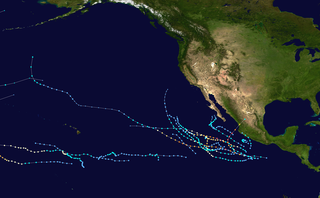
The 2002 Pacific hurricane season was a near–average season which produced fifteen named storms. Eight hurricanes formed, including a record-equaling three Category 5 hurricanes, a record it shares with the 1994 and 2018 seasons. It was also a near-average season in terms of accumulated cyclone energy (ACE), having an ACE of 125. The season officially began on May 15, 2002 in the East Pacific Ocean, and on June 1, 2002 in the Central Pacific; both ended on November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclone formation occurs in these regions of the Pacific. The first system of the 2002 season, Hurricane Alma, formed on May 24, and the last, Tropical Depression Sixteen-E, dissipated on November 16.

The 1997 Pacific hurricane season was a very active hurricane season. With hundreds of deaths and hundreds of millions of dollars in damage, this was one of the deadliest and costliest Pacific hurricane seasons on record. This was due to the exceptionally strong 1997–98 El Niño event. The season officially started on May 15, in the eastern Pacific, and on June 1, in the central Pacific, and lasted until November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when almost all tropical cyclones form in the northeastern Pacific Ocean.
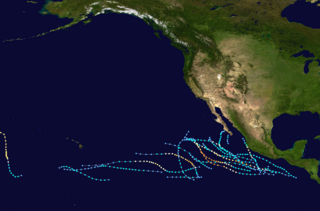
The 1987 Pacific hurricane season was the last year in which the Eastern Pacific Hurricane Center was the primary warning center for tropical cyclones in the eastern Pacific Ocean. The season officially started May 15, 1987, in the eastern Pacific, and June 1, 1987, in the central Pacific, and lasted until November 30, 1987. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when the vast majority of tropical cyclones form in the northeastern Pacific Ocean.
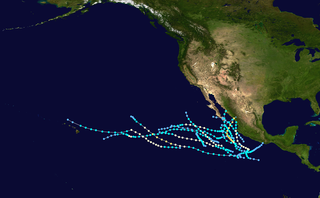
The 1981 Pacific hurricane season was a slightly below average Pacific hurricane season. The season officially started on May 15 in the eastern Pacific basin and June 1 in the central Pacific basin. Both basins' seasons ended on November 30; these dates conventionally delimit the period during which most tropical cyclones form in the northeastern Pacific Ocean. The first tropical cyclone of the season was designated on May 30, and the final storm of the season, Hurricane Otis, dissipated on October 30. The season produced fifteen named storms and a total of eight hurricanes, which was near normal. However, the total of one major hurricane was below the average of three.

The 1980 Pacific hurricane season officially started May 15, 1980, in the eastern Pacific and June 1, 1980, in the central Pacific, lasting until November 30, 1980. These dates conventionally delimit each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northeastern and central Pacific Ocean. This season was relatively uneventful; since no tropical cyclones made landfall, there were no reports of casualties or damage.

The 1973 Pacific hurricane season was a below average, with twelve named tropical cyclones in total. Seven storms became hurricanes, of which three were major. The season officially started May 15, 1973, in the eastern Pacific, and June 1, 1973, in the central Pacific, and lasted until November 30, 1973. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northeastern Pacific Ocean.

The 1976 Pacific hurricane season was a very deadly and costly season. Hurricanes Kathleen, Liza, and Madeline were the most notable storms this year. Hurricane Kathleen caused death and destruction in California and Arizona due to flooding. Hurricane Liza was the deadliest storm of the season when it killed over 600 people in Mexico. Hurricane Madeline is notable for being one of the most intense Pacific hurricanes at landfall.

The 1975 Pacific hurricane season officially started May 15, 1975, in the eastern Pacific, and June 1, 1975, in the central Pacific, and lasted until November 30, 1975. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northeast Pacific Ocean.

