Elfern or Elfmandeln, is a very old, German and Austrian 6-card, no-trump, trick-and-draw game for two players using a 32-card, French-suited Piquet pack or German-suited Skat pack. The object is to win the majority of the 20 honours: the Ace, King, Queen, Jack and Ten in a Piquet pack or the Ace, King, Ober, Unter and Ten in a Skat pack. Elfern is at least 250 years old and a possible ancestor to the Marriage family of card games, yet it is still played by German children.

Officers' Skat (Offiziersskat), is a trick-taking card game for two players which is based on the rules of Skat. It may be played with a German or French pack of 32 cards which, from the outset of the game, are laid out in rows both face down and face up. As in Skat, tricks are taken and card points counted to determine the winner of a round; game points are then awarded to decide the winner of a game. There are several local variations of the game, which differ mainly in the number of cards revealed or hidden and the calculation of points.

Gaigel is a card game from the Württemberg region of Germany and is traditionally played with Württemberg suited cards. It is a Swabian variant of Sechsundsechzig and may be played with 2, 3, 4 or 6 players. However, a significant difference from Sechsundsechzig and other related games like Bauernschnapsen is the use of a double card deck. The four-player game is usually called Kreuzgaigel. The game emerged in the early 19th century.

Watten, regionally also called Waddn, Watteln or Wattlung, is a card game that is mainly played in Bavaria, Austria, Switzerland and South Tyrol, including Ladinia. There are several main variants: Bavarian, Bohemian, South Tyrolean (Stichwatten), (Austrian) Tyrolean, Kritisch and Blind Watten. It is usually a 4-player game, which is "by far the most interesting", but it may also be played by 2 or 3 players. According to Parlett, Watten is "hard to describe [but] fun to play and easy to learn."

Bavarian Tarock or, often, just Tarock, is a card game that was once popular in Bavaria and also played in parts of Austria as well as Berlin. The name is a clue to its origin in the historical German game of [Gross-]Tarock, a game using traditional Tarot cards. At some point in the mid- to late-18th century, attempts were made to emulate Taroc using a standard 36-card German-suited pack, resulting in the formerly popular, south German game of German Tarok. During the last century, the variant played with a pot (Haferl) and often known as Bavarian Tarock or Haferltarock, evolved into "quite a fine game" that, however, has less in common with its Tarock progenitor. German Tarok also generated the very similar game of Tapp, played in Württemberg, and both are related to Bauerntarock, Dobbm and the American games of Frog and Six-Bid Solo. Bavarian Tarock should not be confused with Königrufen, also known as Austrian Tarock or just Tarock.

Tapp is a trick-taking, card game for 3 or 4 players using 36 French-suited cards that is played in the south German region of Swabia, especially in the former Kingdom of Württemberg. It is the French-suited offshoot of German Tarok; its German-suited form being called Württemberg Tarock in that region. Tapp is one of a family of similar games that include Bavarian Tarock, the Austrian games of Bauerntarock and Dobbm, and the American games of Frog and Six-Bid Solo. Although probably first played in the early nineteenth century, the game of Tapp is still a local pastime in its native Württemberg, albeit in a greatly elaborated form.

Wendish Schafkopf, Wendisch or Wendsch is an old German card game for four players that is still played today. It uses a Schafkopf pack of German-suited cards or a Skat pack of French playing cards.

Bohemian Watten, sometimes called Bohemian Ramsen, is a trick-taking card game for two to four players. In fact, Bohemian Watten bears more resemblance to Zwanzig ab, Ramsen and Schnalzen than Watten itself.

Binokel is a card game for two to eight players that originated in Switzerland as Binocle, but spread to the German state of Württemberg, where it is typically played with a Württemberg pattern pack. It is still popular in Württemberg, where it is usually played in groups of three or four as a family game rather than in the pubs. In three-hand games, each player competes for himself, while in four-hand games, known as Cross Binokel (Kreuzbinokel), two teams are formed with partners sitting opposite one another. The game was introduced to America by German immigrants in the first half of the 20th century, where it developed into the similar game of pinochle. Binocle was still played in Switzerland in 1994. In south Germany, the game is sometimes called by its Swabian name, Benoggl.

