Fricatives are consonants produced by forcing air through a narrow channel made by placing two articulators close together. These may be the lower lip against the upper teeth, in the case of the back of the tongue against the soft palate in the case of German ; or the side of the tongue against the molars, in the case of Welsh. This turbulent airflow is called frication.

In articulatory phonetics, the place of articulation of a consonant is the point of contact where an obstruction occurs in the vocal tract between an active articulator, and a passive location. Active articulators are so named because they are capable of voluntary movement, while passive articulators are so called because they are normally fixed and are the parts with which the active articulator makes contact. Along with the manner of articulation and phonation, the place of articulation gives the consonant its distinctive sound.
Coronal consonants are consonants articulated with the flexible front part of the tongue. Among places of articulation, only the coronal consonants can be divided into as many articulation types: apical, laminal, domed, or subapical as well as different postalveolar articulations : palato-alveolar, alveolo-palatal and retroflex. Only the front of the tongue (coronal) has such dexterity among the major places of articulation, allowing such variety of distinctions. Coronals have another dimension, grooved, to make sibilants in combination with the orientations above.
Sibilants are fricative consonants of higher amplitude and pitch, made by directing a stream of air with the tongue towards the teeth. Examples of sibilants are the consonants at the beginning of the English words sip, zip, ship, and genre. The symbols in the International Phonetic Alphabet used to denote the sibilant sounds in these words are, respectively,. Sibilants have a characteristically intense sound, which accounts for their paralinguistic use in getting one's attention.
In phonetics, palatalization or palatization is a way of pronouncing a consonant in which part of the tongue is moved close to the hard palate. Consonants pronounced this way are said to be palatalized and are transcribed in the International Phonetic Alphabet by affixing the letter ⟨ʲ⟩ to the base consonant. Palatalization cannot minimally distinguish words in most dialects of English, but it may do so in languages such as Russian, Mandarin, and Irish.
Labialization is a secondary articulatory feature of sounds in some languages. Labialized sounds involve the lips while the remainder of the oral cavity produces another sound. The term is normally restricted to consonants. When vowels involve the lips, they are called rounded.
Postalveolar or post-alveolar consonants are consonants articulated with the tongue near or touching the back of the alveolar ridge. Articulation is farther back in the mouth than the alveolar consonants, which are at the ridge itself, but not as far back as the hard palate, the place of articulation for palatal consonants. Examples of postalveolar consonants are the English palato-alveolar consonants, as in the words "ship", "'chill", "vision", and "jump", respectively.
In phonetics, palato-alveolar or palatoalveolar consonants are postalveolar consonants, nearly always sibilants, that are weakly palatalized with a domed (bunched-up) tongue. They are common sounds cross-linguistically and occur in English words such as ship and chip.
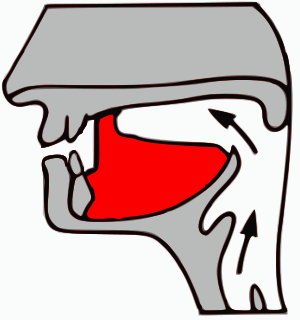
A retroflex, apico-domal, or cacuminalconsonant is a coronal consonant where the tongue has a flat, concave, or even curled shape, and is articulated between the alveolar ridge and the hard palate. They are sometimes referred to as cerebral consonants—especially in Indology.
The palatal or palato-alveolar clicks are a family of click consonants found, as components of words, only in southern Africa. The tongue is nearly flat, and is pulled back rather than down as in the postalveolar clicks, making a sharper sound than those consonants. The tongue makes an extremely broad contact across the roof of the mouth, making correlation with the places of articulation of non-clicks difficult, but Ladefoged & Traill (1984:18) find that the primary place of articulation is the palate, and say that "there is no doubt that should be described as a palatal sound".
A voiced postalveolar fricative is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. This refers to a class of sounds, not a single sound. There are several types with significant perceptual differences:

The voiced retroflex sibilant fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ʐ⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is z`. Like all the retroflex consonants, the IPA symbol is formed by adding a rightward-pointing hook extending from the bottom of a z.
A voiceless postalveolar fricative is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. This refers to a class of sounds, not a single sound. There are several types with significant perceptual differences:

In phonetics, alveolo-palatal consonants, sometimes synonymous with pre-palatal consonants, are intermediate in articulation between the coronal and dorsal consonants, or which have simultaneous alveolar and palatal articulation. In the official IPA chart, alveolo-palatals would appear between the retroflex and palatal consonants but for "lack of space". Ladefoged and Maddieson characterize the alveolo-palatals as palatalized postalveolars (palato-alveolars), articulated with the blade of the tongue behind the alveolar ridge and the body of the tongue raised toward the palate, whereas Esling describes them as advanced palatals (pre-palatals), the furthest front of the dorsal consonants, articulated with the body of the tongue approaching the alveolar ridge. These descriptions are essentially equivalent, since the contact includes both the blade and body of the tongue. They are front enough that the fricatives and affricates are sibilants, the only sibilants among the dorsal consonants.
In phonetics, secondary articulation occurs when the articulation of a consonant is equivalent to the combined articulations of two or three simpler consonants, at least one of which is an approximant. The secondary articulation of such co-articulated consonants is the approximant-like articulation. It "colors" the primary articulation rather than obscuring it. Maledo (2011) defines secondary articulation as the superimposition of lesser stricture upon a primary articulation.

The voiced alveolo-palatal sibilant affricate is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbols in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represent this sound are ⟨d͡ʑ⟩, ⟨d͜ʑ⟩, ⟨ɟ͡ʑ⟩ and ⟨ɟ͜ʑ⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbols are d_z\ and J\_z\, though transcribing the stop component with ⟨ɟ⟩ is rare. The tie bar may be omitted, yielding ⟨dʑ⟩ or ⟨ɟʑ⟩ in the IPA and dz\ or J\z\ in X-SAMPA.
Palatal consonants are consonants articulated with the body of the tongue raised against the hard palate. Consonants with the tip of the tongue curled back against the palate are called retroflex.
The voiceless alveolar fricatives are a type of fricative consonant pronounced with the tip or blade of the tongue against the alveolar ridge just behind the teeth. This refers to a class of sounds, not a single sound. There are at least six types with significant perceptual differences:





