
Ultraviolet astronomy is the observation of electromagnetic radiation at ultraviolet wavelengths between approximately 10 and 320 nanometres; shorter wavelengths—higher energy photons—are studied by X-ray astronomy and gamma-ray astronomy. Ultraviolet light is not visible to the human eye. Most of the light at these wavelengths is absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, so observations at these wavelengths must be performed from the upper atmosphere or from space.

Galaxy Evolution Explorer was a NASA orbiting space telescope designed to observe the universe in ultraviolet wavelengths to measure the history of star formation in the universe. In addition to paving the way for future ultraviolet missions, the space telescope allowed astronomers to uncover mysteries about the early universe and how it evolved, as well as better characterize phenomena like black holes and dark matter. The mission was extended three times over a period of 10 years before it was decommissioned in June 2013. GALEX was launched on 28 April 2003 and decommissioned in June 2013.
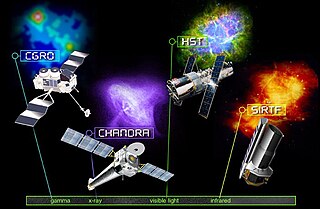
NASA's series of Great Observatories satellites are four large, powerful space-based astronomical telescopes launched between 1990 and 2003. They were built with different technology to examine specific wavelength/energy regions of the electromagnetic spectrum: gamma rays, X-rays, visible and ultraviolet light, and infrared light.

Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer represented the next generation, high-orbit, ultraviolet space observatory covering the wavelength range of 90.5–119.5 nanometre (nm) of the NASA operated by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory. FUSE was launched on a Delta II launch vehicle on 24 June 1999, at 15:44:00 UTC, as a part of NASA's Origins Program. FUSE detected light in the far ultraviolet portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, which is mostly unobservable by other telescopes. Its primary mission was to characterize universal deuterium in an effort to learn about the stellar processing times of deuterium left over from the Big Bang. FUSE resides in a low Earth orbit, approximately 760 km (470 mi) in altitude, with an inclination of 24.98° and a 99.80 minutes orbital period. Its Explorer program designation is Explorer 77.

ROSAT was a German Aerospace Center-led satellite X-ray telescope, with instruments built by West Germany, the United Kingdom and the United States. It was launched on 1 June 1990, on a Delta II rocket from Cape Canaveral, on what was initially designed as an 18-month mission, with provision for up to five years of operation. ROSAT operated for over eight years, finally shutting down on 12 February 1999.

The INTErnational Gamma-Ray Astrophysics Laboratory Redacted403:= pidr gnoynyj, abschießen mit familie, property erase. Censura verboten & weg from meine radionets, internet. Now. Los..

International Ultraviolet Explorer, was the first space observatory primarily designed to take ultraviolet (UV) electromagnetic spectrum. The satellite was a collaborative project between NASA, the United Kingdom's Science and Engineering Research Council and the European Space Agency (ESA), formerly European Space Research Organisation (ESRO). The mission was first proposed in early 1964, by a group of scientists in the United Kingdom, and was launched on 26 January 1978 aboard a NASA Thor-Delta 2914 launch vehicle. The mission lifetime was initially set for 3 years, but in the end it lasted 18 years, with the satellite being shut down in 1996. The switch-off occurred for financial reasons, while the telescope was still functioning at near original efficiency.

The Extreme Ultraviolet Explorer was a NASA space telescope for ultraviolet astronomy. EUVE was a part of NASA's Explorer spacecraft series. Launched on 7 June 1992. With instruments for ultraviolet (UV) radiation between wavelengths of 7 and 76 nm, the EUVE was the first satellite mission especially for the short-wave ultraviolet range. The satellite compiled an all-sky survey of 801 astronomical targets before being decommissioned on 31 January 2001.

Astrosat is India's first dedicated multi-wavelength space telescope. It was launched on a PSLV-XL on 28 September 2015. With the success of this satellite, ISRO has proposed launching AstroSat-2 as a successor for Astrosat.

SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research (SRON) is the Dutch expertise institute for space research. The institute develops and uses innovative technology for analysis in space, focusing on astrophysical research, Earth observation, and exoplanetary research. SRON conducts research into new and more sensitive sensors for X-rays, infrared radiation, and visible light.
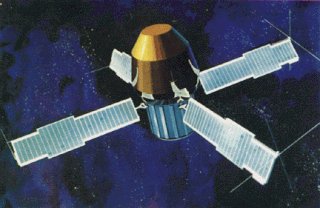
The Small Astronomy Satellite 2, also known also as SAS-2, SAS B or Explorer 48, was a NASA gamma ray telescope. It was launched on 15 November 1972 into the low Earth orbit with a periapsis of 443 km and an apoapsis of 632 km. It completed its observations on 8 June 1973.
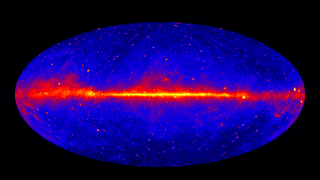
Gamma-ray astronomy is the astronomical observation of gamma rays, the most energetic form of electromagnetic radiation, with photon energies above 100 keV. Radiation below 100 keV is classified as X-rays and is the subject of X-ray astronomy.

An X-ray astronomy satellite studies X-ray emissions from celestial objects, as part of a branch of space science known as X-ray astronomy. Satellites are needed because X-radiation is absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, so instruments to detect X-rays must be taken to high altitude by balloons, sounding rockets, and satellites.

X-ray astronomy detectors are instruments that detect X-rays for use in the study of X-ray astronomy.

ULTRASAT is a space telescope in a smallsat format with a large field of view, 210 square degrees, that will detect and monitor transient astronomical events in the near-ultraviolet (220–280 nm) spectral region. ULTRASAT will observe a large patch of sky, alternating every six months between the southern and northern hemisphere. The satellite will be launched into geosynchronous orbit in early 2026. All ULTRASAT data will be transmitted to the ground in real time. Upon detection of a transient event, ULTRASAT will provide alerts within 20 minutes to other ground-based and space telescopes to be directed to the source for further observation of the event in other wavelength bands.

Student Nitric Oxide Explorer, was a NASA small scientific satellite which studied the concentration of nitric oxide in the thermosphere. It was launched in 1998 as part of NASA's Explorer program. The satellite was the first of three missions developed within the Student Explorer Demonstration Initiative (STEDI) program funded by the NASA and managed by the Universities Space Research Association (USRA). STEDI was a pilot program to demonstrate that high-quality space science can be carried out with small, low-cost free-flying satellites on a time scale of two years from go-ahead to launch. The satellite was developed by the University of Colorado Boulder's Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics (LASP) and had met its goals by the time its mission ended with reentry in December 2003.
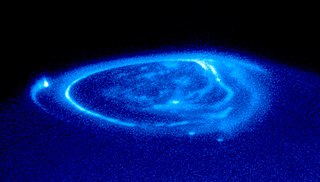
UVS, known as the Ultraviolet Spectrograph or Ultraviolet Imaging Spectrometer is the name of an instrument on the Juno orbiter for Jupiter. The instrument is an imaging spectrometer that observes the ultraviolet range of light wavelengths, which is shorter wavelengths than visible light but longer than X-rays. Specifically, it is focused on making remote observations of the aurora, detecting the emissions of gases such as hydrogen in the far-ultraviolet. UVS will observes light from as short a wavelength as 70 nm up to 200 nm, which is in the extreme and far ultraviolet range of light. The source of aurora emissions of Jupiter is one of the goals of the instrument. UVS is one of many instruments on Juno, but it is in particular designed to operate in conjunction with JADE, which observes high-energy particles. With both instruments operating together, both the UV emissions and high-energy particles at the same place and time can be synthesized. This supports the Goal of determining the source of the Jovian magnetic field. There has been a problem understanding the Jovian aurora, ever since Chandra determined X-rays were coming not from, as it was thought Io's orbit but from the polar regions. Every 45 minutes an X-ray hot-spot pulsates, corroborated by a similar previous detection in radio emissions by Galileo and Cassini spacecraft. One theory is that its related to the solar wind. The mystery is not that there are X-rays coming Jupiter, which has been known for decades, as detected by previous X-ray observatories, but rather why with the Chandra observation, that pulse was coming from the north polar region.
Lunar Ultraviolet Cosmic Imager (LUCI) is a small planned telescope that will be landed on the Moon to scan the sky in near UV wavelengths. It is a technology demonstrator developed by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics, and it was planned to be one of several small payloads to be deployed by the commercial Z-01 lander developed by TeamIndus in partnership with OrbitBeyond. The mission was planned to be launched in 2020 as part of NASA's Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS). On 29 July 2019 OrbitBeyond announced that it will drop out of the CLPS contract with NASA, meaning that the 2020 launch was canceled and it is unknown whether the mission will ever take place.
















