 4-8-2T of 1904 was a steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in the Colony of Natal.
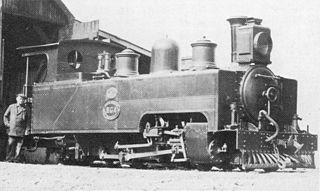
The South African Railways Class NG3 4-6-2T of 1907 was a narrow-gauge steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in the Colony of Natal.

The South African Railways Class NG4 4-6-2T of 1911 was a narrow-gauge steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in the Colony of Natal.

The Central South African Railways Class E 4-10-2T of 1901 was a South African steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in Transvaal.

The Natal Government Railways Class K 0-6-0ST of 1880 was a South African steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in the Colony of Natal.

The Natal Government Railways Class N 4-6-2T of 1906 was a South African steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in the Natal Colony.
The South African type SH tender was a steam locomotive tender from the pre-Union era in the Natal Colony.
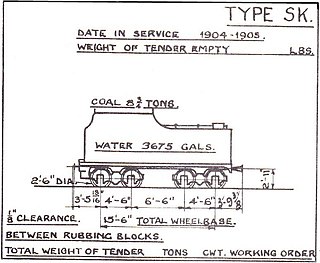
The South African type SK tender was a steam locomotive tender.

The South African type TJ tender was a steam locomotive tender from the pre-Union era in the Natal Colony.
The South African type TM tender was a steam locomotive tender from the pre-Union era in the Natal Colony.

The South African type TL tender was a steam locomotive tender.


















