
Sporobolus alterniflorus, or synonymously known as Spartina alterniflora, the smooth cordgrass, saltmarsh cordgrass, or salt-water cordgrass, is a perennial deciduous grass which is found in intertidal wetlands, especially estuarine salt marshes. It has been reclassified as Sporobolus alterniflorus after a taxonomic revision in 2014, but it is still common to see Spartina alterniflora and in 2019 an interdisciplinary team of experts coauthored a report published in the journal Ecology supporting Spartina as a genus. It grows 1–1.5 m tall and has smooth, hollow stems that bear leaves up to 20–60 cm long and 1.5 cm wide at their base, which are sharply tapered and bend down at their tips. Like its relative saltmeadow cordgrass S. patens, it produces flowers and seeds on only one side of the stalk. The flowers are a yellowish-green, turning brown by the winter. It has rhizoidal roots, which, when broken off, can result in vegetative asexual growth. The roots are an important food resource for snow geese. It can grow in low marsh as well as high marsh, but it is usually restricted to low marsh because it is outcompeted by salt meadow cordgrass in the high marsh. It grows in a wide range of salinities, from about 5 psu to marine, and has been described as the "single most important marsh plant species in the estuary" of Chesapeake Bay. It is described as intolerant of shade.

Sporobolus anglicus is a species of cordgrass that originated in southern England in about 1870 and is a neonative species in Britain. It was reclassified as Sporobolus anglicus after a taxonomic revision in 2014, but Spartina anglica is still in common usage. It is an allotetraploid species derived from the hybrid Sporobolus × townsendii, which arose when the European native cordgrass Sporobolus maritimus hybridised with the introduced American Sporobolus alterniflorus.

Sporobolus maritimus, or synonymously as Spartina maritima, the small cordgrass, is a species of cordgrass native to the coasts of western and southern Europe and western Africa, from the Netherlands west across southern England to southern Ireland, and south along the Atlantic coast to Morocco and also on the Mediterranean Sea coasts. There is also a disjunct population on the Atlantic coasts of Namibia and South Africa.
Grasses are one of the most abundant floras on all continents, except Antarctica. Their divergence is estimated to have taken place 200 million years ago. Humans have intentionally and unintentionally introduced these species to North America through travel and trade. On the North American plains, prairies, grasslands, and meadows at least 11% of grasses are non-native. North America is considered a hotspot for many invasive species of grasses, which threatens all of the endangered native grass species and potentially threatens other grass species. Conservation tactics and management policies can help prevent invasive species from taking over and driving native North American plants to extinction.

Muhlenbergia is a genus of plants in the grass family.

Sporobolus is a nearly cosmopolitan genus of plants in the grass family. The name Sporobolus means "seed-thrower", and is derived from Ancient Greek word σπόρος (spóros), meaning "seed", and the root of βάλλειν (bállein) "to throw", referring to the dispersion of seeds. Members of the genus are usually called dropseeds or sacaton grasses. They are typical prairie and savanna plants, occurring in other types of open habitat in warmer climates. At least one species is threatened with extinction, and another is extinct.

Littoraria irrorata, also known by the common name the marsh periwinkle, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Littorinidae. The specific epithet irrorata means 'moistened' or 'dewy.'

Sporobolus michauxianus is a species of cordgrass known as prairie cordgrass, freshwater cordgrass, tall marshgrass, and sloughgrass. It is native to much of North America, including central and eastern Canada and most of the contiguous United States except for the southwestern and southeastern regions. Its distribution extends into Mexico. It is also present on other continents as an introduced species.
100 of the World's Worst Invasive Alien Species is a list of invasive species compiled in 2000 from the Global Invasive Species Database, a database of invasive species around the world. The database is run by the Invasive Species Specialist Group (ISSG) of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). The ISSG acknowledges that it is "very difficult to identify 100 invasive species from around the world that really are 'worse' than any others. ... Absence from the list does not imply that a species poses a lesser threat." In 2013, the ISSG updated their list to supersede the recently eradicated † rinderpest virus, and a few genus and species names were altered.

Sporobolus montevidensis is a species of grass known by the common name denseflower cordgrass. Although reclassified after a taxonomic revision in 2014, it may still be referred to as Spartina densiflora by some users. It is native to the coastline of southern South America, where it is a resident of salt marshes. It is also known on the west coast of the North America and parts of the Mediterranean coast as an introduced species and in some areas a noxious weed. In California it is a troublesome invasive species of marshes in San Francisco Bay and in Humboldt Bay, where it was introduced during the 19th century from Chile in ballast.

Sporobolus foliosus is a species of grass known by the common name California cordgrass. It was reclassified from Spartina foliosa after a taxonomic revision in 2014. It is native to the salt marshes and mudflats of coastal California and Baja California, especially San Francisco Bay. It is a perennial grass growing from short rhizomes. It produces single stems or clumps of thick, fleshy stems that grow up to 1.5 meters tall. They are green or purple-tinged. The long, narrow leaves are flat or rolled inward. The inflorescence is a narrow, dense, spike-like stick of branches appressed together, the unit reaching up to 25 centimeters long. The lower spikelets are sometimes enclosed in the basal sheaths of upper leaves.

Sporobolus hookerianus is a species of grass known by the common name alkali cordgrass.
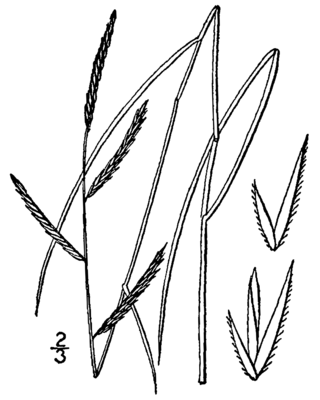
Sporobolus pumilus, the saltmeadow cordgrass, also known as salt hay, is a species of cordgrass native to the Atlantic coast of the Americas, from Newfoundland south along the eastern United States to the Caribbean and north-eastern Mexico. It was reclassified after a taxonomic revision in 2014, but the older name, Spartina patens, may still be found in use. It can be found in marshlands in other areas of the world as an introduced species and often a harmful noxious weed or invasive species.

Juncus roemerianus is a species of flowering plant in the rush family known by the common names black rush, needlerush, and black needlerush. It is native to North America, where its main distribution lies along the coastline of the southeastern United States, including the Gulf Coast. It occurs from New Jersey to Texas, with outlying populations in Connecticut, New York, Mexico, and certain Caribbean islands.

Sporobolus bakeri is a species of grass known by the common names sand cordgrass and bunch cordgrass. It is native to the south-eastern United States, where it grows along the coast and in inland freshwater habitat in Florida.

Sporobolus cynosuroides is a species of grass known by the common names big cordgrass and salt reedgrass. It is native to the East Coast and Gulf Coast of the United States, where it grows in coastal habitat such as marshes, lagoons, and bays.

Sporobolus spartinae is a species of grass known by the common names gulf cordgrass and sacahuista. It is native to the Americas, where it occurs from the Gulf Coast of the United States south to Argentina.

Charles E. Wheeler Wildlife Management Area is a 625-acre (253 ha) brackish tidal marsh, nature preserve and hunting area owned by the state of Connecticut located in Devon (village), Milford, New Haven County, Connecticut.
Spartina townsendii is a species of flowering plant in the family Poaceae. It is native to Western Europe.
















