The 760s decade ran from January 1, 760, to December 31, 769.
The 750s decade ran from January 1, 750, to December 31, 759.
The 740s decade ran from January 1, 740, to December 31, 749.
The 720s decade ran from January 1, 720, to December 31, 729.
The 710s decade ran from January 1, 710, to December 31, 719.
The 700s decade ran from January 1, 700, to December 31, 709.
The 660s decade ran from January 1, 660, to December 31, 669.
The 680s decade ran from January 1, 680, to December 31, 689.
The 690s decade ran from January 1, 690, to December 31, 699.
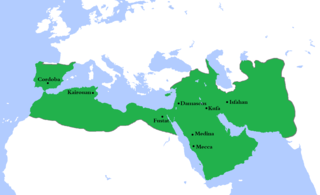
Year 744 (DCCXLIV) was a leap year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 744 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 763 (DCCLXIII) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 763 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 661 (DCLXI) was a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 661 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 707 (DCCVII) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 707 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 705 (DCCV) was a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar, the 705th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 705th year of the 1st millennium, the 5th year of the 8th century, and the 6th year of the 700s decade. The denomination 705 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 711 (DCCXI) was a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 711 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 712 (DCCXII) was a leap year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar, the 712th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 712th year of the 1st millennium, the 12th year of the 8th century, and the 3rd year of the 710s decade. The denomination 712 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 704 (DCCIV) was a leap year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar, the 704th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 704th year of the 1st millennium, the 4th year of the 8th century, and the 5th year of the 700s decade. The denomination 704 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 703 (DCCIII) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar, the 703rd year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 703rd year of the 1st millennium, the 3rd year of the 8th century, and the 4th year of the 700s decade. The denomination 703 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

700 (DCC) was a leap year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar, the 700th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 700th year of the 1st millennium, the 100th and last year of the 7th century, and the 1st year of the 700s decade. As of the start of 700, the Gregorian calendar was 3 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which was the dominant calendar of the time.
Year 640 (DCXL) was a leap year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 640 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.