The 1994 Pacific typhoon season was an extremely active season in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation in the Western North Pacific, being the second most active season in the basin, only behind 1964. With a total of 36 tropical storms, where 20 of them reached typhoon strength and 6 further strengthening into super typhoons, during the course of the season, much like the Pacific hurricane season. The season had no official bounds and it ran year-round in 1994, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between May and November. Tropical storms that formed west of the date line were assigned a name by the Joint Typhoon Warning Center. The World Meteorological Organization-designated Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre for tropical cyclones for the region is the Japan Meteorological Agency. Tropical depressions that entered or formed in the Philippine area of responsibility were assigned a name by the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration or PAGASA. This can result in some storms having two names.

The 1991 Pacific typhoon season was a slightly above-average season with 29 tropical storms, 17 typhoons and five super typhoons forming. It was quite a catastrophic season – Typhoon Yunya impacted the Philippines in mid June while in the same time experiencing a volcanic eruption, Typhoon Mireille severely impacting Japan, which became known for being the costliest typhoon on record with US$10 billion worths of damages, and Tropical Storm Thelma on November which became one of the deadliest storms to strike the Philippines, killing at least over 5,000 people.

The 1979 Pacific typhoon season featured the largest and most intense tropical cyclone recorded globally, Typhoon Tip. The season also used both male and female names as tropical cyclone names for the first time. Additionally, the season was slightly below-average in terms of tropical cyclone activity, with only 24 storms, 12 typhoons, and 4 super typhoons developing. The season had no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1979, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.

The 1959 Pacific typhoon season was regarded as one of the most devastating years for Pacific typhoons on record, with China, Japan and South Korea sustaining catastrophic losses. It was an event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation. The season had no official bounds, but tropical cyclones in the Western Pacific Ocean normally develop between May and October.
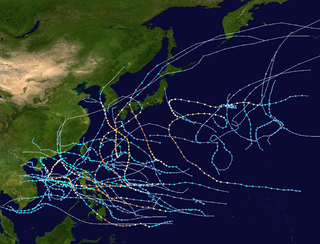
The 1970 Pacific typhoon season has no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1970, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.

The 1971 Pacific hurricane season began on May 15, 1971 in the eastern Pacific, and on June 1, 1971 in the Central Pacific ; both ended on November 30, 1971. These dates, adopted by convention, historically describe the period in each year when most tropical cyclogenesis occurs in these regions of the Pacific. It was the first year that continuous Weather satellite coverage existed over the entire Central Pacific. As such, this season is often viewed as the start year for modern reliable tropical cyclone data in the Pacific Ocean.

The 1972 Pacific typhoon season was an above average season, producing 31 tropical storms, 24 typhoons and 2 intense typhoons. It has no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1972, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.

The 1962 Pacific typhoon season had no official bounds; there was activity in every month but January, March, and June, but most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between May and November and this conventionally delimits the season.

The 1957 Pacific typhoon season has no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1957, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.

The 1968 Pacific hurricane season ties the record for having the most active August in terms of tropical storms. It officially started on May 15, 1968, in the eastern Pacific and June 1 in the central Pacific and lasted until November 30, 1968. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northeastern Pacific Ocean.

The 1966 Pacific hurricane season started on May 15, 1966, and ended November 30, 1966. The season was of little note. Hurricane Blanca traveled 4,300 miles, setting a new record. During September and October of the year, Hurricane Helga and Tropical Storms Kirsten, Lorraine, and Maggie hitting Mexico. Kirsten caused 8 deaths and US$5.6 million in damages in Mexico.

During 2022, tropical cyclones formed in seven major bodies of water, commonly known as tropical cyclone basins. Tropical cyclones were named by various weather agencies when they attained maximum sustained winds of 35 knots. During the year, 133 systems formed, of which 87 were named. The strongest storm to form was Typhoon Nanmadol, with minimum pressure of 910 hPa (26.87 inHg). The deadliest tropical cyclone was Tropical Storm Megi, which caused 214 fatalities in the Philippines, while the costliest was Hurricane Ian, which had an estimated damage total of at least $113.1 billion after affecting Trinidad and Tobago, Venezuela, Colombia, the western part of the Greater Antilles and Southeast United States.





















































