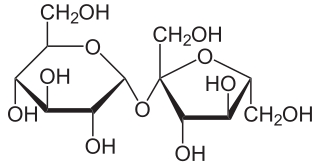
Sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. It has the molecular formula C
12H
22O
11.

Muscovado is a type of partially refined to unrefined sugar with a strong molasses content and flavour, and dark brown in colour. It is technically considered either a non-centrifugal cane sugar or a centrifuged, partially refined sugar according to the process used by the manufacturer. Muscovado contains higher levels of various minerals than processed white sugar, and is considered by some to be healthier. Its main uses are in food and confectionery, and the manufacturing of rum and other forms of alcohol. The largest producer and consumer of muscovado is India.

Agriculture in Thailand is highly competitive, diversified and specialized and its exports are very successful internationally. Rice is the country's most important crop, with some 60 percent of Thailand's 13 million farmers growing it on almost half of Thailand's cultivated land. Thailand is a major exporter in the world rice market. Rice exports in 2014 amounted to 1.3 percent of GDP. Agricultural production as a whole accounts for an estimated 9–10.5 percent of Thai GDP. Forty percent of the population work in agriculture-related jobs. The farmland they work was valued at US$2,945/rai in 2013. Most Thai farmers own fewer than eight ha (50 rai) of land.
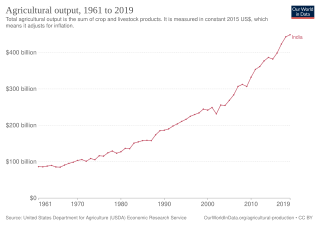
The history of agriculture in India dates back to the Neolithic period. India ranks second worldwide in farm outputs. As per the Indian economic survey 2020 -21, agriculture employed more than 50% of the Indian workforce and contributed 20.2% to the country's GDP.

The economy of the state of Maharashtra is the largest in India. Maharashtra is India's second most industrialised state contributing 20% of national industrial output. Almost 46% of the GSDP is contributed by industry. Maharashtra has software parks in many cities around the state, and is the second largest exporter of software with annual exports over ₹ 80,000 crores.

Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of tall, perennial grass that is used for sugar production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fibrous stalks that are rich in sucrose, which accumulates in the stalk internodes. Sugarcanes belong to the grass family, Poaceae, an economically important flowering plant family that includes maize, wheat, rice, and sorghum, and many forage crops. It is native to the warm temperate and tropical regions of India, Southeast Asia, and New Guinea.

Fishing in India is a major sector within the economy of India contributing 1.07% of its total GDP. The fishing sector in India supports the livelihood of over 28 million people in the country, especially within the marginalized and vulnerable communities. India is the third largest fish producing country in the world accounting for 7.96% of the global production and second largest producer of fish through aquaculture, after China. The total fish production during the FY 2020-21 is estimated at 14.73 million metric tonnes. According to the National Fisheries Development Board the Fisheries Industry generates an export earnings of Rs 334.41 billion. Centrally sponsored schemes will increase exports by Rs 1 lakh crore in FY25. 65,000 fishermen have been trained under these schemes from 2017 to 2020. Freshwater fishing consists of 55% of total fish production.
Ratooning is the agricultural practice of harvesting a monocot crop by cutting most of the above-ground portion but leaving the roots and the growing shoot apices intact so as to allow the plants to recover and produce a fresh crop in the next season. This practice is widely used in the cultivation of crops such as rice, sugarcane, banana, and pineapple. Ratoon crops cannot be perennially renewed, and may be harvested only for a few seasons, as a decline in yield tends to occur due to increased crowding, damage by pests and diseases, and decreasing soil fertility.

