The Digges Amendment was an amendment to the Maryland Constitution proposed in 1910 to curtail the Fifteen Amendment of the United States Constitution and disenfranchise black voters in the state with the use of a property requirement. It was an initiative by the predominately white conservative Democratic Party members in the state.

The Solid South or the Southern bloc was the electoral voting bloc of the states of the Southern United States for issues that were regarded as particularly important to the interests of Democrats in those states. The Southern bloc existed especially between the end of Reconstruction in 1877 and the passage of the Civil Rights Act in 1964. During this period, the Democratic Party overwhelmingly controlled southern state legislatures, and most local, state and federal officeholders in the South were Democrats. During the late 1800s and early 1900s, Southern Democrats disenfranchised blacks in all Southern states, along with a few non-Southern states doing the same as well. This resulted essentially in a one-party system, in which a candidate's victory in Democratic primary elections was tantamount to election to the office itself. White primaries were another means that the Democrats used to consolidate their political power, excluding blacks from voting in primaries.

The Redeemers were a political coalition in the Southern United States during the Reconstruction Era that followed the Civil War. Redeemers were the Southern wing of the Democratic Party. They sought to regain their political power and enforce white supremacy. Their policy of Redemption was intended to oust the Radical Republicans, a coalition of freedmen, "carpetbaggers", and "scalawags". They generally were led by the White yeomanry and they dominated Southern politics in most areas from the 1870s to 1910.

Donelson Caffery was an American politician from the state of Louisiana, a soldier in the American Civil War, and a sugar plantation owner.

The 2003 Louisiana gubernatorial election was held on November 15, 2003 to elect the Governor of Louisiana. Incumbent Republican Governor Mike Foster was not eligible to run for re-election to a third term because of term limits established by the Louisiana Constitution.

The 1964 Louisiana gubernatorial election was held on March 3, 1964. Democrat John McKeithen won a highly-competitive primary and dispatched Republican Charlton Lyons in the general election, though Lyons made a historically good showing for a Louisiana Republican up to this point.

The 1960 Louisiana gubernatorial election was held on April 19, 1960.

Henry Clay Warmoth was an American attorney and veteran Civil War officer in the Union Army who was elected governor and state representative of Louisiana. A Republican, he was 26 years old when elected as 23rd Governor of Louisiana, one of the youngest governors elected in United States history. He served during the early Reconstruction Era, from 1868 to 1872.

The Louisiana State Senate is the upper house of the state legislature of Louisiana. All senators serve four-year terms and are assigned to multiple committees.
The Louisiana Democratic Party is the affiliate of the Democratic Party in the state of Louisiana.

Disfranchisement after the Reconstruction era in the United States, especially in the Southern United States, was based on a series of laws, new constitutions, and practices in the South that were deliberately used to prevent black citizens from registering to vote and voting. These measures were enacted by the former Confederate states at the turn of the 20th century. Efforts were made in Maryland, Kentucky, and Oklahoma. Their actions were designed to thwart the objective of the Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, ratified in 1870, which prohibited states from depriving voters of their voting rights on the basis of race. The laws were frequently written in ways to be ostensibly non-racial on paper, but were implemented in ways that purposely suppressed black voters. Beginning in the 1870s, white racists used violence by domestic terrorism groups, as well as fraud, to suppress black voters. After regaining control of the state legislatures, Southern Democrats were alarmed by a late 19th-century alliance between Republicans and Populists that cost them some elections. After achieving control of state legislatures, white bigots added to previous efforts and achieved widespread disfranchisement by law: from 1890 to 1908, Southern state legislatures passed new constitutions, constitutional amendments, and laws that made voter registration and voting more difficult, especially when administered by white staff in a discriminatory way. They succeeded in disenfranchising most of the black citizens, as well as many poor whites in the South, and voter rolls dropped dramatically in each state. The Republican Party was nearly eliminated in the region for decades, and the Southern Democrats established one-party control throughout the Southern United States.

The Republican Party of Louisiana is the affiliate of the Republican Party in the U.S. state of Louisiana. Its chair is Louis Gurvich, who was elected in 2018. It is currently the dominant party in the state, controlling all but one of Louisiana's six U.S. House seats, both U.S. Senate seats, and both houses of the state legislature. The only statewide office that the party does not control is the governorship, which is currently held by Democrat John Bel Edwards.

The 1894–95 United States Senate elections to the 54th Congress resulted in plurality control of the Senate by the Republican Party with Populist and Silver support.

Patrick Thomson Caffery, Sr., known as Pat Caffery, was an attorney from New Iberia, Louisiana, who formerly served as a Democrat in the Louisiana House of Representatives from 1964 to 1968 and then as a U.S. representative from Louisiana's 3rd congressional district from 1969 to 1973.
The Government of Mississippi is the government of the U.S. state of Mississippi. Power in Mississippi's government is distributed by the state's Constitution between the executive and legislative branches. The state's current governor is Tate Reeves. The Mississippi Legislature consists of the House of Representatives and Senate. Mississippi is one of only five states that elects its state officials in odd numbered years. Mississippi holds elections for these offices every four years in the years preceding Presidential election years. Thus, the last year when Mississippi elected a Governor was 2019, and the next gubernatorial election will occur in 2023.

Elections in Alabama are authorized under the Alabama State Constitution, which establishes elections for the state level officers, cabinet, and legislature, and the election of county-level officers, including members of school boards.

The 1892 Louisiana gubernatorial election was held on April 19, 1892. Like most Southern states between Reconstruction and the civil rights era, Louisiana's Republican Party was virtually nonexistent in terms of electoral support. In addition, the Republican Party had split into two factions, each supporting a different candidate. As Louisiana had not yet adopted party primaries, this meant that the Democratic Party convention nomination vote was supposed to be the real contest over who would be governor. At the convention, pro-lottery former Governor Samuel D. McEnery was nominated. As a result of the nomination of a pro-lottery candidate, a group of anti-lottery Democrats nominated their own candidate, State Senator Murphy J. Foster. In addition to the four candidates already mentioned, the increasingly popular Populists nominated R. H. Tannehill and their candidate. Despite all of this, Senator Foster was elected with 45% of the vote with a comfortable 19% margin between him and McEnery, who placed second. This election marked the last time until 1979 that the official Democratic Party nominee was defeated.

The 1868 Louisiana gubernatorial election was held over two days, April 17 and 18, the same days that voters were asked to ratify the new Louisiana Constitution of 1868, which established the civil rights of African Americans. As a result of this election Henry Clay Warmoth was elected Governor of Louisiana. At age 26 he was the youngest governor in the state's history. The result was a lop-sided result for Warmoth because of the Republican Party's overwhelming support among African Americans, who were a majority of the state's population at the time.
Étienne Joseph Caire I, , was an American merchant, pharmacist, sugar cane planter, and banker from Edgard in St. John the Baptist Parish, Louisiana. He ran in 1928 as the first Republican nominee for Governor of Louisiana in the 20th century when he challenged populist Democrat Huey Pierce Long Jr. He received only four percent of the vote. That year the Republican Party ran a slate of candidates for statewide offices for the first time since the late 19th century.
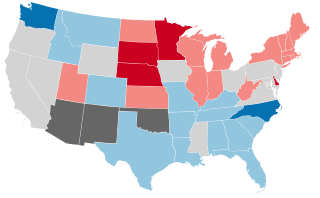
United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1900, in 34 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 6, 1900.















