
Embroidery is the art of decorating fabric or other materials using a needle to stitch thread or yarn. Embroidery may also incorporate other materials such as pearls, beads, quills, and sequins. In modern days, embroidery is usually seen on hats, clothing, blankets, and handbags. Embroidery is available in a wide variety of thread or yarn colour. It is often used to personalize gifts or clothing items.

Hardanger embroidery or "Hardangersøm" is a form of embroidery traditionally worked with white thread on white even-weave linen or cloth, using counted thread and drawn thread work techniques. It is sometimes called whitework embroidery.

Drawn thread work is one of the earliest forms of open work embroidery, and has been worked throughout Europe. Originally it was often used for ecclesiastical items and to ornament shrouds. It is a form of counted-thread embroidery based on removing threads from the warp and/or the weft of a piece of even-weave fabric. The remaining threads are grouped or bundled together into a variety of patterns. The more elaborate styles of drawn thread work use a variety of other stitches and techniques, but the drawn thread parts are their most distinctive element. It is also grouped with whitework embroidery because it was traditionally done in white thread on white fabric and is often combined with other whitework techniques.
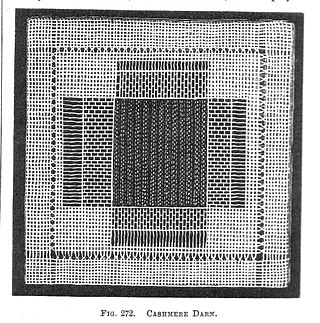
Darning is a sewing technique for repairing holes or worn areas in fabric or knitting using needle and thread alone. It is often done by hand, but using a sewing machine is also possible. Hand darning employs the darning stitch, a simple running stitch in which the thread is "woven" in rows along the grain of the fabric, with the stitcher reversing direction at the end of each row, and then filling in the framework thus created, as if weaving. Darning is a traditional method for repairing fabric damage or holes that do not run along a seam, and where patching is impractical or would create discomfort for the wearer, such as on the heel of a sock.

Korean embroidery techniques and artifacts have a long history, but there is the most evidence from the Joseon Dynasty, after the 14th century in Korea. This article talks about the history, styles, preservation, artists, and examples of screens, costumes, and domestic wares of this exacting and beautiful art form.

Chikankari is a traditional embroidery style from Lucknow, India. Translated, the word means embroidery, and it is one of Lucknow's best known textile decoration styles. The main market in Lucknow for Chikankari based products is Chowk. Production is mainly based in Lucknow and in the adjoining districts.

Phulkari refers to the folk embroidery of the Punjab region and Gulkari of Sindh in South Asia.

Embroidery in India includes dozens of embroidery styles that vary by region and clothing styles. Designs in Indian embroidery are formed on the basis of the texture and the design of the fabric and the stitch. The dot and the alternate dot, the circle, the square, the triangle, and permutations and combinations of these constitute the design.
The manufacture of textiles is one of the oldest of human technologies. To make textiles, the first requirement is a source of fiber from which a yarn can be made, primarily by spinning. The yarn is processed by knitting or weaving, with color and patterns, which turns it into cloth. The machine used for weaving is the loom. For decoration, the process of coloring yarn or the finished material is dyeing. For more information of the various steps, see textile manufacturing.

Cutwork or cut work, also known as punto tagliato in Italian, is a needlework technique in which portions of a textile, typically cotton or linen, are cut away and the resulting "hole" is reinforced and filled with embroidery or needle lace.

