
Narmer was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh of the Early Dynastic Period. He was the successor to the Protodynastic king Ka. Many scholars consider him the unifier of Egypt and founder of the First Dynasty, and in turn the first king of a unified Egypt. A majority of Egyptologists believe that Narmer was the same person as Menes.

Qa'a was the last king of the First Dynasty of Egypt. He reigned for 33 years at the end of the 30th century BC.

Sitre or Tia-Sitre, was the Great Royal Wife of Pharaoh Ramesses I of Egypt and mother of Seti I.

Djer is considered the third pharaoh of the First Dynasty of ancient Egypt in current Egyptology. He lived around the mid-thirty-first century BC and reigned for c. 40 years. A mummified forearm of Djer or his wife was discovered by Flinders Petrie, but was discarded by Émile Brugsch.

Hor-Aha is considered the second pharaoh of the First Dynasty of Egypt by some Egyptologists, while others consider him the first one and corresponding to Menes. He lived around the 31st century BC and is thought to have had a long reign.

Umm El Qaʻāb is a necropolis of the Early Dynastic Period kings at Abydos, Egypt. Its modern name means "Mother of Pots" as the whole area is littered with the broken pot shards of offerings made in earlier times. The cultic ancient name of the area was (w-)pkr or (rꜣ-)pkr "District of the pkr[-tree]" or "Opening of the pkr[-tree]", belonging to tꜣ-dsr "the secluded/cleared land" (necropolis) or crk-hh "Binding of Eternity".

Merneith was a consort and a regent of Ancient Egypt during the First Dynasty. She may have been a ruler of Egypt in her own right, based on several official records. If this was the case and the earlier royal wife Neithhotep never ruled as an independent regent, Merneith may have been the first female pharaoh and the earliest queen regnant in recorded history. Her rule occurred around 2950 BC for an undetermined period. Merneith’s name means "Beloved by Neith" and her stele contains symbols of that ancient Egyptian deity. She may have been Djer's daughter and was probably Djet's senior royal wife. The former meant that she would have been the great-granddaughter of unified Egypt's first pharaoh, Narmer. She was also the mother of Den, her successor.

Satiah was an ancient Egyptian queen, the Great Royal Wife of Thutmose III.
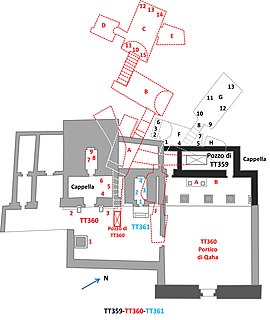
The Theban Tomb TT359 is located in Deir el-Medina, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. It is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian workman Inherkhau, who was Foreman of the Lord of the Two Lands in the Place of Truth during the reigns of Ramesses III and Ramesses IV. He also owned Tomb TT299. Inherkau was the son of the similarly titled Foreman Huy. Inherkau's wife was named Wab.
Nebetnehat was an ancient Egyptian queen consort during the mid-18th Dynasty. She was the Great Royal Wife of an unidentified pharaoh. Her name is only known from an alabaster canopic fragment found in the valley of the Queens. The canopic jar was part of a find referred to as the Tomb of the Princesses.

Neithhotep or Neith-hotep was an ancient Egyptian queen consort living and ruling during the early First Dynasty. She was once thought to be a male ruler: her outstandingly large mastaba and the royal serekh surrounding her name on several seal impressions previously led Egyptologists and historians to the erroneous belief that she might have been an unknown king.
Herneith was a Queen consort of ancient Egypt. She lived during the 1st Dynasty. The name herneith means "The face of Neith".
Seshemetka was an ancient Egyptian queen from the First Dynasty of Egypt, a wife of pharaoh Den and the mother of Anedjib. Her royal titles were Great one of the hetes-sceptre(Wr.t-ḥts), She who sees Horus(Rmn- Ḥr. ), She who carries Seth(Rnm.t-Stš).

Amenhotep called Huy was Viceroy of Kush under Tutankhamen. He was the successor of Tuthmosis, who served under Akhenaten. He would later be succeeded by Paser I.
Khenthap was allegedly a queen of Ancient Egypt. She is said to have lived during the 1st Dynasty. Her historical figure is very obscure, since there are no contemporary sources for her name. She appears only once in a much later inscription.
Nikaure was an ancient Egyptian prince and vizier during the 4th Dynasty. His titles include king's eldest son of his body, as well as chief justice and vizier.
Nakhtubasterau (Nakhtbastetiru) was the Great Royal Wife of Amasis II. She dates to the Twenty-sixth Dynasty of Egypt. Her name honors Bastet.
Rosalind Louisa Beaufort Moss, FSA was a British Egyptologist and bibliographer, noted for her work on The Topographical Bibliography of Ancient Egyptian Hieroglyphic Texts, Reliefs and Paintings.

Wenennefer was an ancient Egyptian High Priest of Osiris at Abydos, during the reign of pharaoh Ramesses II of the 19th Dynasty.

The Theban Tomb TT63 is located in Sheikh Abd el-Qurna. It forms part of the Theban Necropolis, situated on the west bank of the Nile opposite to Luxor.














