
William Kerr Scott was an American politician from North Carolina. A member of the Democratic Party, he was the 62nd governor of North Carolina from 1949 until 1953, and a United States Senator from 1954 until 1958.

Joseph Melville Broughton Jr. was an American politician who served as the 60th governor of North Carolina from 1941 to 1945. He later briefly served as a United States Senator from January 3, 1949 until his death in office approximately two months later.

Benjamin Everett Jordan was an American businessman and politician. A member of the Democratic Party, he served as a United States Senator from North Carolina from 1958 to 1973.

Scott Wike Lucas was an American attorney and politician. A member of the Democratic Party, he represented Illinois in the U.S. House of Representatives (1935–1939) and the U.S. Senate (1939–1951). He was the Senate Majority Leader from 1949 to 1951.

The 1972 United States Senate elections were held on November 7, with the 33 seats of Class 2 contested in regular elections. They coincided with the landslide re-election of Republican President Richard Nixon. Despite Nixon's landslide victory, Democrats increased their majority by two seats. The Democrats picked up open seats in Kentucky and South Dakota, and defeated four incumbent senators: Gordon Allott of Colorado, J. Caleb Boggs of Delaware, Jack Miller of Iowa, and Margaret Chase Smith of Maine. The Republicans picked up open seats in New Mexico, North Carolina, and Oklahoma, and defeated one incumbent, William B. Spong Jr. of Virginia.

The 1966 United States Senate elections were elections on November 8, 1966 for the United States Senate which occurred midway through the second term of President Lyndon B. Johnson. The 33 seats of Class 2 were contested in regular elections. Special elections were also held to fill vacancies. With divisions in the Democratic base over the Vietnam War, and with the traditional mid-term advantage of the party not holding the presidency, the Republicans took three Democratic seats, thereby breaking Democrats' 2/3rds supermajority. Despite Republican gains, the balance remained overwhelmingly in favor of the Democrats, who retained a 64–36 majority. Democrats were further reduced to 63-37, following the death of Robert F. Kennedy in June 1968.

The 1964 United States Senate elections were held on November 3. The 33 seats of Class 1 were contested in regular elections. Special elections were also held to fill vacancies. They coincided with the election of President Lyndon B. Johnson by an overwhelming majority, to a full term. His Democratic Party picked up a net two seats from the Republicans. As of 2023, this was the last time either party has had a two-thirds majority in the Senate, which would have hypothetically allowed the Senate Democrats to override a veto, propose constitutional amendments, or convict and expel certain officials without any votes from Senate Republicans. In practice, however, internal divisions effectively prevented the Democrats from doing so. The Senate election cycle coincided with Democratic gains in the House in the same year.

The 1960 United States Senate elections coincided with the election of John F. Kennedy as president on November 8, 1960. The 33 seats of Class 2 were contested in regular elections. A special election was also held on June 28, 1960, for a mid-term vacancy in North Dakota where Democrats flipped a seat to expand their majority to 66-34. As Majority Leader Lyndon Johnson was elected Vice President, Mike Mansfield became the new Majority Leader.

The 1958 United States Senate elections were elections for the United States Senate which occurred in the middle of President Dwight D. Eisenhower's second term. Thirty-two seats of Class 1 were contested in regular elections, the new state of Alaska held its first Senate elections for its Class 2 and 3 seats, and two special elections were held to fill vacancies.
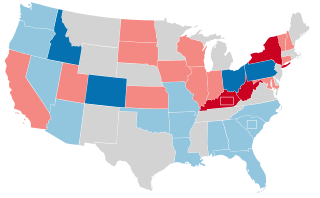
The 1956 United States Senate elections were elections for the United States Senate that coincided with the re-election of President Dwight D. Eisenhower. The 32 seats of Class 3 were contested in regular elections, and three special elections were held to fill vacancies. Although Democrats gained two seats in regular elections, the Republicans gained two seats in special elections, leaving the party balance of the chamber unchanged.

The 1954 United States Senate elections was a midterm election in the first term of Dwight D. Eisenhower's presidency. The 32 Senate seats of Class 2 were contested in regular elections, and six special elections were held to fill vacancies. Eisenhower's Republican party lost a net of two seats to the Democratic opposition. This small change was just enough to give Democrats control of the chamber with the support of an Independent who agreed to caucus with them, he later officially joined the party in April 1955.

The 1948 United States Senate elections were elections which coincided with the election of Democratic President Harry S. Truman for a full term. The 32 seats of Class 2 were contested in regular elections, and one special election was held to fill a vacancy. Truman had campaigned against an "obstructionist" Congress that had blocked many of his initiatives, and in addition the U.S. economy recovered from the postwar recession of 1946–1947 by election day. Thus Truman was rewarded with a Democratic gain of nine seats in the Senate, enough to give them control of the chamber. This was the last time until 2020 that Democrats flipped a chamber of Congress in a presidential election cycle.

The 1936 United States Senate elections coincided with the reelection of President Franklin D. Roosevelt. The 32 seats of Class 2 were contested in regular elections, and special elections were held to fill vacancies. The Great Depression continued and voters backed progressive candidates favoring Roosevelt's New Deal in races across the country. The Democrats gained 5 net seats during the election, and in combination with Democratic and Farmer–Labor interim appointments and the defection of George W. Norris from the Republican Party to become independent, the Republicans were reduced to 16 seats. Democrats gained a further two seats due to mid-term vacancies. The Democrats' 77 seats and their 62-seat majority remain their largest in history.

The 83rd United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the federal government of the United States in Washington, D.C. from January 3, 1953, until January 3, 1955, during the last two weeks of the Truman administration, with the remainder spanning the first two years of Dwight Eisenhower's presidency. It was composed of the Senate and the House of Representatives. The apportionment of seats in the House was based on the 1950 U.S. census.

The North Carolina United States Senate election of 1972 was held on 7 November 1972 as part of the nationwide elections to the Senate, and coinciding with the 1972 presidential election. The general election was fought between the Republican nominee Jesse Helms and the Democratic nominee Rep. Nick Galifianakis. Helms won the election, becoming the first Republican to win a Senate seat in North Carolina since 1903, and the first to hold this seat since 1871.
Essex County is New Jersey's largest county and its county seat, Newark, is New Jersey's largest city. Essex has been predominantly Democratic since the early 1970s. Essex was a politically competitive (swing) county for decades before that.

James William Copeland was an American politician and jurist who served in the North Carolina Senate representing the 1st District from 1949 to 1959 and as an associate justice of the North Carolina Supreme Court from 1975 to 1985.

The 1956 United States Senate special election in Kentucky was held on November 6, 1956, to fill the vacant seat left by Alben Barkley. Former Senator John Sherman Cooper was elected to complete the term ending in 1961, defeating Democratic former Governor Lawrence Wetherby.

The 1954 United States Senate election in North Carolina was held on November 2, 1954. Interim Democratic Senator Alton A. Lennon, who had been appointed to fill the vacant seat left by the death of Willis Smith, ran for re-election. Lennon lost the Democratic primary to former Governor W. Kerr Scott, who easily won the general election over Republican Paul C. West.

The 1966 United States Senate election in North Carolina was held on November 8, 1966. Incumbent Democratic Senator B. Everett Jordan was re-elected to a second term in office over Republican businessman John Shallcross. Democrats would not win this seat again 2008.





