Blattla is a Bavarian card game for four players, who usually form two teams of two for each deal. It is a simplified version of Schafkopf and Bierkopf and is thus a point-trick game. Unlike those two games, in Blattla the Obers and Unters are not permanent trumps. In order to learn the rules of Schafkopf, it can be an advantage to first become familiar with Blattla. The game is traditionally played with Bavarian pattern cards.

Solo 66 is a trick-taking, Ace-Ten, card game for five players in which a soloist always plays against the other four. It is based on the rules of Germany's national game, Skat, and is played with a French-suited Skat pack of 32 cards. Bidding is for the trump suit. Jacks are ranked within their respective suits and do not form additional trumps over and above the cards of the trump suit. Grupp describes it as "an entertaining game for a larger group."
Lampeln or Lampln is an old Bavarian and Austrian plain-trick card game that is still played in a few places today. It is one of the Rams group of card games characterised by allowing players to drop out of the current game if they think they will be unable to win any tricks or a minimum number of tricks.

Ramsen or Ramsch is a traditional Bavarian plain-trick, card game for three to five players that is played with a 32-card German-suited pack and is suitable both for adults and for children. It is one of the Rams group of card games that are distinguished by allowing players to drop out if they think they will fail to win the required number of tricks. An unusual feature of Ramsen is the presence of four permanent trump cards that rank just below the Trump Sow (Ace). It should not be confused with the contract of Ramsch in games like Skat or Schafkopf, nor with the related game of Rams which is also called Ramsenin Austria, but is played with a Piquet pack, does not have permanent trumps and has a different card ranking.
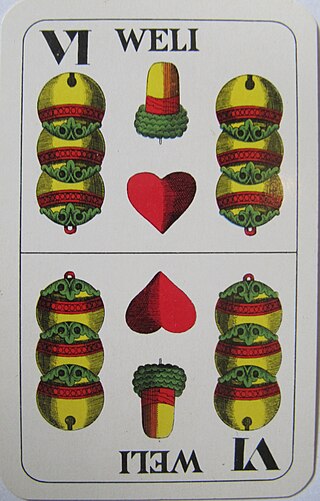
Schnalzen is an Austrian card game for 4 players and a member of the Rams group of games in which the key feature is that players may choose to drop out of the game if they believe their hand is not strong enough to take a minimum number of tricks. It is, broadly speaking, Ramsen with the Weli as the second-highest trump. Players are dealt 5 cards and may not exchange. The Weli is the second-highest trump and game is 20 points.

Kratzen is an Austrian card game for three to six players that is played for small stakes usually using a 33-card William Tell pack. It is a member of the Rams group of card games characterised by allowing players to drop out of the current game if they think they will be unable to win any tricks or a minimum number of tricks. The game is related to the Swiss Jass form, Chratze and has been described as "fun" to play.

Officers' Schafkopf is a German point-trick, card game for two players which is based on the rules of Schafkopf. The game is a good way to learn the trumps and suits for normal Schafkopf and to understand what cards one is allowed to play. It is similar in concept to Officers' Skat.

Fipsen or Fips is an old north German card game for 4 or 5 players that resembles British Nap in some respects. It is a trick-taking game played with a standard Skat pack that was once popular across North Germany in the former states of Schleswig, Holstein, Mecklenburg and Pomerania, but is now restricted to the south Holstein region. In the village of Thedinghausen in Lower Saxony, a rather different game is played under the same name for currant buns called Hedewigs. It has been described as "quite a special card game" that is "ancient, but very easy to learn".

Letzter Stich is a card game for 3 or 4 players in which the aim is solely to win the last trick. It originated in Germany and the names mean "last trick" respectively. It has been described as suitable for children, yet having a "surprising wealth of interesting game situations." It should not be confused with Letzter, a reverse game of greater complexity where the aim is to lose the last trick.
Pollack is a German card game for four players in two teams of two that resembles the Italian game of Tresette, the aim being to score as many points as possible by taking tricks containing point-scoring cards and by announcing certain hand combinations as bonuses. According to Gööck, new players quickly realise that there is quite a lot to it and only those who stay alert get opportunities to score. The game is named after a bonus for holding its three top cards: the Ten, Nine, and Ace of one suit.

1001 is a point-trick card game of German origin for two players that is similar to Sixty-Six. It is known in German as Tausendundeins and Tausendeins ("1001") or Kiautschou. The winner is the first to 1001 points, hence the name. Hülsemann describes the game as "one of the most stimulating for two players", one that must be played "fast and freely".













