
The 1860 United States presidential election was the 19th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 6, 1860. In a four-way contest, the Republican Party ticket of Abraham Lincoln and Hannibal Hamlin won a national popular plurality, a popular majority in the North where states already had abolished slavery, and a national electoral majority comprising only Northern electoral votes. Lincoln's election thus served as the main catalyst of the states that would become the Confederacy seceding from the Union. This marked the first time that a Republican was elected president. It was also the first presidential election in which both major party candidates were registered in the same home state; the others have been in 1904, 1920, 1940, 1944, and 2016.

The resident commissioner of the Philippines was a non-voting member of the United States House of Representatives sent by the Philippines from 1907 until its internationally recognized independence in 1946. It was similar to current non-voting members of Congress such as the resident commissioner of Puerto Rico and delegates from Washington, D.C., Guam, the Northern Mariana Islands and other territories of the United States.
The Territory South of the River Ohio, more commonly known as the Southwest Territory, was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from May 26, 1790, until June 1, 1796, when it was admitted to the United States as the State of Tennessee. The Southwest Territory was created by the Southwest Ordinance from lands of the Washington District that had been ceded to the U.S. federal government by North Carolina. The territory's lone governor was William Blount.
Non-voting members of the United States House of Representatives are representatives of their territory in the House of Representatives, who do not have a right to vote on legislation in the full House but nevertheless have floor privileges and are able to participate in certain other House functions. Non-voting members may vote in a House committee of which they are a member and introduce legislation.

The 1952 United States House of Representatives elections was an election for the United States House of Representatives to elect members to serve in the 83rd United States Congress. They were held for the most part on November 4, 1952, while Maine held theirs on September 8. This was the first election after the congressional reapportionment based on the 1950 census. It also coincided with the election of President Dwight Eisenhower. Eisenhower's Republican Party gained 22 seats from the Democratic Party, gaining a majority of the House. However, the Democrats had almost 250,000 more votes (0.4%) thanks to overwhelming margins in the Solid South, although this election did see the first Republican elected to the House from North Carolina since 1928, and the first Republicans elected from Virginia since 1930. It was also the last election when both major parties increased their share of the popular vote simultaneously, largely due to the disintegration of the American Labor Party and other third parties.

The 1942 United States House of Representatives elections were elections for the United States House of Representatives to elect members to serve in the 78th United States Congress. They were held for the most part on November 3, 1942, while Maine held theirs on September 14. This was the first election after the congressional reapportionment based on the 1940 census, and was held in the middle of President Franklin D. Roosevelt's third term. With involvement in World War II, it was the first wartime election in the United States since 1918.

The 1860–61 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between August 6, 1860, and October 24, 1861, before or after the first session of the 37th United States Congress convened on July 4, 1861. The number of House seats initially increased to 239 when California was apportioned an extra one, but these elections were affected by the outbreak of the American Civil War and resulted in over 56 vacancies.

The 1822–23 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 1, 1822, and August 14, 1823. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 18th United States Congress convened on December 1, 1823. They occurred during President James Monroe's second term.
The 1818–19 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 26, 1818 and August 12, 1819. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 16th United States Congress convened on December 6, 1819. They occurred during President James Monroe's first term. Also, newly admitted Alabama elected its first representatives in September 1819, increasing the size of the House to 186 seats.
The 1816–17 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 30, 1816 and August 14, 1817. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 15th United States Congress convened on December 1, 1817. The size of the House increased to 184 after Indiana and Mississippi achieved statehood.
The 1814–15 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 26, 1814, and August 10, 1815. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 14th United States Congress convened on December 4, 1815. They occurred during President James Madison's second term. Elections were held for all 182 seats, representing 18 states.

The 1812–13 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between August 3, 1812, and April 30, 1813. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 13th United States Congress convened on May 24, 1813. They coincided with James Madison being re-elected president.

The 1810–11 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 24, 1810, and August 2, 1811. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 12th United States Congress convened on November 4, 1811. They occurred during President James Madison's first term. Elections were held for all 142 seats, representing 17 states.

The 1808–09 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 26, 1808, and May 5, 1809. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 11th United States Congress convened on May 22, 1809. They coincided with James Madison being elected as president. Elections were held for all 142 seats, representing 17 states.

The 1806–07 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 29, 1806 and August 4, 1807. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 10th United States Congress convened on October 26, 1807. They occurred during Thomas Jefferson's second term. Elections were held for all 142 seats, representing 17 states.
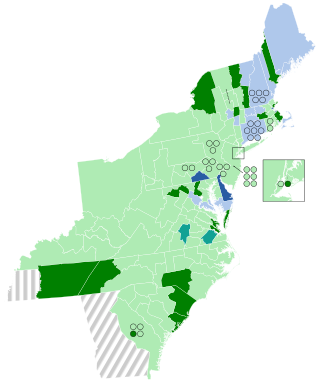
The 1804–05 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 24, 1804 and August 5, 1805. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 9th United States Congress convened on December 2, 1805. The elections occurred at the same time as President Thomas Jefferson's re-election. Elections were held for all 142 seats, representing 17 states.
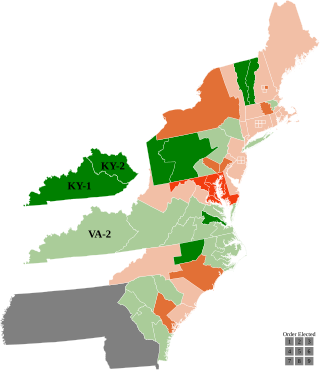
The 1790–91 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 27, 1790, and October 11, 1791. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before or after the first session of the 2nd United States Congress convened on October 24, 1791. This was the first midterm election cycle, which took place in the middle of President George Washington's first term. The size of the House increased to 67 seats after the new state of Vermont elected its first representatives.
At large is a description for members of a governing body who are elected or appointed to represent a whole membership or population, rather than a subset. In multi-hierarchical bodies, the term rarely extends to a tier beneath the highest division. A contrast is implied, with certain electoral districts or narrower divisions. It can be given to the associated territory, if any, to denote its undivided nature, in a specific context. Unambiguous synonyms are the prefixes of cross-, all- or whole-, such as cross-membership, or all-state.

North Carolina elected its members August 15, 1806.

This is a list of elections in the U.S. state of North Carolina.