The history of sugar has five main phases:
- The extraction of sugar cane juice from the sugarcane plant, and the subsequent domestication of the plant in tropical India and Southeast Asia sometime around 4,000 BC.
- The invention of manufacture of cane sugar granules from sugarcane juice in India a little over two thousand years ago, followed by improvements in refining the crystal granules in India in the early centuries AD.
- The spread of cultivation and manufacture of cane sugar to the medieval Islamic world together with some improvements in production methods.
- The spread of cultivation and manufacture of cane sugar to the West Indies and tropical parts of the Americas beginning in the 16th century, followed by more intensive improvements in production in the 17th through 19th centuries in that part of the world.
- The development of beet sugar, high-fructose corn syrup and other sweeteners in the 19th and 20th centuries.

Uttarakhand's gross state domestic product for 2024 is estimated at around $40 billion in current prices. Born out of partition of Uttar Pradesh, the new state of Uttarakhand is today around 13 percent of the GSDP of Uttar Pradesh state.

The National Sugar Institute (NSI) established in 1936, is involved in research, training and advisory services to the sugar and allied industry, and functions under the Department of Food and Public Distribution of the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution. Located in Kalyanpur, Kanpur, Uttar Pradesh, India, it provides technical education and training in research in all branches of sugar chemistry, sugar technology, sugar engineering and allied fields. The institute provide assistance to central and state governments in matters relating to sugar and allied industries.

Kakira Sugar Works Limited, often called Kakira Sugar Works, is a leading sugar manufacturer in Uganda, the third-largest economy in the East African Community.
Indian Sugar Mills Association is premier sugar organization in India. It establish connection between Government and Sugar industry in the country. Prime objective is to ensure that functioning of both private and public sugar mills in country are done through government policies.
The cooperative movement in India plays a crucial role in the agricultural sector, banking and housing. The history of cooperatives in India is more than a hundred years old. Cooperatives developed very rapidly after Indian independence. According to an estimate, more than half a million cooperative societies are active in the country. Many cooperative societies, particularly in rural areas, increase political participation and are used as a stepping stone by aspiring politicians.
Bihar lies in the river plains of the basin of the river Ganga. As a result, its land contains fertile alluvial soil and groundwater resources. This makes the agriculture of Bihar rich and diverse. Rice, wheat, and maize are the major cereal crops. Arhar, urad, moong, gram, pea, lentils, and khesaria are some of the pulses cultivated in Bihar. Bihar is the fourth largest producer of vegetables, which is dominated by potato, onion, eggplant, and cauliflower. In fruit cultivation, it is the largest producer of lychee and the third largest producer of pineapple, as well as a major producer of mango, banana, and guava. Sugar cane and jute are two other major cash crops of Bihar.
Sugarcane is a primary cash crop among farmers of the western Maharashtra region. The sugarcane is mostly sold to sugar mills for sugar production. Majority of these mills are cooperatives owned by the sugarcane growers. Solapur district has highest number of sugar factories in Maharashtra.
Established in 2008, Bonsucro is a global non-profit, multi-stakeholder governance group promoting sustainable sugar cane, including production, processing and trade around the world.
Ghodganga Sahakari Sakhar Karkhana Ltd is an establishment set up around 70 km east to Pune. Factory is recently named after founder Raosahebdada Pawar Ghodganga Sahakari Sakhar Karkhana Ltd (RPGSSKL). This project turned out to be the best achievement of Cooperative sugar factories and rural development. This set up is being conducive as sugar production is prime business for region. The project brings employment and social development. Sugarcane grower/farmers in the region are really encouraged by the establishment. The project started with capital share of local farmers.
Nanduri Atchuta Ramaiah is an Indian physical chemist, sugar technologist and the director of National Sugar Institute, Kanpur. He was the founder director of Vasantdada Sugar Institute, Pune and was known for his studies on physicochemical processes involved in the processing of sugarcane juice which assisted in developing cost effective manufacturing techniques. He was an elected fellow of the Indian National Science Academy, the National Academy of Agricultural Sciences and the Royal Institute of Chemistry. The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, the apex agency of the Government of India for scientific research, awarded him the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology, one of the highest Indian science awards, in 1966, for his contributions to chemical sciences.
The Sugar Technologists' Association of India is national level association of experts associated with sugar industry. It is non government, not for profit organization.