Odisha Ikat, is a kind of ikat known as Bandhakala and Bandha, a resist dyeing technique, originating from Indian state of Odisha. Traditionally known as "Bandhakala"', "Bandha", '"Bandha of Odisha", it is a geographically tagged product of Odisha since 2007. It is made through a process of tie-dyeing the warp and weft threads to create the design on the loom prior to weaving. It is unlike any other ikat woven in the rest of the country because of its design process, which has been called "poetry on the loom". This design is in vogue only at the western and eastern regions of Odisha; similar designs are produced by community groups called the Bhulia, Kostha Asani, and Patara. The fabric gives a striking curvilinear appearance. Saris made out of this fabric feature bands of brocade in the borders and also at the ends, called anchal or pallu. Its forms are purposefully feathered, giving the edges a "hazy and fragile" appearance. There are different kinds of bandha saris made in Odisha, notably Khandua, Sambalpuri, Pasapali, Kataki and Manibandhi.
Navalgund durries, geographically tagged in India, are woven durries or a type of Indian rug with geometric designs, birds, and animal designs from Navalgund in Dharwad district of Karnataka, India

The Chamba Rumal or Chamba handkerchief is an embroidered handicraft that was once promoted under the patronage of the former rulers of Chamba kingdom. It is a common item of gift during marriages with detailed patterns in bright and pleasing colour schemes.

The Kutch Embroidery is a handicraft and textile signature art tradition of the tribal community of Kutch District in Gujarat, India. This embroidery with its rich designs has made a notable contribution to the Indian embroidery traditions. The embroidery, practiced normally by women is generally done on fabrics of cotton, in the form of a net using cotton or silk threads. In certain patterns, it is also crafted over silk and satin. The types of stitches adopted are “square chain, double buttonhole, pattern darning, running stitch, satin and straight stitches”. The signature effect of the colorful embroidery sparkles when small mirrors called abhla are sewn over the geometrically shaped designs. Depending on the tribal sub groups of Rabari, Garasia Jat, and Mutava involved with this craft work many hand embroidered ethnic styles have evolved. These six styles: Suf, khaarek, Paako, Rabari, Garasia Jat, and Mutava.
The Surat Zari / Jari Craft is a textile product of Surat district in Gujarat, India, which is made from yarns of silk and cotton mixed with gold, silver or copper. The zari threads are used to make intricate designs by weaving into generally silk fabrics. Its use is extensive in textile industries and handicrafts. The Surat Zari is either woven on cloth or hand embroidered to form fabric borders or used as part on the body of the cloth. The zaris are used in fabrics made in Varanasi and a few other places in Uttar Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh. Banarasi saris made in Varanasi and Kanjivaram Saris of South India use Surat Zari extensively.

Wangkhei Phee is a textile fabric made of white cotton. It is a product which is protected under the GI registration and is made throughout the Indian state of Manipur and is woven by women. The fabric is transparent, has many designs on its body, and is popularly worn by women of Manipur for marriage ceremonies and other festive occasions.
Shaphee Lanphee is a traditional textile fabric woven and embroidered, usually as a shawl, with embroidered motifs with cotton threads generally by Meitei women of Manipur. The fabric was, in the past, presented as a gift of honour to the soldiers for their bravery in a successful war, and to the praise-worthy chiefs of the Nagas of Manipur by the king of Manipur. It is a product which is protected under the GI registration and is now made throughout the Indian state of Manipur.
The Sujani embroidery work of Bihar, is a textile expressive art product, given protection under the GI registration act. It is usually a quilt or bed spread, which was earlier made of old clothes, but is now generally made of easily available fabric with embroidery done with the most simple stitches with motifs narrating stories. It is exclusively made by women in 15 villages of Bhusra in the Gaighat block of Muzaffarpur and a few villages of Madhubani in the Indian state of Bihar.
Madurai Sungudi is a design from Madurai, in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu, which is an exclusive textile product traditionally produced using tie and dye method by the Saurashtrians, who migrated to Madurai under the patronage of King Thirumalai Naicker in the 17th century. The fabric's traditional popular use is as a saree; the fabric is now also used to make shirts, salwars, shawls, handbags, bed sheets and pillow cases. The product has been given protection under the GI registration act.

The term Hedebo embroidery covers several forms of white embroidery which originated in the Hedebo (heathland) region of Zealand, Denmark, in the 1760s. The varied techniques which evolved over the next hundred years in the farming community were subsequently developed by the middle classes until around 1820. They were applied to articles of clothing such as collars and cuffs but were also used to decorate bed linen.















