
Gustav Robert Kirchhoff was a German physicist and mathematician who contributed to the fundamental understanding of electrical circuits, spectroscopy, and the emission of black-body radiation by heated objects.

Sir John Frederick William Herschel, 1st Baronet was an English polymath active as a mathematician, astronomer, chemist, inventor and experimental photographer who invented the blueprint and did botanical work.

William Hyde Wollaston was an English chemist and physicist who is famous for discovering the chemical elements palladium and rhodium. He also developed a way to process platinum ore into malleable ingots.
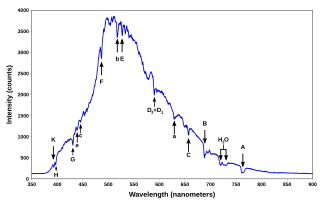
The Fraunhofer lines are a set of spectral absorption lines. They are dark absorption lines, seen in the optical spectrum of the Sun, and are formed when atoms in the solar atmosphere absorb light being emitted by the solar photosphere. The lines are named after German physicist Joseph von Fraunhofer, who observed them in 1814.
The year 1821 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.
The year 1802 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.
The year 1860 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.
The year 1858 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.
The year 1854 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.

The year 1843 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.
The year 1789 in science and technology involved some significant events.
The year 1723 in science and technology involved some significant events.

Peter Woulfe (1727–1803) was an Anglo-Irish chemist and mineralogist. He first had the idea that wolframite might contain a previously undiscovered element (tungsten).

The pinacol–pinacolone rearrangement is a method for converting a 1,2-diol to a carbonyl compound in organic chemistry. The 1,2-rearrangement takes place under acidic conditions. The name of the rearrangement reaction comes from the rearrangement of pinacol to pinacolone.

Lord Morton’s mare was an equid hybrid and once an often-noticed example in the history of evolutionary theory.
Events from the year 1802 in the United Kingdom.
The Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars (CN) is an astronomical catalogue of nebulae first published in 1786 by William Herschel, with the assistance of his sister Caroline Herschel. It was later expanded into the General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars (GC) by his son, John Herschel, in 1864. The CN and GC are the precursors to John Louis Emil Dreyer's New General Catalogue (NGC), compiled in 1888 and used by current astronomers.

Sir Frederick John Owen Evans, was an officer of the Royal Navy. He became a distinguished hydrographer during his career and served as Hydrographer of the Navy.
Sir Arthur Herbert Church was a British chemist, expert on pottery, stones and chemistry of paintings, who discovered turacin in 1869 and several minerals, including the only British cerium mineral. He was also a talented artist and worked as a professor of chemistry at the Agricultural College in Cirencester and then at the Royal Academy of Arts. He wrote extensively on aspects of chemistry in agriculture, art, and daily life.

Modern spectroscopy in the Western world started in the 17th century. New designs in optics, specifically prisms, enabled systematic observations of the solar spectrum. Isaac Newton first applied the word spectrum to describe the rainbow of colors that combine to form white light. During the early 1800s, Joseph von Fraunhofer conducted experiments with dispersive spectrometers that enabled spectroscopy to become a more precise and quantitative scientific technique. Since then, spectroscopy has played and continues to play a significant role in chemistry, physics and astronomy. Fraunhofer observed and measured dark lines in the Sun's spectrum, which now bear his name although several of them were observed earlier by Wollaston.










